Abstract
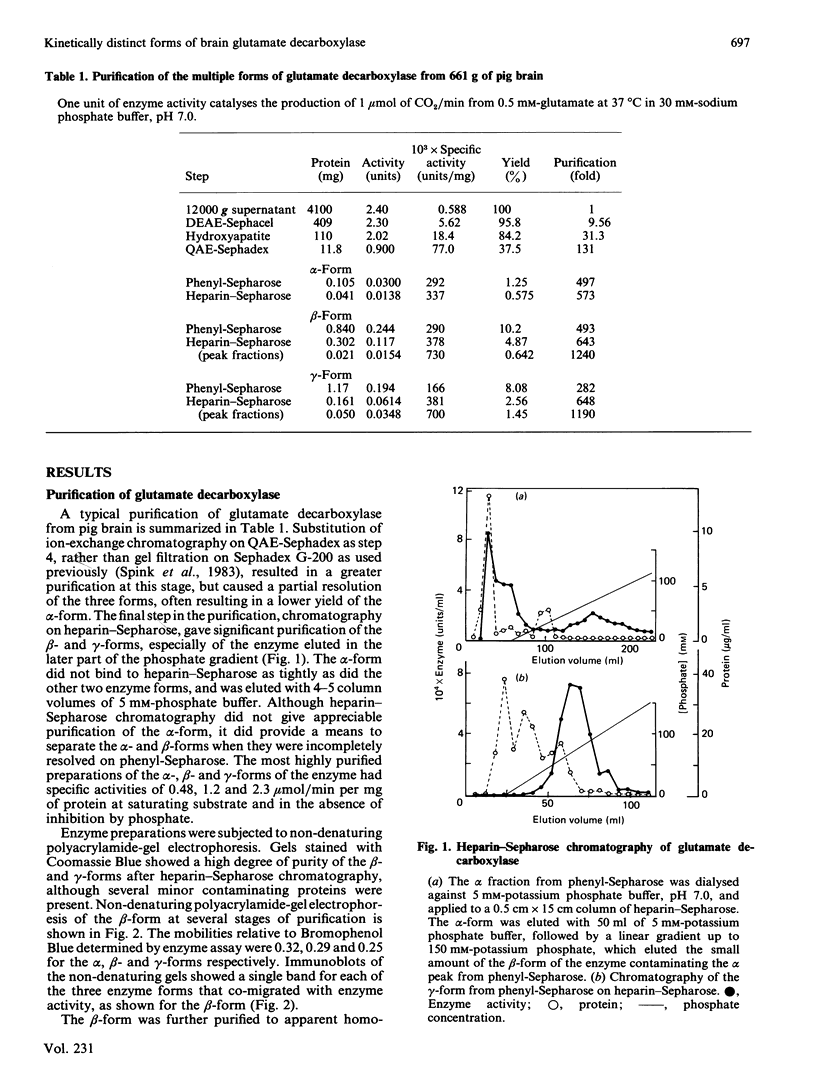
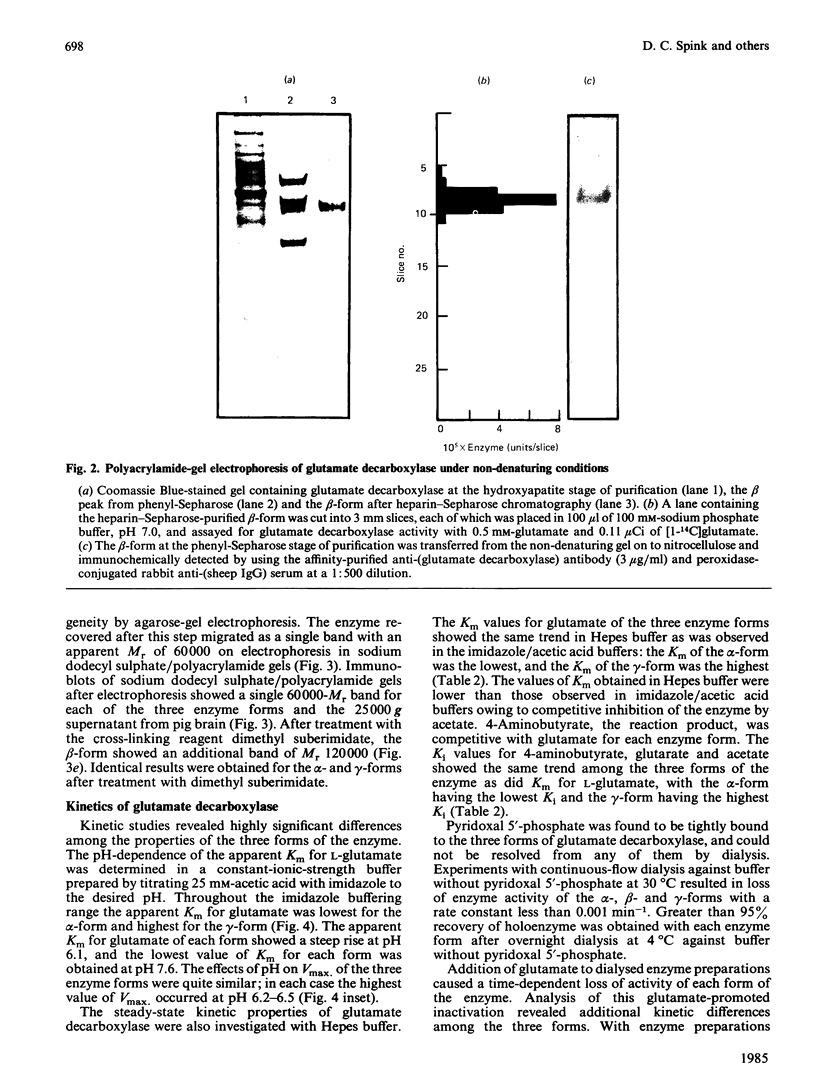
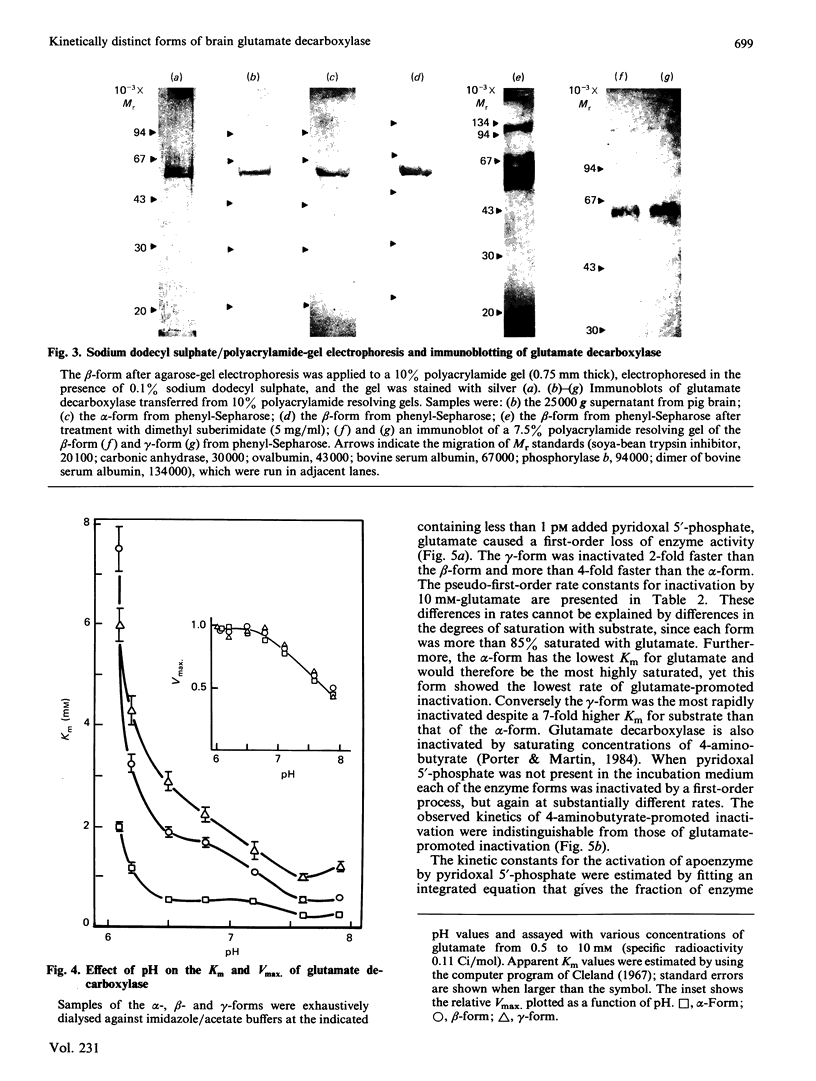
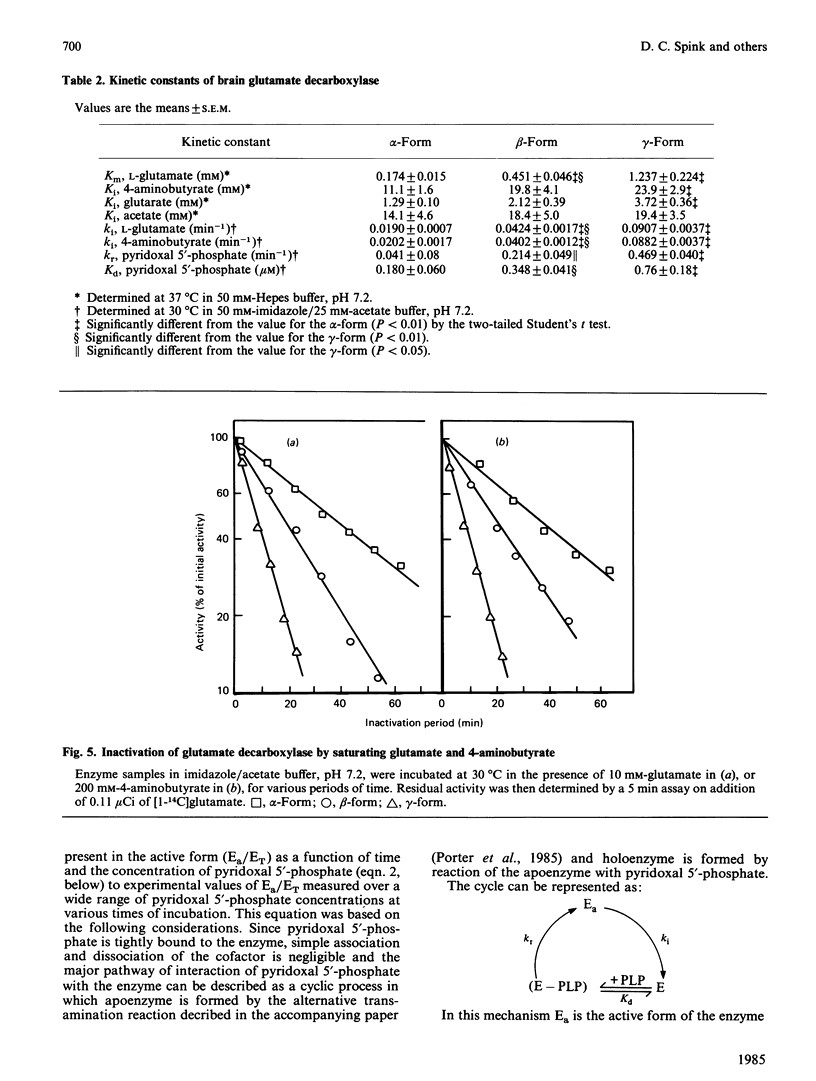
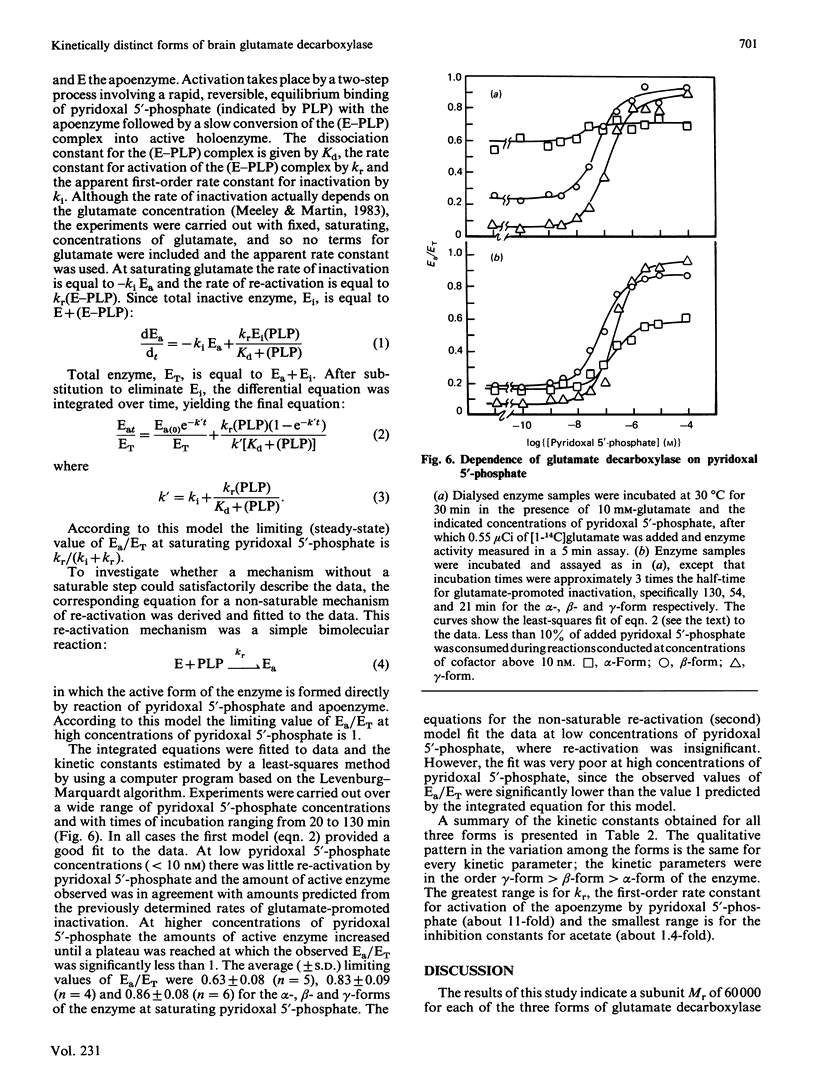
Pig brain contains three forms of glutamate decarboxylase with pI values of 5.3, 5.5 and 5.8, referred to as the alpha-, beta- and gamma-forms respectively. These forms were purified and kinetically characterized. The major synaptic form of glutamate decarboxylase (the beta-form) migrated as a single band on electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gels with an apparent Mr of 60 000. Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by immunoblotting with an affinity-purified antibody to the enzyme indicated a subunit Mr of 60 000 for the alpha- and gamma-forms as well. An extensive kinetic analysis, aided by an integrated equation that describes the inactivation and re-activation cycle of the enzyme, revealed that the three forms of the enzyme differ markedly in kinetic properties. The Km values for L-glutamate were 0.17, 0.45 and 1.24 mM respectively for the alpha-, beta- and gamma-forms. The Ki for 4-aminobutyrate, the first-order rate constants for inactivation by L-glutamate and 4-aminobutyrate, the rate constant for re-activation of the apoenzyme by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and the dissociation constant for pyridoxal 5'-phosphate also differed in a similar way among the three forms; the values were in the order alpha-form less than beta-form less than gamma-form.