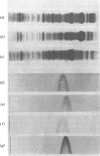
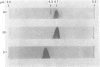
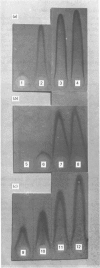
Abstract
The enzyme propanediol oxidoreductase, which converts the lactaldehyde formed in the metabolism of fucose and rhamnose into propane-1,2-diol under anaerobic conditions, was investigated in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Salmonella typhimurium. Structural analysis indicated that the enzymes of E. coli and K. pneumoniae have the same Mr and pI, whereas that of Salm. typhimurium also has the same Mr but a slightly different pI. One-dimensional peptide mapping showed identity between the E. coli and K. pneumoniae enzymes when digested with alpha-chymotrypsin, Staphylococcus aureus V8 proteinase or subtilisin. In the case of Salm. typhimurium, this held only for the subtilisin-digested enzymes, indicating that the hydrophobic regions were preserved to a considerable extent. Anaerobically, the three species induced an active propanediol oxidoreductase when grown on fucose or rhamnose. An inactive propanediol oxidoreductase was induced in Salm. typhimurium by either fucose or rhamnose under aerobic conditions, and this was activated once anaerobiosis was established. An inactive propanediol oxidoreductase was also induced in E. coli under aerobic conditions, but only by growth on fucose. The inactive enzyme was not induced by either of the sugars in K. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badía J., Ros J., Aguilar J. Fermentation mechanism of fucose and rhamnose in Salmonella typhimurium and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.435-437.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boronat A., Aguilar J. Metabolism of L-fucose and L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli: differences in induction of propanediol oxidoreductase. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):181–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.181-185.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boronat A., Aguilar J. Rhamnose-induced propanediol oxidoreductase in Escherichia coli: purification, properties, and comparison with the fucose-induced enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):320–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.320-326.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Dual control of a common L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase by L-fucose and L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):828–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.828-832.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Post-transcriptional control of L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase in the L-fucose pathway of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):341–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.341-344.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C., Ros J., Aguilar J. Use of operon fusions to examine the regulation of the L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase gene of the fucose system in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Nov;129(11):3355–3362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-11-3355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Feingold D. S. L-rhamnulose 1-phosphate aldolase from Escherichia coli. Crystallization and properties. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):98–108. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blomberg F. Immunochemical studies of thylakoid membrane polypeptides from spinach and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. A modified procedure for crossed immunoelectrophoresis of dodecyl sulfate.protein complexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Aguilar T., Lin E. C. Evolution of L-1, 2-propanediol catabolism in Escherichia coli by recruitment of enzymes for L-fucose and L-lactate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.83-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHALAMBOR M. A., HEATH E. C. The metabolism of L-fucose. II. The enzymatic cleavage of L-fuculose 1-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2427–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., COHEN S. S. Enzymatic conversion of L-fucose to L-fuculose. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):557–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH E. C., GHALAMBOR M. A. The metabolism of L-fucose. I. The purification and properties of L-fuculose kinase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2423–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamy J., Compin S., Lamy J. N. Immunological correlates between multiple isolated subunits of Androctonus australis and Limulus polyphemus hemocyanins: an evolutionary approach. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):584–603. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90623-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H. Molecular evolution, intracellular organization, and the quinary structure of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3236–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros J., Aguilar J. Genetic and structural evidence for the presence of propanediol oxidoreductase isoenzymes in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Mar;130(3):687–692. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-3-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhara S., Wu T. T. Purification and properties of lactaldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5233–5238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. High-resolution preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: fluorescent visualization and electrophoretic elution-concentration of protein bands. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI Y., SAWADA H. THE METABOLISM OF L-RHAMNOSE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. L-RHAMNOSE ISOMERASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 23;92:10–17. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI Y., SAWADA H. THE METABOLISM OF L-RHAMNOSE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. II. L-RHAMNULOSE KINASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 23;92:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90264-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijssen P., Kurstak E. A simple and sensitive method for the purification and peptide mapping of proteins solubilized from densonucleosis virus with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]