Abstract
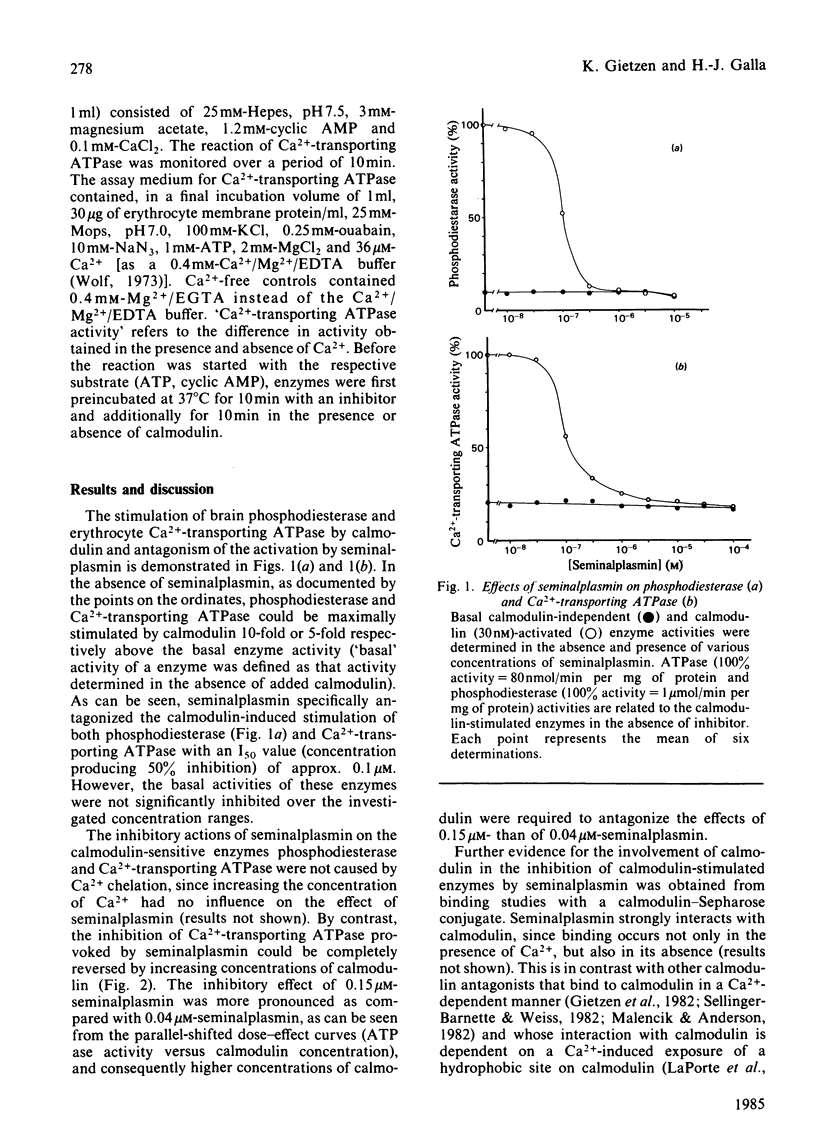
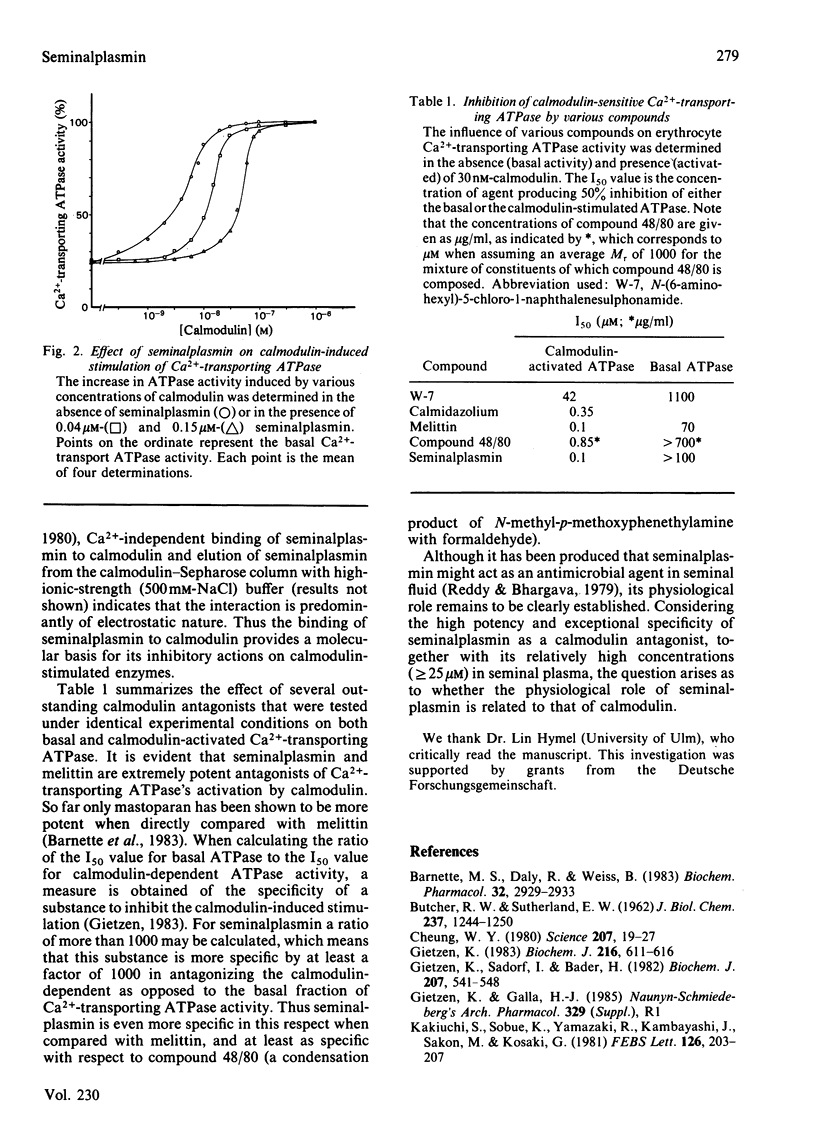
Seminalplasmin, a strongly basic protein isolated from bull semen, was found to antagonize with high potency and extraordinary specificity the function of calmodulin. Calmodulin antagonism is the result of an interaction between the two proteins, which is mainly determined by electrostatic forces. The stimulation of Ca2+-transporting ATPase and phosphodiesterase by calmodulin was half-maximally inhibited at approx. 0.1 microM-seminalplasmin. However, the basal activity of calmodulin-dependent enzymes was not significantly altered by seminalplasmin over the concentration range investigated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnette M. S., Daly R., Weiss B. Inhibition of calmodulin activity by insect venom peptides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Oct 1;32(19):2929–2933. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90398-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K. Comparison of the calmodulin antagonists compound 48/80 and calmidazolium. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):611–616. doi: 10.1042/bj2160611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K., Sadorf I., Bader H. A model for the regulation of the calmodulin-dependent enzymes erythrocyte Ca2+-transport ATPase and brain phosphodiesterase by activators and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj2070541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Sobue K., Yamazaki R., Kambayashi J., Sakon M., Kosaki G. Lack of tissue specificity of calmodulin: a rapid and high-yield purification method. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Raynor R. L., Wise B. C., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Helfman D. M., Fain J. N., Kuo J. F. Inhibition by melittin of phospholipid-sensitive and calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):217–224. doi: 10.1042/bj2020217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Wierman B. M., Storm D. R. Calcium-induced exposure of a hydrophobic surface on calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3814–3819. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Anderson S. R. Binding of simple peptides, hormones, and neurotransmitters by calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3480–3486. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Bhargava P. M. Seminalplasmin--an antimicrobial protein from bovine seminal plasma which acts in E. coli by specific inhibition of rRNA synthesis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):725–728. doi: 10.1038/279725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellinger-Barnette M., Weiss B. Interaction of beta-endorphin and other opioid peptides with calmodulin. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. Sensitive automated methods for phosphate and (Na+ plus K+)-ATPase. Anal Biochem. 1974 Dec;62(2):349–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil R., Scheit K. H. Amino acid sequence of seminalplasmin, an antimicrobial protein from bull semen. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1159–1163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Desai R. Modulator binding protein. Bovine brain protein exhibiting the Ca2+-dependent association with the protein modulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4175–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