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERS R. W., BRADY R. O. The distribution of glutamic decarboxylase in the nervous system of the rhesus monkey. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):926–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayón A., Possani L. D., Tapia M., Tapia R. Kinetics of brain glutamate decarboxylase. Interactions with glutamate, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and glutamate-pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Schiff base. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blindermann J. M., Maitre M., Ossola L., Mandel P. Purification and some properties of L-glutamate decarboxylase from human brain. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Evans M. C. Cortical GABA turnover during bicuculline seizures in rats. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):886–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christenson J. G., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. On the identity of DOPA decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase (immunological titration-aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-serotonin-dopamine-norepinephrine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):343–347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner L. A., Wu J. Y. Two forms of rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase differ in their dependence on free pyridoxal phosphate. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K., Casu M. Dynamic utilization of GABA in substantia nigra: regulation by dopamine and GABA in the striatum, and its clinical and behavioral implications. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Sep 25;39:369–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00232586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold B. I., Roth R. H. Glutamate decarboxylase activity in striatal slices: characterization of the increase following depolarization. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):883–888. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K., Udenfriend S. A method for immediate visualization of proteins in acrylamide gels and its use for preparation of antibodies to enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1969 Sep;30(3):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitre M., Blindermann J. M., Ossola L., Mandel P. Comparison of the structures of L-glutamate decarboxylases from human and rat brains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 14;85(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90626-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Wu J. Y., Roberts E. Electrophoresis of glutamic acid decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.15) from mouse brain in sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gels. J Neurochem. 1973 Jul;21(1):167–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeley M. P., Martin D. L. Inactivation of brain glutamate decarboxylase and the effects of adenosine 5'-triphosphate and inorganic phosphate. