Abstract
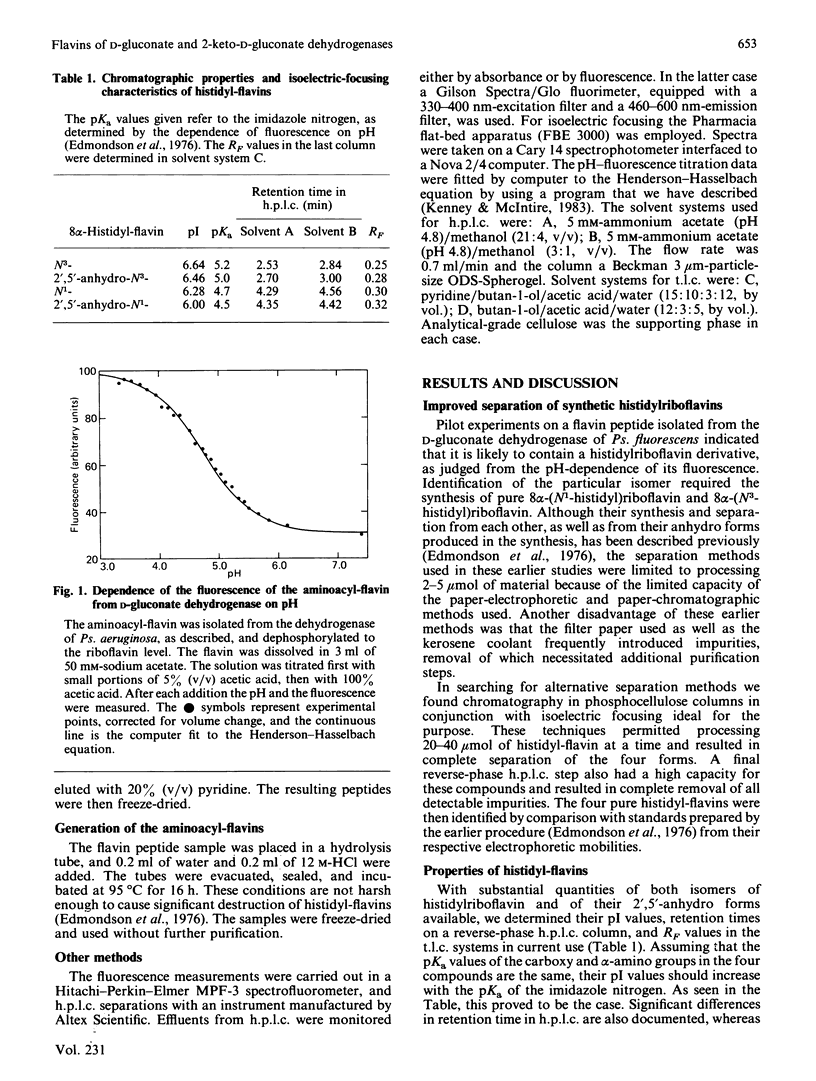
An improved method is presented for the purification of 8 alpha-(N1-histidyl)riboflavin, 8 alpha-(N3-histidyl)riboflavin and their 2',5'-anhydro forms, which permits the isolation of sizeable quantities of each of these compounds from a synthetic mixture in pure form. Flavin peptides were isolated from the D-gluconate dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas fluorescens and from the 2-keto-D-gluconate dehydrogenase of Gluconobacter melanogenus. After conversion into the aminoacyl-riboflavin, the flavin in all three enzymes was identified as 8 alpha-(N3-histidyl)riboflavin. By sequential treatment with nucleotide pyrophosphatase and alkaline phosphatase, the flavin in each enzyme was shown to be in the dinucleotide form.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edmondson D. E., Kenney W. C., Singer T. P. Structural elucidation and properties of 8alpha-(N1-histidyl)riboflavin: the flavin component of thiamine dehydrogenase and beta-cyclopiazonate oxidocyclase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):2937–2945. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney W. C., Edmondson D. E., Singer T. P., Nishikimi M., Noguchi E., Yagi K. Identification of the covalently-bound flavin of L-galactonolactone oxidase from yeast. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):40–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney W. C., McIntire W. Characterization of methylamine dehydrogenase from bacterium W3A1. Interaction with reductants and amino-containing compounds. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3858–3868. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Shinagawa E., Adachi O., Ameyama M. Membrane-bound D-gluconate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Its kinetic properties and a reconstitution of gluconate oxidase. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):249–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Shinagawa E., Adachi O., Ameyama M. Membrane-bound D-gluconate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Purification and structure of cytochrome-binding form. J Biochem. 1979 May;85(5):1173–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Shinagawa E., Ameyama M. D-Gluconate dehydrogenase from bacteria, 2-keto-D-gluconate-yielding, membrane-bound. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):187–193. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire W., Edmondson D. E., Hopper D. J., Singer T. P. 8 alpha-(O-Tyrosyl)flavin adenine dinucleotide, the prosthetic group of bacterial p-cresol methylhydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3068–3075. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. H., Singer T. P., Ghisla S., Hemmerich P. Studies on succinate dehydrogenase. 8 -Histidyl-FAD as the active center of succinate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 27;26(2):279–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. H., Singer T. P. Identification of the covalently bound flavin of succinate dehydrogenase as 8-alpha-(histidyl) flavin adenine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4224–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


