Abstract
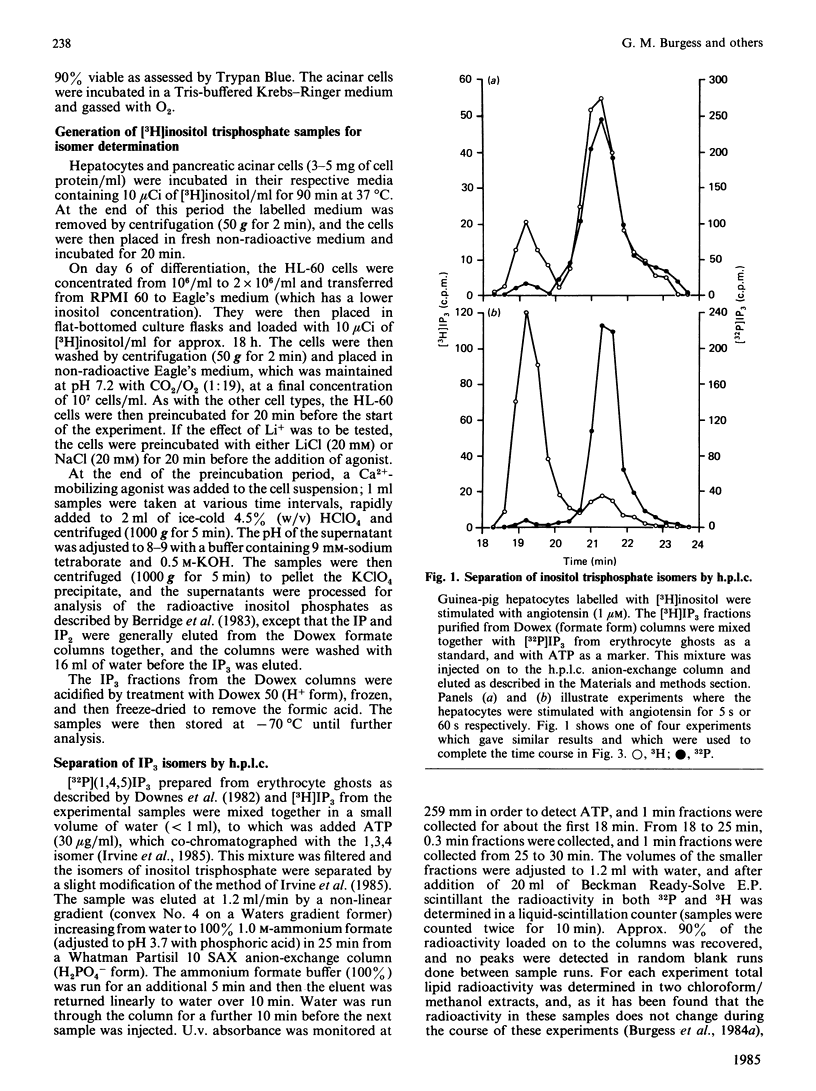
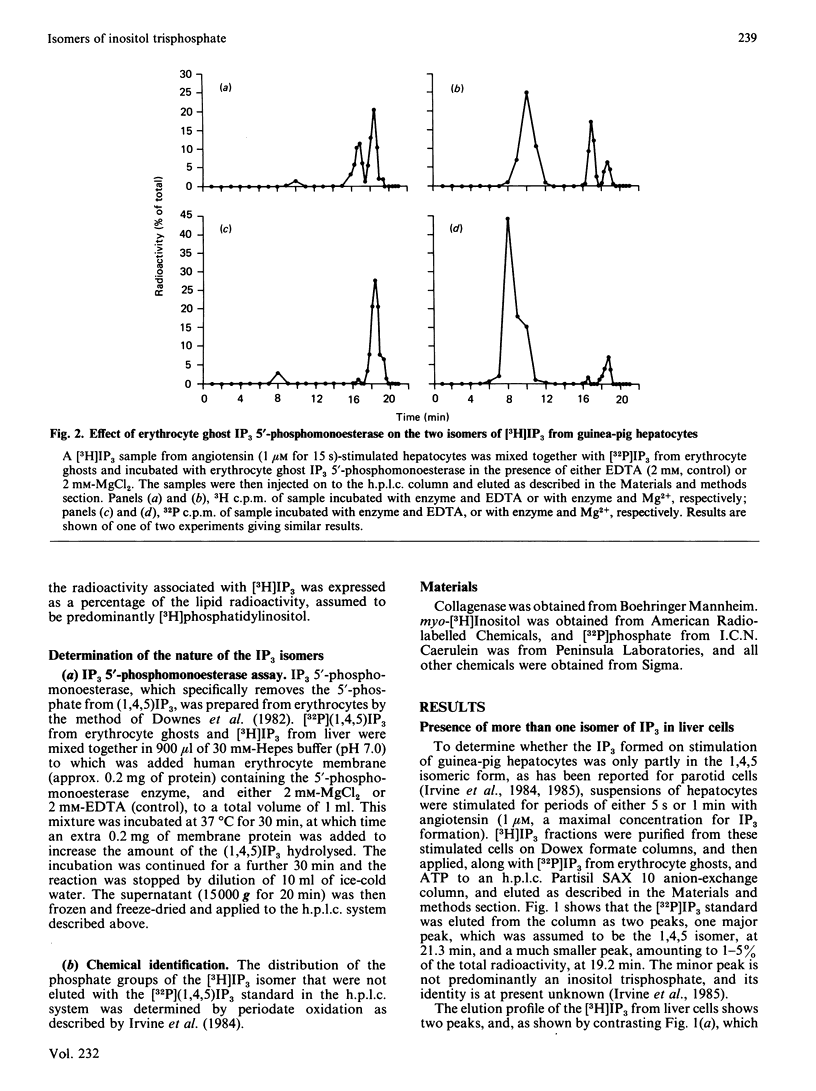
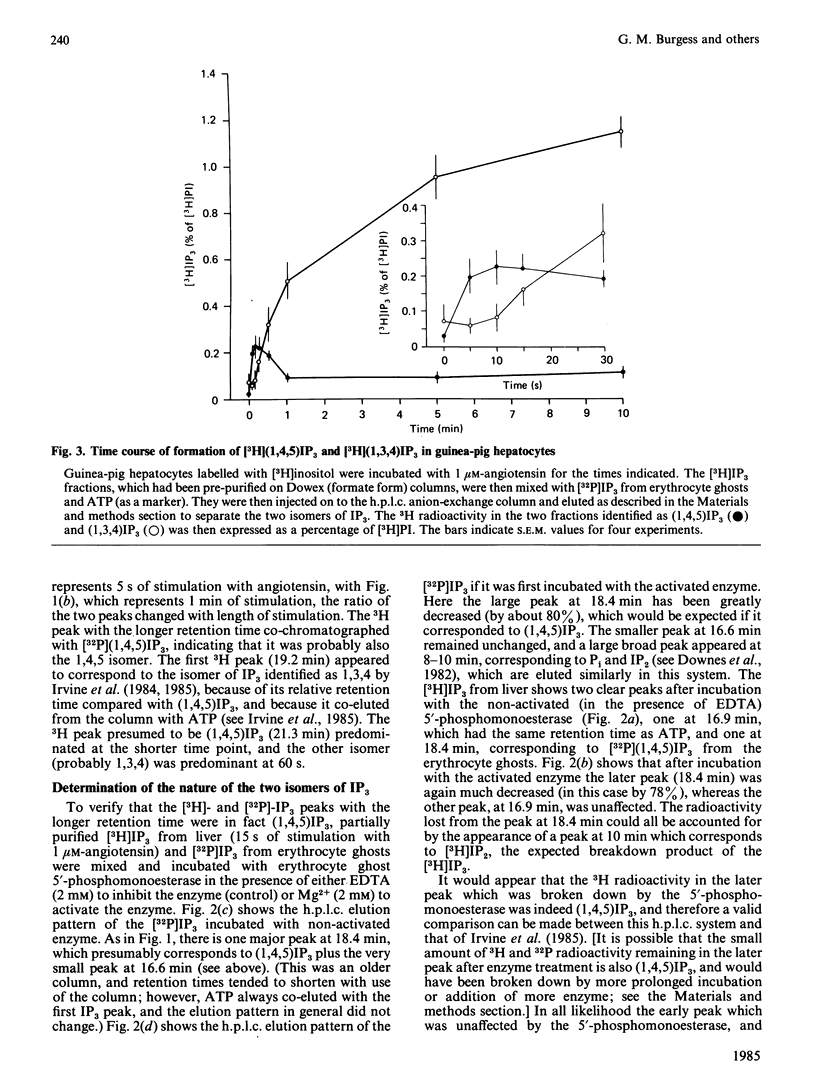
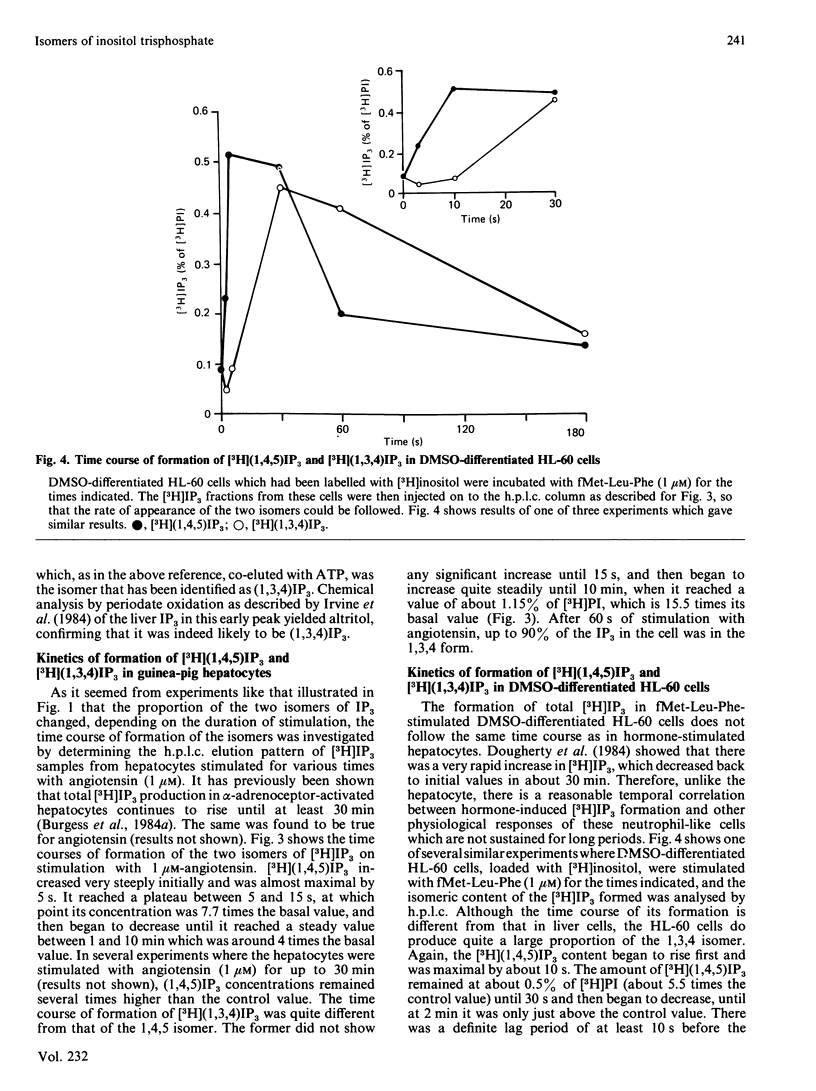
The inositol trisphosphate liberated on stimulation of guinea-pig hepatocytes, pancreatic acinar cells and dimethyl sulphoxide-differentiated human myelomonocytic HL-60 leukaemia cells is composed of two isomers, the 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the 1,3,4-trisphosphate. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate was released rapidly, with no measurable latency on hormone stimulation, and, consistent with its proposed role as an intracellular messenger for Ca2+ mobilization, there was good temporal correlation between its formation and Ca2+-mediated events in these tissues. There was a definite latency before an increase in the formation of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate could be detected. In all of these tissues, however, it formed a substantial proportion of the total inositol trisphosphate by 1 min of stimulation. In guinea-pig hepatocytes, where inositol trisphosphate increases for at least 30 min after hormone application, inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate made up about 90% of the total inositol trisphosphate by 5-10 min. In pancreatic acinar cells, pretreatment with 20 mM-Li+ caused an increase in hormone-induced inositol trisphosphate accumulation. This increase was accounted for by a rise in inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate; inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate was unaffected. This finding is consistent with the observation that Li+ has no effect on Ca2+-mediated responses in these cells. The role, if any, of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in cellular function is unknown.