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1983 Mar;3(1):39–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00734997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. P., Martin D. L., Mazumder A., Walters J. R. Studies on the regulation of GABA synthesis: substrate-promoted dissociation of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate from GAD. J Neurochem. 1978 Feb;30(2):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. P., Walters J. R. Effects of depolarization on cofactor regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase in substantia nigra synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1979 Aug;33(2):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. P., Walters J. R., Martin D. L. Post-mortem changes implicate adenine nucleotides and pyridoxal-5' -phosphate in regulation of brain glutamate decarboxylase. Nature. 1977 Apr 28;266(5605):847–848. doi: 10.1038/266847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. G., Martin D. L. Evidence for feedback regulation of glutamate decarboxylase by gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1464–1467. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. G., Spink D. C., Martin S. B., Martin D. L. Transaminations catalysed by brain glutamate decarboxylase. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):705–712. doi: 10.1042/bj2310705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B., Miller L. P., Brockman D. E., Martin D. L. Studies on the regulation of GABA synthesis: the interaction of adenine nucleotides and glutamate with brain glutamate decarboxylase. J Neurochem. 1978 Feb;30(2):371–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spink D. C., Wu S. J., Martin D. L. Multiple forms of glutamate decarboxylase in porcine brain. J Neurochem. 1983 Apr;40(4):1113–1119. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susz J. P., Haber B., Roberts E. Purification and some properties of mouse brain L-glutamic decarboxylase. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2870–2877. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turský T. Inhibition of brain glutamate decarboxylase by adenosine triphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(3):544–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS D. E., REISFELD R. A. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS IN POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS: EXTENSION TO NEW CONDITIONS OF PH AND BUFFER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Matsuda T., Roberts E. Purification and characterization of glutamate decarboxylase from mouse brain. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3029–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Wong E., Saito K., Roberts E., Schousboe A. Properties of L-glutamate decarboxylase from brains of adult and newborn mice. J Neurochem. 1976 Sep;27(3):653–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb10390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]