Abstract
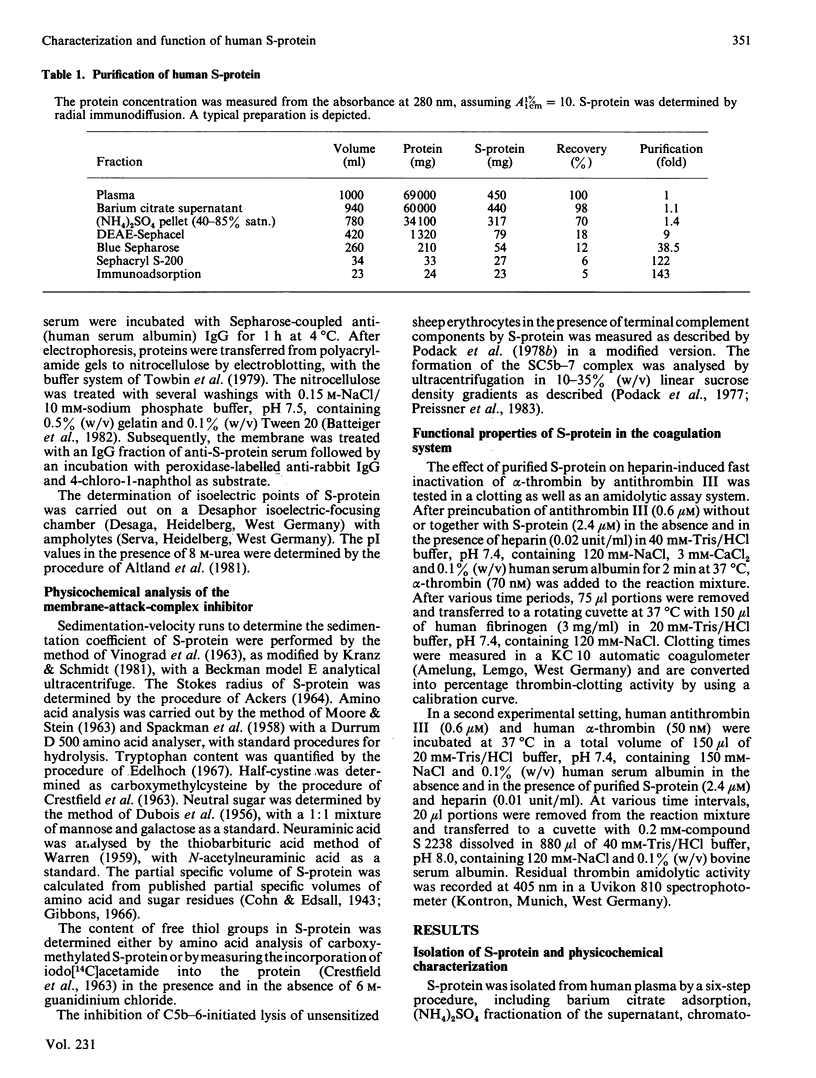
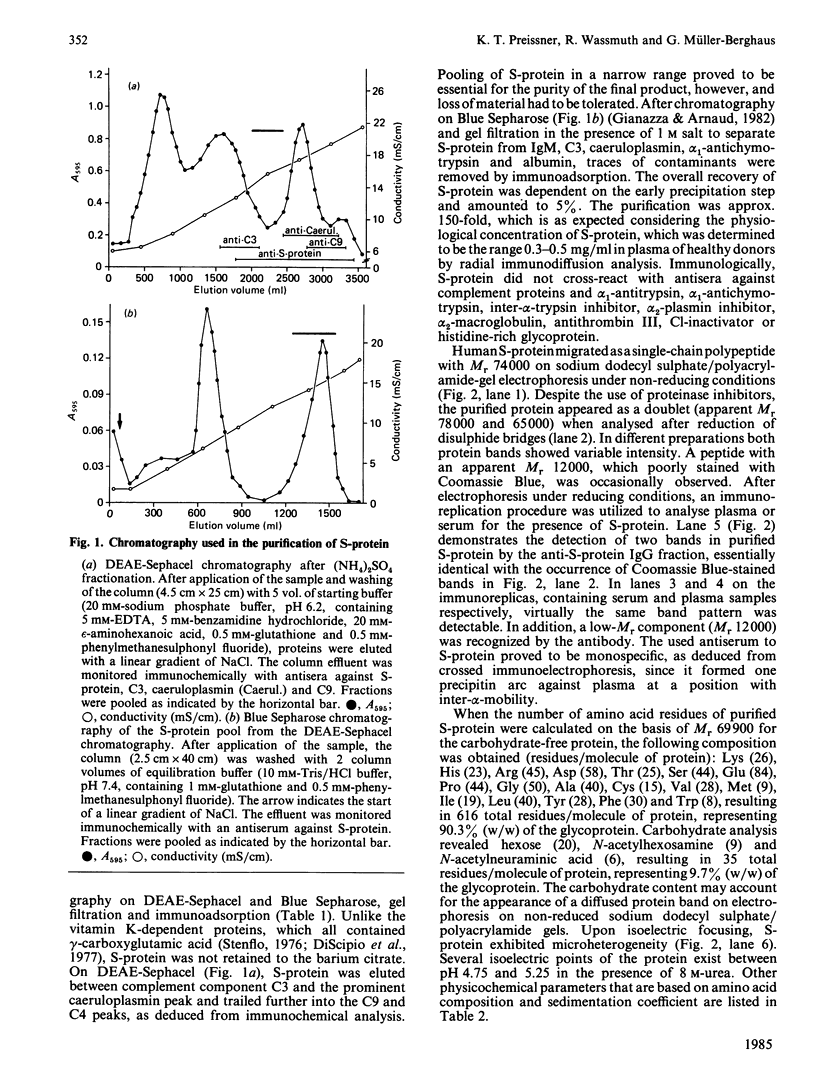
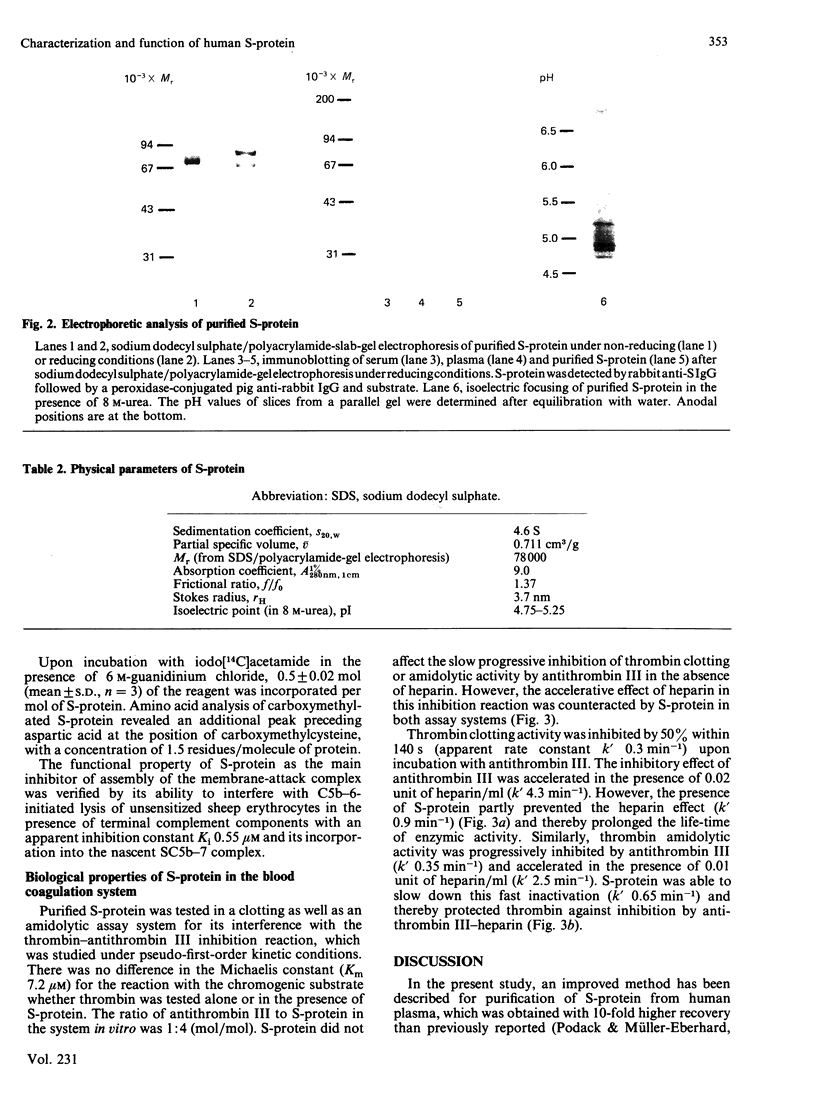
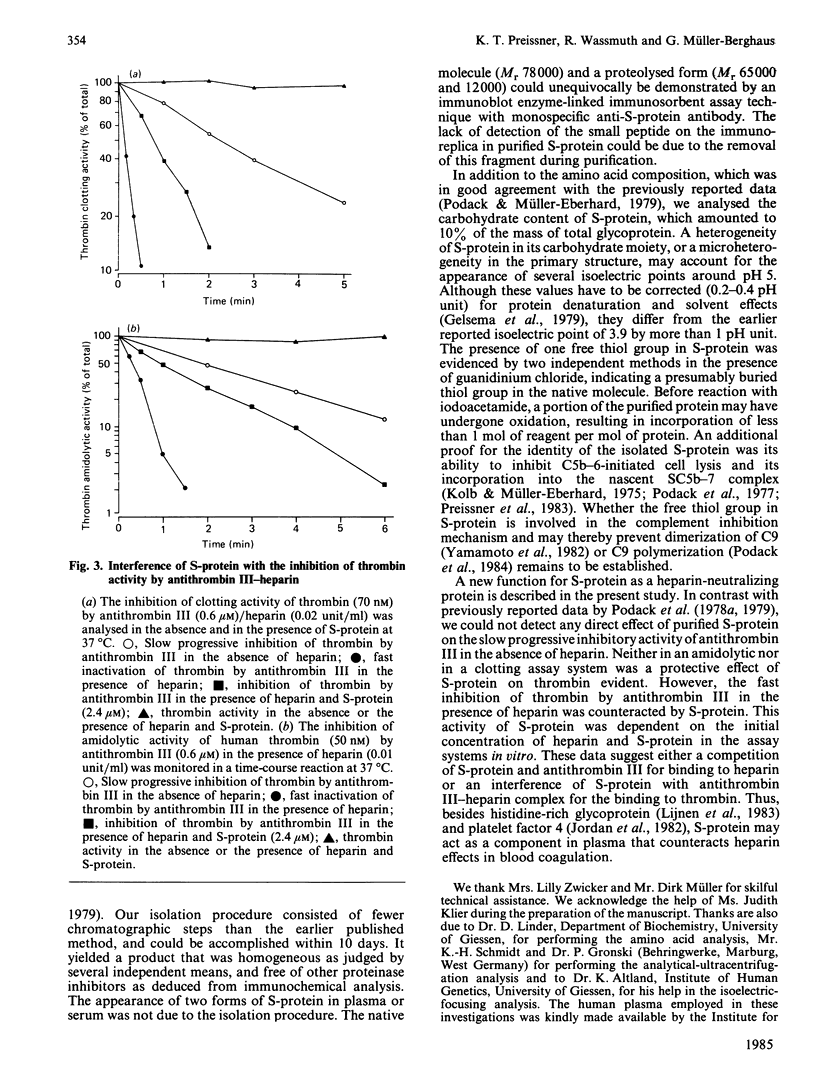
S-protein, the main inhibitor of the assembly of the membrane attack complex of complement, was isolated from human plasma by a simple purification procedure, which includes barium citrate adsorption, ammonium sulphate precipitation, chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel and Blue Sepharose and gel filtration on Sephacryl S-200. The homogeneous protein (sedimentation coefficient 4.6 S) was obtained in approx. 5% yield relative to its concentration in plasma, which was found to be 0.3-0.5 mg/ml. The final product did not cross-react with antisera against complement proteins or other proteinase inhibitors of human plasma. On polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate, S-protein migrated as a single-chain band with an apparent Mr of 74000 under non-reducing conditions and as a doublet of Mr 78000 and 65000 upon reduction. In plasma or serum S-protein also existed in two forms of corresponding Mr values, as was evidenced by an immunoblot enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique. S-protein was found to be an acidic glycoprotein with 10% (W/W) carbohydrate content and several isoelectric points in the range pH 4.75-5.25, and it contained one free thiol group per molecule of protein. The functional properties of S-protein in the complement system were demonstrated by its ability to inhibit complement-dependent cell lysis in a concentration-dependent manner (Ki 0.6 microM) and by its incorporation into the nascent SC5b-7 complex. A new function for S-protein could be revealed in the blood coagulation system. The slow progressive inhibition of thrombin by antithrombin III was not affected by S-protein, whereas the purified protein interfered with the fast inactivation of thrombin clotting as well as amidolytic activity by antithrombin III-heparin complex. The acceleration of this inhibition reaction by heparin was counteracted by S-protein, indicating the ability of S-protein to neutralize heparin activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Tranum-Jensen J. Proteolytic transformation of SC5b-9 into an amphiphilic macromolecule resembling the C5b-9 membrane attack complex of complement. Immunology. 