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aub D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Metabolism of inositol phosphates in parotid cells: implications for the pathway of the phosphoinositide effect and for the possible messenger role of inositol trisphosphate. Life Sci. 1984 Apr 2;34(14):1347–1355. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Brown K. D. Inositol trisphosphate formation and calcium mobilization in Swiss 3T3 cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2220195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Godfrey P. P., McKinney J. S., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr The second messenger linking receptor activation to internal Ca release in liver. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):63–66. doi: 10.1038/309063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of inositol phosphates on Ca2+ pools in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):741–746. doi: 10.1042/bj2240741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate may be a signal for f-Met-Leu-Phe-induced intracellular Ca mobilisation in human leucocytes (HL-60 cells). FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80939-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P., Irvine R. F. Inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate-promoted Ca2+ release from microsomal fractions of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):858–864. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Godfrey P. P., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr, Freer R. J. Secretagogue-induced phosphoinositide metabolism in human leucocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2220307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey P. P., Putney J. W., Jr Receptor-mediated metabolism of the phosphoinositides and phosphatidic acid in rat lacrimal acinar cells. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):187–195. doi: 10.1042/bj2180187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Biden T. J., Janjic D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):562–564. doi: 10.1038/309562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Burgess G. M., Halenda S. P., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P. Effects of secretagogues on [32P]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism in the exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2120483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Landis C. A., van de Walle C. M. Effect of carbachol on radiosodium uptake by dispersed pancreatic acinar cells. Pflugers Arch. 1980 May;385(2):131–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00588692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. Stimulation of inositol trisphosphate accumulation and amylase secretion by caerulein in pancreatic acini. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Dec;231(3):623–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Leavitt A. L., Honchar M. P., Hallcher L. M., Phillips B. E. Evidence that lithium alters phosphoinositide metabolism: chronic administration elevates primarily D-myo-inositol-1-phosphate in cerebral cortex of the rat. J Neurochem. 1981 Jun;36(6):1947–1951. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu E., Hirata M., Hashimoto T., Kuriyama H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from intracellular store sites in skinned single cells of porcine coronary artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P. Mitogens increase phosphorylation of phosphoinositides in thymocytes. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):462–465. doi: 10.1038/312462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Alexander J., Williamson J. R. Relationship between inositol polyphosphate production and the increase of cytosolic free Ca2+ induced by vasopressin in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5574–5584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



