Abstract
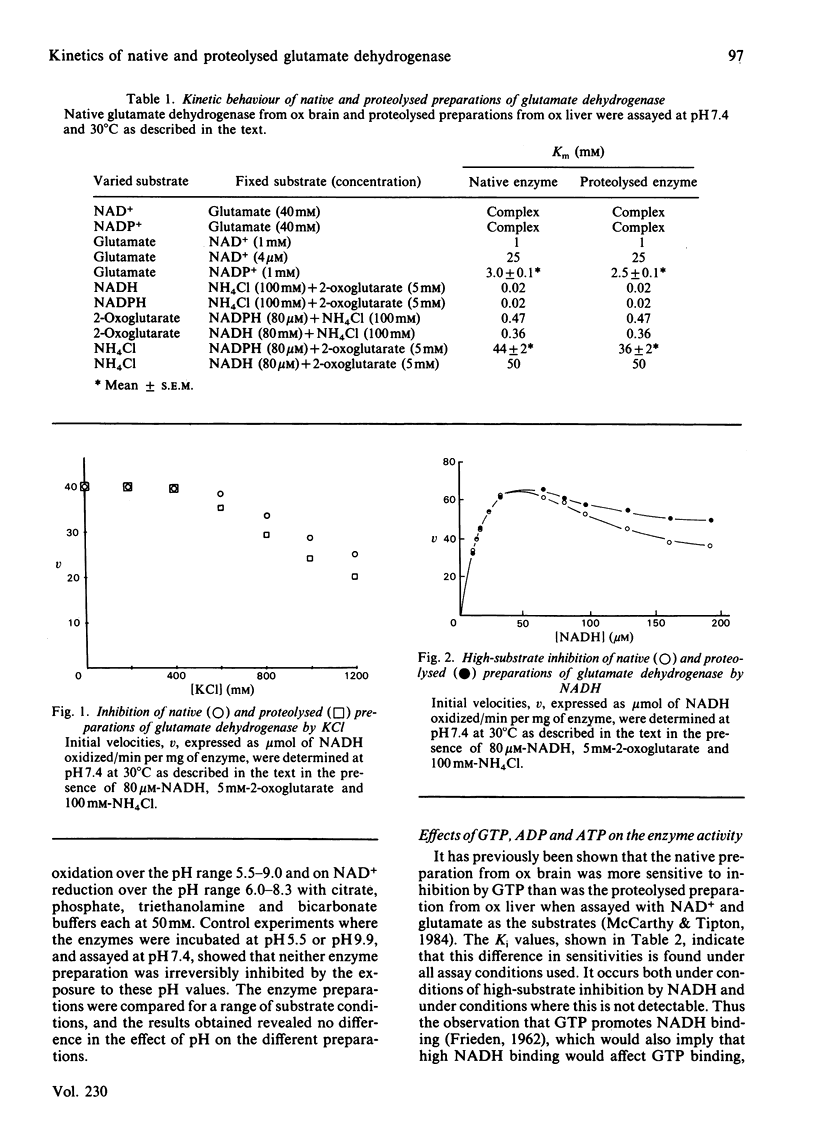
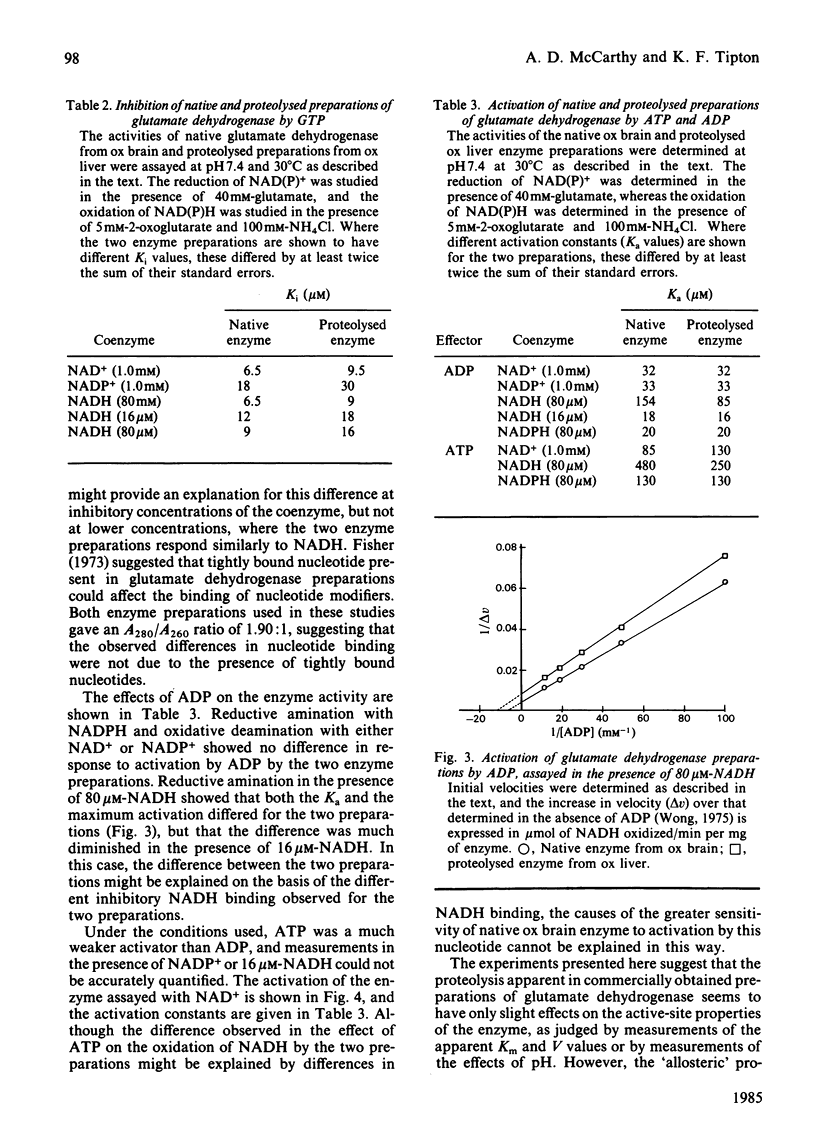
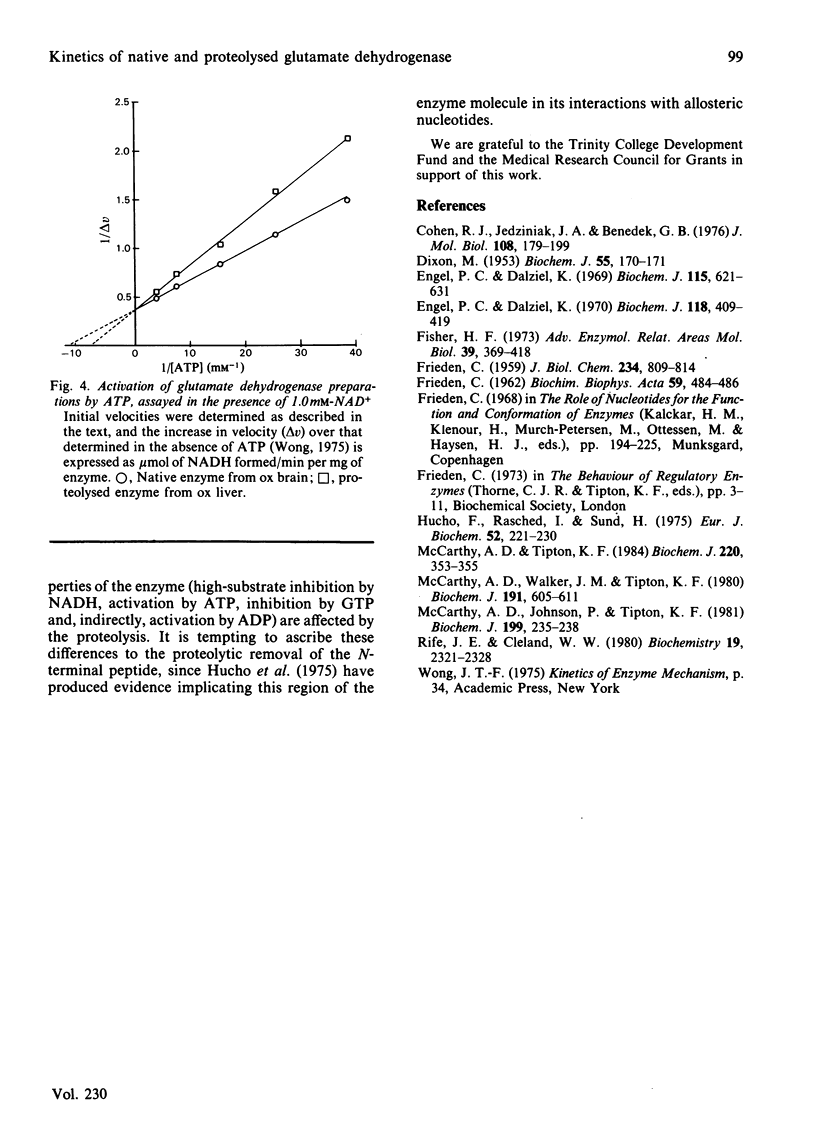
Kinetic constants were determined for commercially available samples of ox liver glutamate dehydrogenase, which had previously been shown to have suffered limited proteolysis during preparation, with a range of substrates and effectors. These were compared with the values obtained with enzyme preparations purified in such a way as to prevent this proteolysis from occurring [McCarthy, Walker & Tipton (1980) Biochem. J. 191, 605-611]. The Km values and maximum velocities determined with different substrates revealed little difference between the two preparations although the proteolysed enzyme had lower Km values for NH4+ and glutamate when the activities were determined with NADPH and NADP+ respectively. This preparation was more sensitive to inhibition by Cl- ions but less sensitive to inhibition by high concentrations of the substrate NADH. The two preparations also differed in their sensitivities to allosteric effectors, with the proteolysed enzyme being the less sensitive to inhibition by GTP. At high concentrations of NADH, this preparation was also more sensitive to activation by ADP and ATP.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen R. J., Jedziniak J. A., Benedek G. B. The functional relationship between polymerization and catalytic activity of beef liver glutamate dehydrogenase. II. Experiment. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):179–199. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase with glutamate and norvaline as substrates. Coenzyme activation and negative homotropic interactions in allosteric enzymes. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):621–631. doi: 10.1042/bj1150621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. The reductive amination of 2-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):409–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1180409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. Glutamic dehydrogenase. I. The effect of coenzyme on the sedimentation velocity and kinetic behavior. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. The unusual inhibition of glutamate dehydrogenase by guanosine di- and triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 21;59:484–486. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. F. Glutamate dehydrogenase--ligand complexes and their relationship to the mechanism of the reaction. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;39:369–417. doi: 10.1002/9780470122846.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Rasched I., Sund H. Studies of glutamate dehydrogenase: analysis of functional areas and functional groups. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. D., Johnson P., Tipton K. F. Sedimentation properties of native and proteolysed preparations of ox glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):235–238. doi: 10.1042/bj1990235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. D., Walker J. M., Tipton K. F. Purification of glutamate dehydrogenase from ox brain and liver. Evidence that commercially available preparations of the enzyme from ox liver have suffered proteolytic cleavage. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):605–611. doi: 10.1042/bj1910605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rife J. E., Cleland W. W. Kinetic mechanism of glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2321–2328. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