1979 Aug;37(4):901–912. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R. The structural events associated with the attachment of complement components to cell membranes in reactive lysis. Immunology. 1978 Aug;35(2):205–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J. Polyethylene glycol 6,000 enhancement of the clotting of fibrinogen solutions in visual and mechanical assays. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelsema W. J., de Ligny C. L., van der Veen N. G. Isoelectric points of proteins, determined by isoelectric focusing in the presence of urea and ethanol. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 1;171:171–181. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)95297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianazza E., Arnaud P. Chromatography of plasma proteins on immobilized Cibacron Blue F3-GA. Mechanism of the molecular interaction. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):637–641. doi: 10.1042/bj2030637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Nicholson A., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cytolysis by complement: evidence on insertion of C5b and C7 subunits of the C5b,6,7 complex into phospholipid bilayers of erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Favreau L. V., Braswell E. H., Rosenberg R. D. Heparin with two binding sites for antithrombin or platelet factor 4. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz T., Schmidt K. H. Improved methodology for the analysis of mixtures by band centrifugation. Quantitative determination of components in protein mixtures. J Biol Stand. 1981 Jan;9(1):51–65. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(81)80065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Neutralization of heparin activity by binding to human histidine-rich glycoprotein. Thromb Res. 1983 Feb 15;29(4):443–446. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90248-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lint T. F., Behrends C. L., Baker P. J., Gewurz H. Activation of the complement attack mechanism in the fluid phase and its control by C567-INH: lysis of normal erythrocytes initiated by zymosan, endotoxin, and immune complexes. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1440–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod B. C., Baker P., Gewurz H. Studies on the inhibition of C56-initiated lysis (reactive lysis). II. C567-INH--an inhibitor of the C567 trimolecular complex of complement. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(4):623–632. doi: 10.1159/000231255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod B., Baker P., Gewurz H. Studies on the inhibition of C56 initiated lysis (reactive lysis). I. Description of the phenomenon and methods of assay. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1145–1157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):93–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01893017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Yamamoto K. I., Lint T. F. Restriction of complement-mediated membrane damage by the eighth component of complement: a dual role for C8 in the complement attack sequence. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Nyström C., Björk I. The size and shape of human and bovine antithrombin III. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway of complement. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):163–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01893019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Esser A. F., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: a structural analysis of its assembly. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):301–313. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: formation, isolation, and inhibition of its activity by lipoprotein and the S-protein of human serum. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The SC5b-7 complex: formation, isolation, properties, and subunit composition. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2024–2029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Binding of desoxycholate, phosphatidylcholine vesicles, lipoprotein and of the S-protein to complexes of terminal complement components. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1025–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. SC5b-9 complex of complement: formation of the dimeric membrane attack complex by removal of S-protein. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1779–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Preissner K. T., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Inhibition of C9 polymerization within the SC5b-9 complex of complement by S-protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1984;284:89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschoop J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization of C9 within the membrane attack complex of complement. Induction of circular C9 polymerization by the C5b-8 assembly. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):268–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschopp J. Membrane attack by complement. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jul;21(7):589–603. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex of complement: relation of C7 to the metastable membrane binding site of the intermediate complex C5b-7. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Lachmann P. J. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. I. The characterization of the indicator factor and its identification as C7. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):629–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Ultrastructure of the membrane attack complex of complement: detection of the tetramolecular C9-polymerizing complex C5b-8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7474–7478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINOGRAD J., BRUNER R., KENT R., WEIGLE J. Band-centrifugation of macromolecules and viruses in self-generating density gradients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:902–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Kawashima T., Migita S. Glutathione-catalyzed disulfide-linking of C9 in the membrane attack complex of complement. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8573–8576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



