Abstract
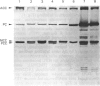
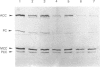
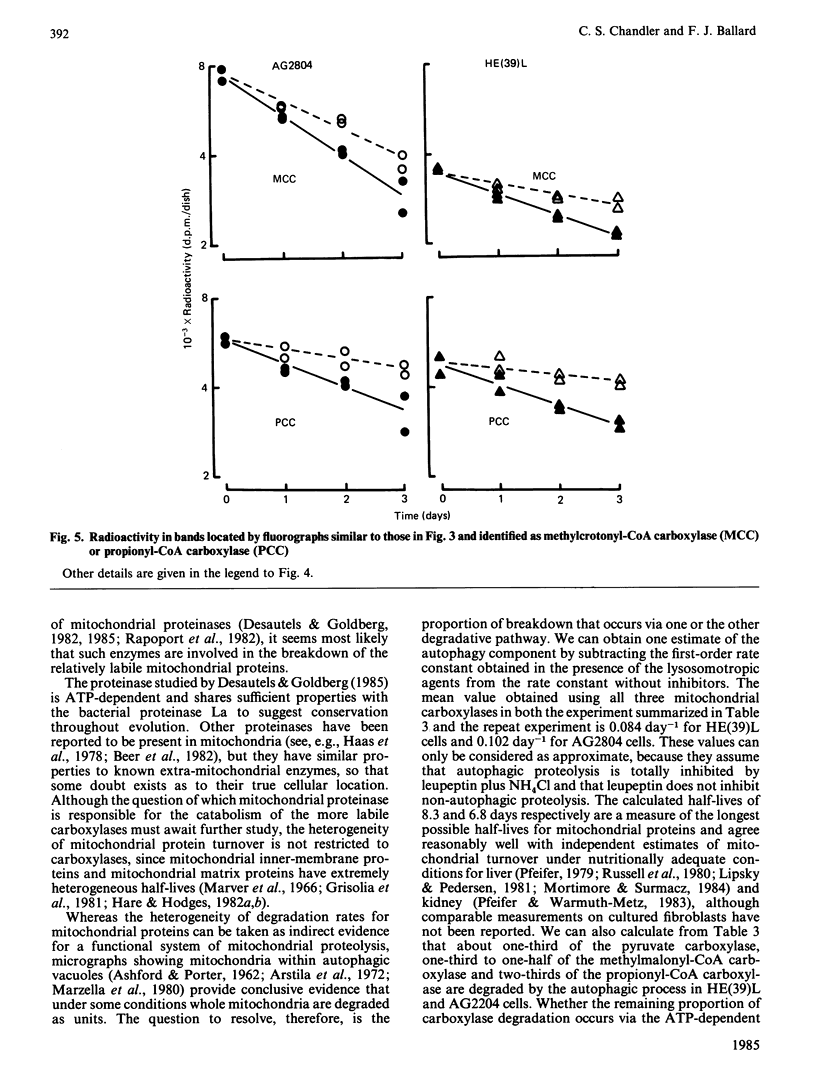
Incubation of cultured cells with [3H]biotin leads to the labelling of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, propionyl-CoA carboxylase and methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase. The biotin-containing subunits of the last two enzymes from rat cell lines are not separated by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, but adequate separation is achieved with the enzymes from human cells. Since incorporated biotin is only released upon complete protein breakdown, the loss of radioactivity from gel slices coinciding with fluorograph bands was used to quantify degradation rates for each protein. In HE(39)L diploid human fibroblasts, the degradation rate constants are 0.55, 0.40, 0.31 and 0.19 day-1 for acetyl-CoA carboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase respectively. A similar series of rate constants is found for AG2804 transformed fibroblasts. The degradation rate constants are decreased by 31-67% in the presence of 50 micrograms of leupeptin/ml plus 5 mM-NH4Cl. Although the largest percentage effect was noted with the most stable enzyme, propionyl-CoA carboxylase, the absolute change in rate constant produced by the lysosomotropic inhibitors was similar for the three mitochondrial carboxylases, but greater for the cytosolic enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase. The heterogeneity in degradation rate constants for the mitochondrial carboxylases indicates that only part of their catabolism can occur via the autophagy-mediated unit destruction of mitochondria. Calculations showed that the autophagy-linked process had degradation rate constants of 0.084 and 0.102 day-1 respectively in HE(39)L and AG2804 cells. It accounted for two-thirds of the catabolic rate of propionyl-CoA carboxylase and a lesser proportion for the other enzymes.
