Abstract
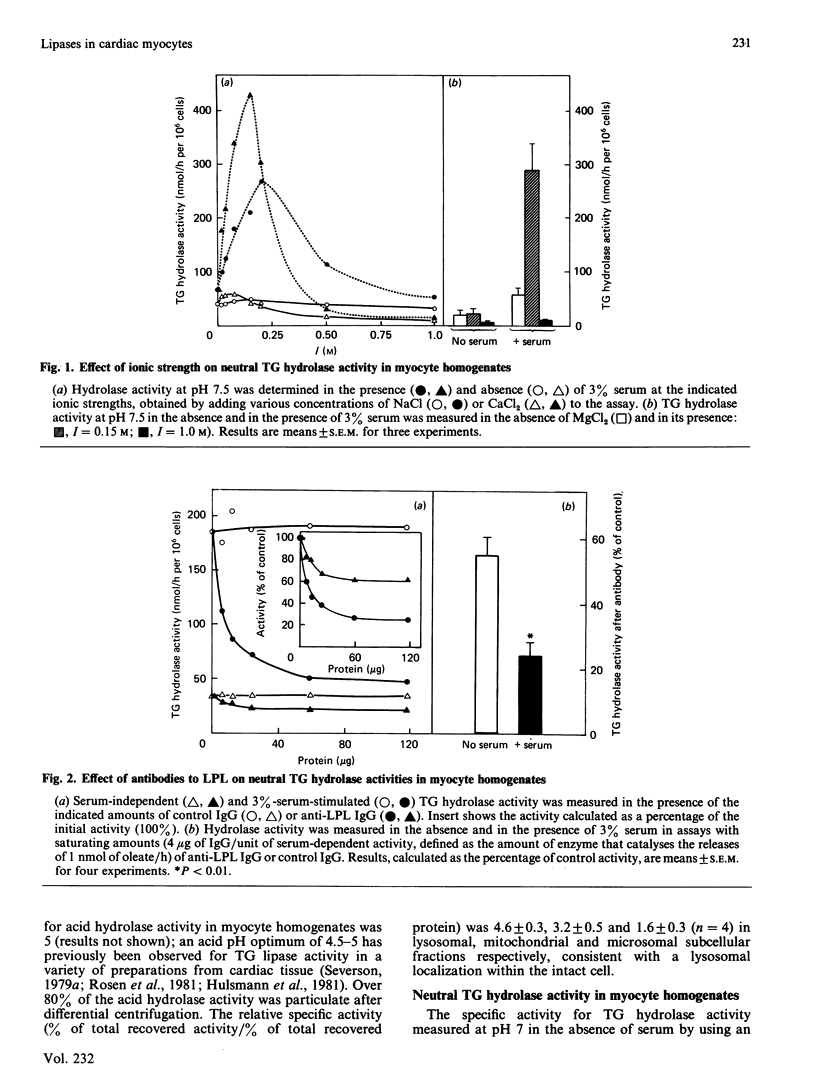
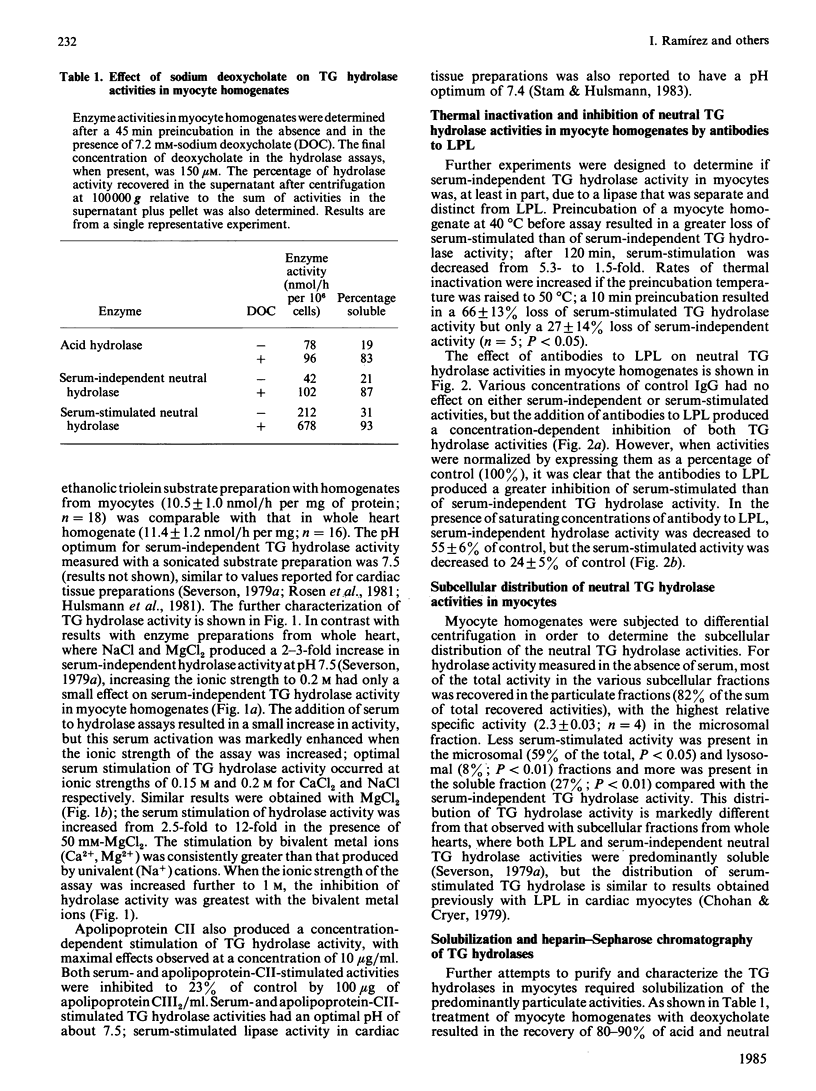
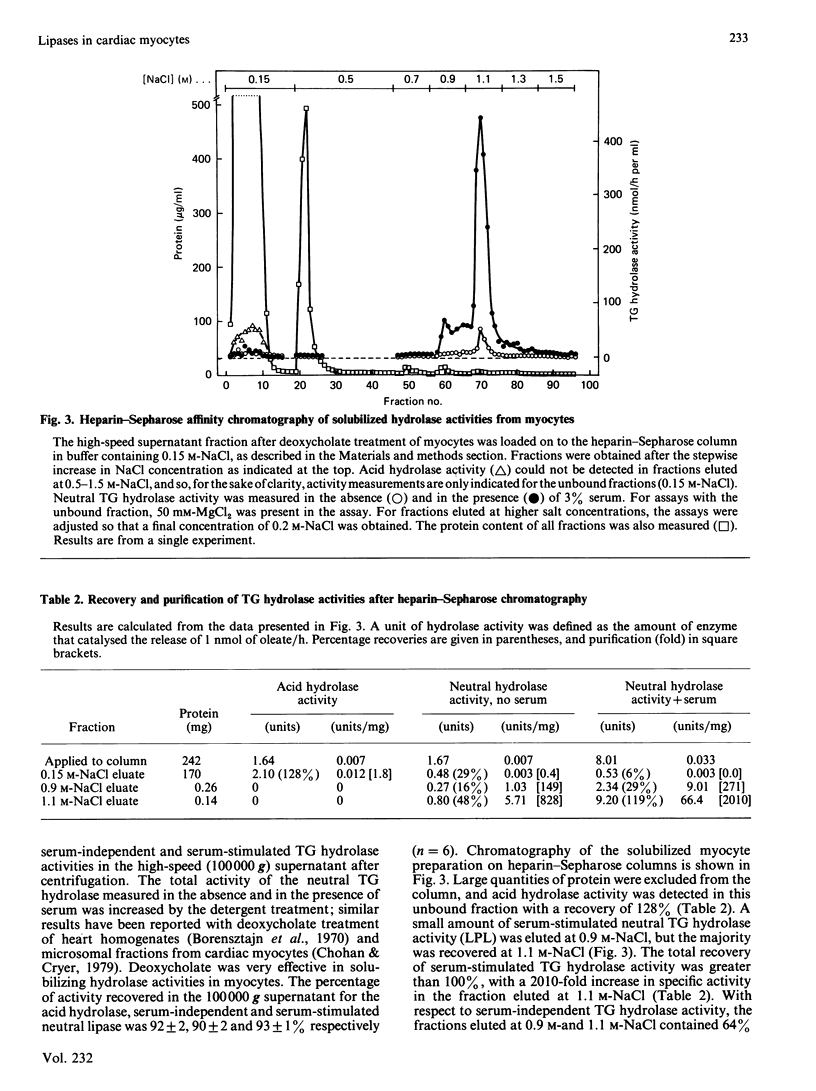
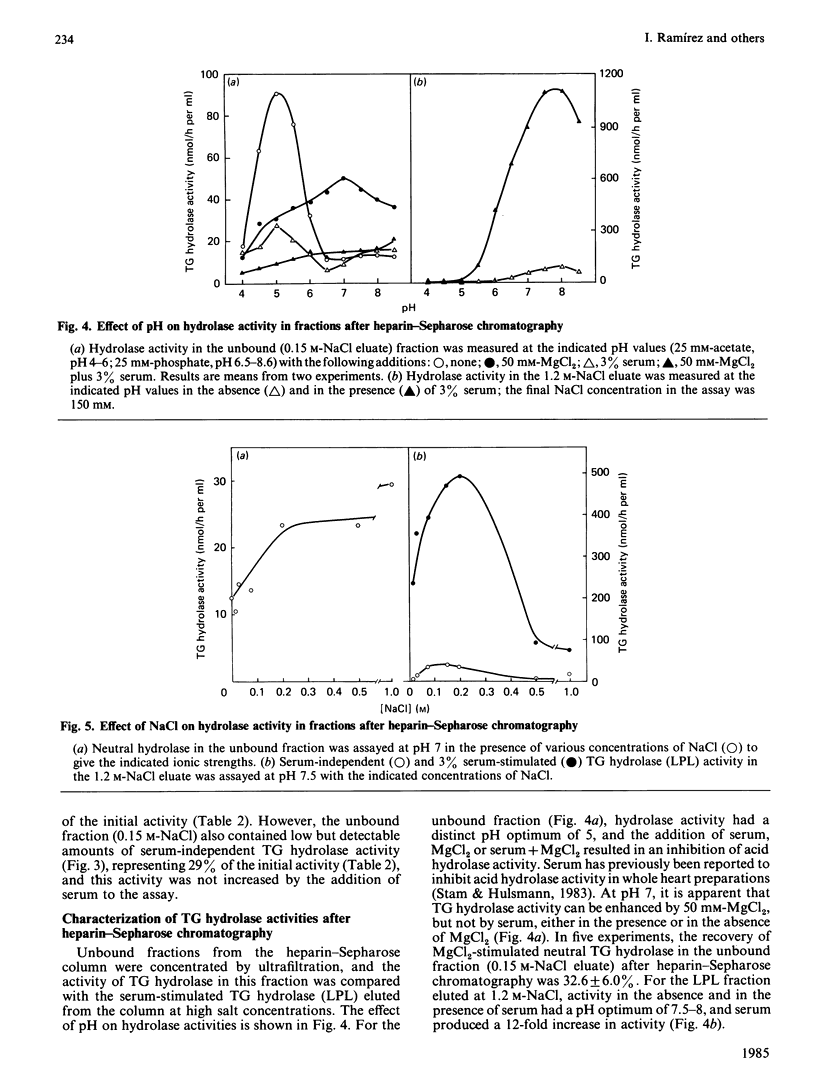
Triacylglycerol (TG) hydrolase activities were characterized in myocytes isolated from rat hearts. Acid hydrolase activity with a pH optimum of 5 could be measured in myocyte homogenates, and the subcellular distribution suggested that this activity originated in lysosomes. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) was also present in myocyte homogenates, as evidenced by TG hydrolase activity that was stimulated by serum and apolipoprotein CII, and inhibited by apolipoprotein CIII2, high ionic strength (NaCl and MgCl2, I = 1 M) and antibodies to LPL. Serum-independent neutral (pH 7.5) TG hydrolase activity was less sensitive to inhibition by 1 M-NaCl, by antibodies to LPL and by preincubation at 40 degrees C than was serum-stimulated hydrolase activity. Furthermore, there were modest but significant differences in the subcellular distribution of the serum-independent and serum-stimulated hydrolase activities. Hydrolase activities in myocyte homogenates could be solubilized by 7.2 mM-deoxycholate. Acid hydrolase activity was recovered in the unbound fraction after heparin-Sepharose chromatography, whereas LPL was bound to the affinity column and was eluted by 0.9-1.2 M-NaCl. Approximately one-third of the serum-independent TG hydrolase activity was not bound to the heparin-Sepharose affinity column. This unbound TG hydrolase activity had a pH optimum of 7 and was stimulated by 50 mM-MgCl2, but not by serum and was resistant to inhibition by high ionic strength (1 M-NaCl), to preincubation at 40 degrees C for 2 h, and by antibodies to LPL. It is concluded that, in addition to an acid lysosomal TG hydrolase and LPL, myocytes from rat heart contain a serum-independent TG hydrolase with unique characteristics.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagby G. J., Liu M. S., Spitzer J. A. Lipoprotein lipase activity in rat heart myocytes. Life Sci. 1977 Aug 1;21(3):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90529-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfrage P., Vaughan M. Simple liquid-liquid partition system for isolation of labeled oleic acid from mixtures with glycerides. