Abstract
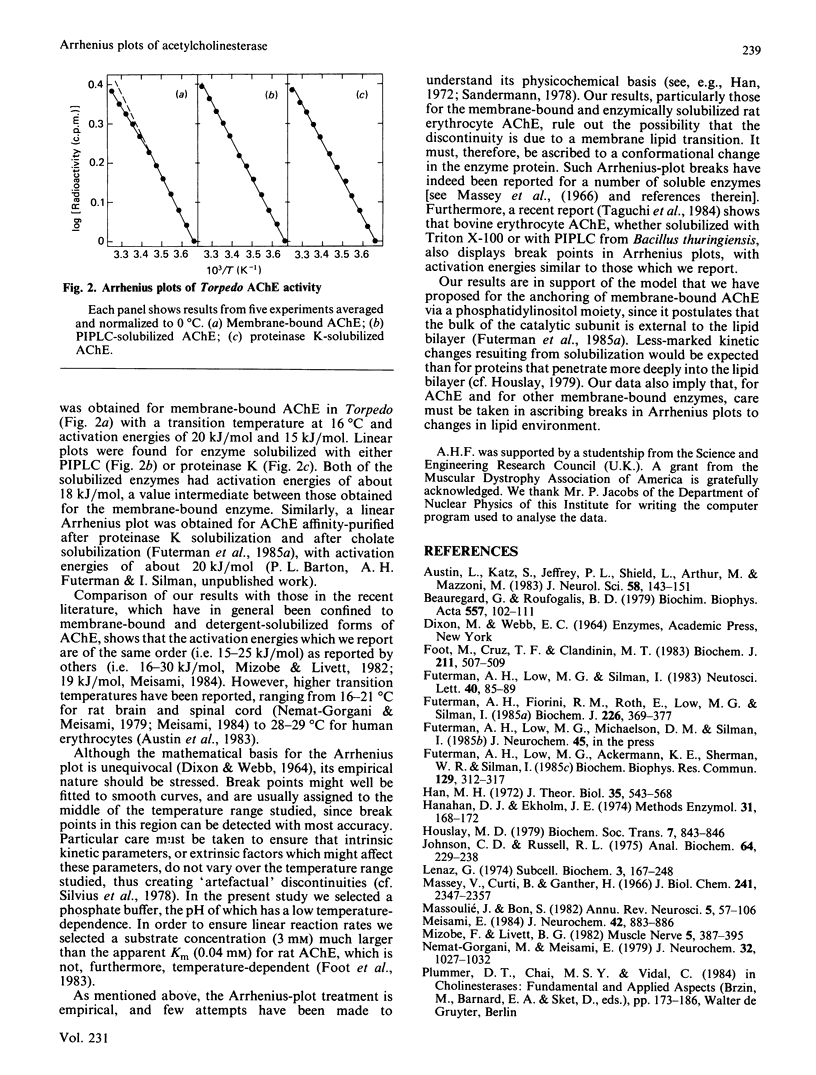
The temperature-dependence of the catalytic activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) from rat erythrocyte-ghost membranes and from Torpedo electric-organ membranes was examined. In the case of rat erythrocyte AChE, a non-linear Arrhenius plot was observed both before and after solubilization by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C or by proteinase treatment. Similarly, no significant differences were observed in Arrhenius plots of Torpedo electric-organ AChE before or after solubilization. These results support our suggestion that the catalytic subunit of AChE does not penetrate deeply into the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane and also suggest that care must be taken in ascribing break points in Arrhenius plots of membrane-bound enzymes to changes in their lipid environment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin L., Katz S., Jeffrey P. L., Shield L., Arthur H., Mazzoni M. Thermodynamic behaviour of membrane enzymes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Jan;58(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauregard G., Roufogalis B. D. Involvement of calcium ions in the properties of cardiolipin-associated erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):102–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foot M., Cruz T. F., Clandinin M. T. Effect of dietary lipid on synaptosomal acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):507–509. doi: 10.1042/bj2110507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Fiorini R. M., Roth E., Low M. G., Silman I. Physicochemical behaviour and structural characteristics of membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo electric organ. Effect of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):369–377. doi: 10.1042/bj2260369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Low M. G., Ackermann K. E., Sherman W. R., Silman I. Identification of covalently bound inositol in the hydrophobic membrane-anchoring domain of Torpedo acetylcholinesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):312–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Low M. G., Silman I. A hydrophobic dimer of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica electric organ is solubilized by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Sep 19;40(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M. H. Non-linear Arrhenius plots in temperature-dependent kinetic studies of enzyme reactions. I. Single transition processes. J Theor Biol. 1972 Jun;35(3):543–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(72)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J., Ekholm J. E. The preparation of red cell ghosts (membranes). Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:168–172. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D. Coupling of the glucagon receptor to adenylate cyclase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):843–846. doi: 10.1042/bst0070843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaz G. Lipid-protein interactions in the structure of biological membranes. Subcell Biochem. 1974 Sep;3(3):167–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Curti B., Ganther H. A temperature-dependent conformational change in D-amino acid oxidase and its effect on catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2347–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisami E. Is butyrylcholinesterase of the rat CNS a membrane-bound enzyme? J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):883–886. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizobe F., Livett B. G. Evidence against a generalized membrane defect in dystrophic mice platelets. Muscle Nerve. 1982 May-Jun;5(5):387–395. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemat-Gorgani M., Meisami E. Use of Arrhenius plots of Na-K ATPase and acetylcholinesterase as a tool for studying changes in lipid-protein interactions in neuronal membranes during brain development. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):1027–1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Scoggin D. M. Structure of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Characterization of intersubunit disulfide bonding and detergent interaction. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5643–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr Regulation of membrane enzymes by lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):209–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. R., Read B. D., McElhaney R. N. Membrane enzymes: artifacts in Arrhenius plots due to temperature dependence of substrate-binding affinity. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):902–904. doi: 10.1126/science.146257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi R., Suzuki K., Nakabayashi T., Ikezawa H. Acetylcholinesterase release from mammalian erythrocytes by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus thuringiensis and characterization of the released enzyme. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):437–446. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viratelle O. M., Bernhard S. A. Major component of acetylcholinesterase in Torpedo electroplax is not basal lamina associated. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):4999–5007. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