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Zeev O., Schwalb H., Schotz M. C. Heparin-releasable and nonreleasable lipoprotein lipase in the perfused rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10550–10554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Otway S., Robinson D. S. Effect of fasting on the clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) activity of fresh and defatted preparations of rat heart muscle. J Lipid Res. 1970 Mar;11(2):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Robinson D. S. The effect of fasting on the utilization of chylomicron triglyceride fatty acids in relation to clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) releasable by heparin in the perfused rat heart. J Lipid Res. 1970 Mar;11(2):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL K. K. Separation of lipid classes by chromatography on Florisil. J Lipid Res. 1961 Apr;2:135–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Rat heart in culture as a tool to elucidate the cellular origin of lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 20;488(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Cryer A. Lipoprotein lipase activity of rat cardiac muscle. The intracellular distribution of the enzyme between fractions prepared from cardiac muscle and cells isolated from the hearts of fed and starved animals. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1810083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Cryer A. The lipoprotein lipase (clearing-factor lipase) activity of cells isolated from rat cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):663–666. doi: 10.1042/bj1740663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Scanu A. M. Isolation, molecular properties, and kinetic characterization of lipoprotein lipase from rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4202–4209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass M. F., 3rd Regulation of triglyceride metabolism in the isotopically prelabeled perfused heart. Fed Proc. 1977 Jun;36(7):1995–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Kinnunen P. K., Huttunen J. K., Nikkilä E. A., Ota M. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from pig myocardium. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):649–655. doi: 10.1042/bj1490649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hülsmann W. C., Stam H., Breeman W. A. Acid-and neutral lipases involved in endogenous lipolysis in small intestine and heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):440–448. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91540-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hülsmann W. C., Stam H., Breeman W. A. On the nature of neutral lipase in rat heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91876-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H., Stam H., Kalkman C., Hülsmann W. C. On the dual localization of lipoprotein lipase in rat heart. Studies with a modified perfusion technique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer T. E., Weglicki W. B. Characteristics of multiple forms of the acidic triacylglycerol lipase(s) of canine cardiac myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 20;753(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryski A., Jr, Kenno K. A., Severson D. L. Stimulation of lipolysis in rat heart myocytes by isoproterenol. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):H208–H216. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.2.H208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech J. J., Jesmok G. J., Calvert D. N. Effects of drugs and hormones on lipolysis in heart. Fed Proc. 1977 Jun;36(7):2000–2008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer W. K., Caruso R. A., Oscai L. B. Possible role of lipoprotein lipase in the regulation of endogenous triacylglycerols in the rat heart. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):159–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1980159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer W. K., Kane T. A. Hormonal activation of type-L hormone-sensitive lipase measured in defatted heart powders. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):379–383. doi: 10.1042/bj2120379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer W. K., Kane T. A. Hormone-stimulated lipolysis in cardiac myocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):241–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2160241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen M. E., Cohen M., Schotz M. C. Immunocytochemical localization of the functional fraction of lipoprotein lipase in the perfused heart. J Lipid Res. 1983 May;24(5):512–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robrish S. A., Kemp C., Bowen W. H. The use of the o-phthalaldehyde reaction as a sensitive assay for protein and to determine protein in bacterial cells and dental plaque. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jan;84(1):196–204. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösen P., Budde T., Reinauer H. Triglyceride lipase activity in the diabetic rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):539–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(81)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz M. C., Twu J. S., Pedersen M. E., Chen C. H., Garfinkel A. S., Borensztajn J. Antibodies to lipoprotein lipase. Application to perfused heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 24;489(2):214–224. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L. Characterization of triglyceride lipase activities in rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Jun;11(6):569–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(79)90431-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Lefebvre F. A., Sloan S. K. Effect of chloroquine on rates of lipolysis in the isolated perfused rat heart and in rat epididymal fat pads. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1980 Oct;12(10):977–992. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(80)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L. Regulation of lipid metabolism in adipose tissue and heart. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;57(9):923–937. doi: 10.1139/y79-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Sloan S. K., Kryski A., Jr Acid and neutral triacylglycerol ester hydrolases in rat heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):247–253. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam H., Hülsmann W. C. Comparison of heparin-releasable lipase and tissue neutral lipase activity of rat heart. Biochem Int. 1983 Aug;7(2):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam H., Hülsmann W. C. Effects of hormones, amino acids and specific inhibitors on rat heart heparin-releasable lipoprotein lipase and tissue neutral lipase activities during long-term perfusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):72–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from human heart. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Jul-Aug;24(1-2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Rat heart lipoprotein lipase. Atherosclerosis. 1975 Nov-Dec;22(3):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(75)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahouny G. V., Tamboli A., Vander Maten M., Jansen H., Twu J. S., Schotz M. C. Lipoprotein lipase activity of adult rat cardiocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 6;620(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. W., Menahan L. A., Lech J. J. Subcellular localization of marker enzymes, lipase and triglyceride in rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1977 Jan;9(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(77)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