Full text
PDF



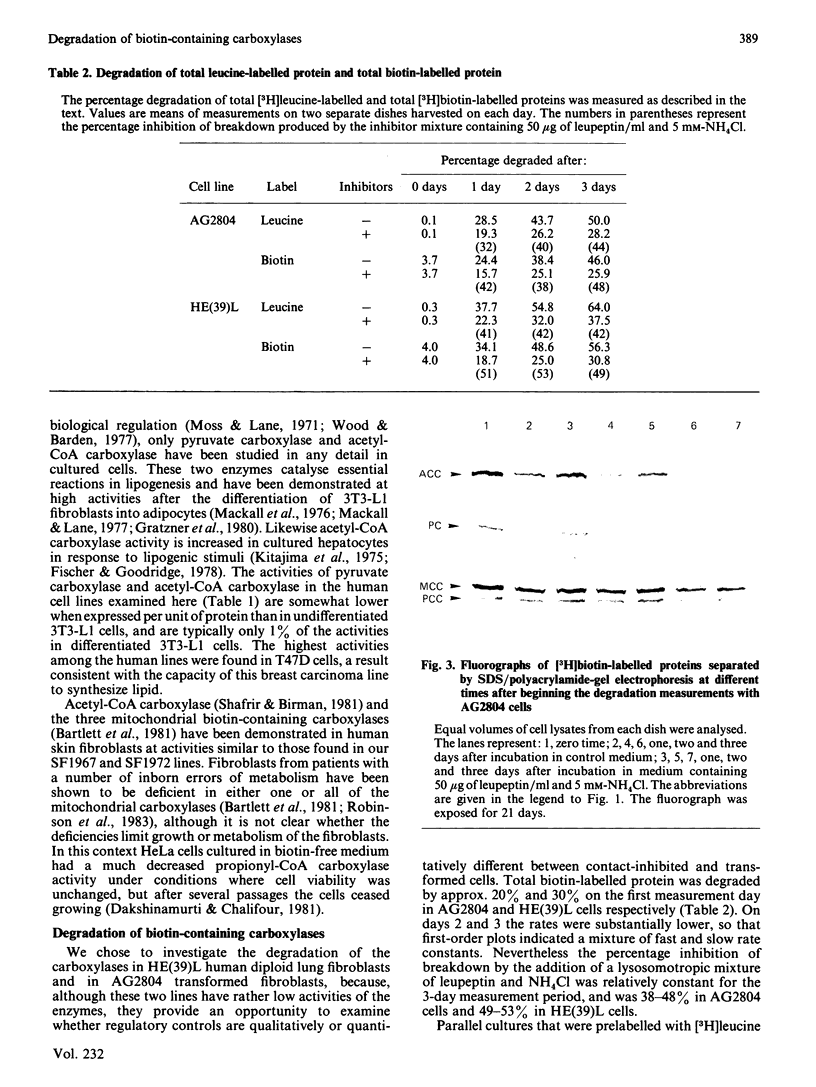
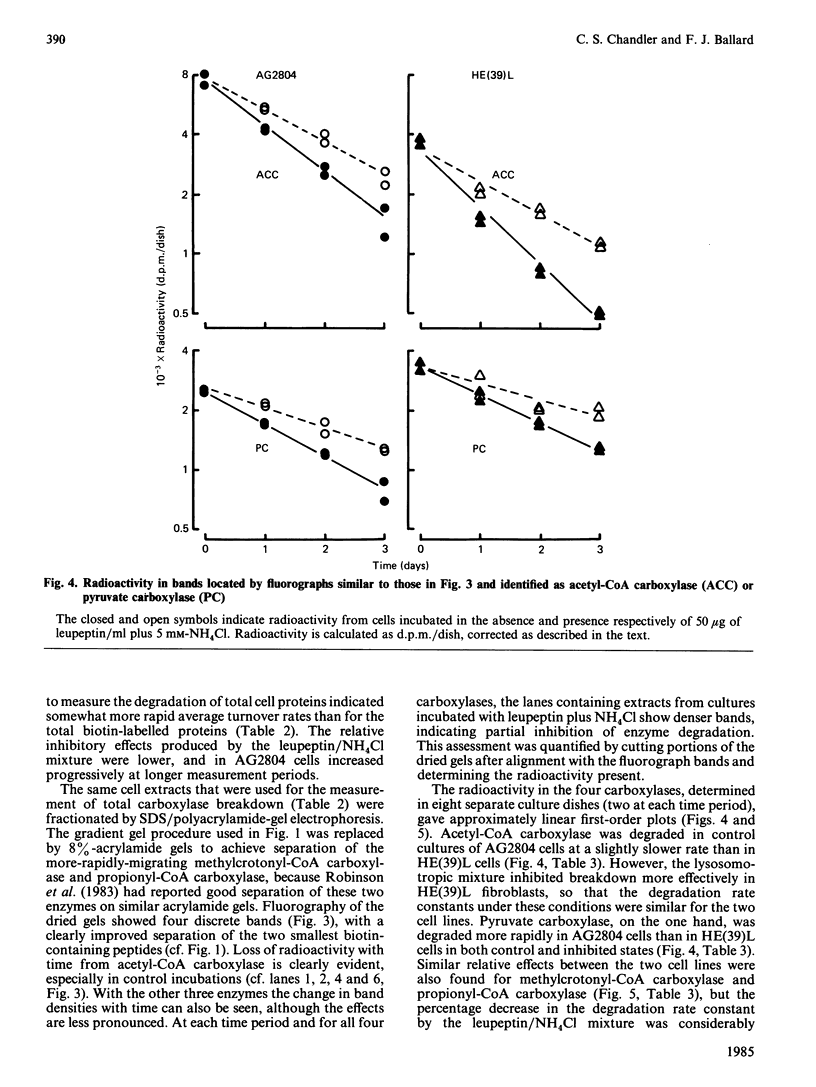


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHFORD T. P., PORTER K. R. Cytoplasmic components in hepatic cell lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jan;12:198–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amenta J. S., Brocher S. C. Mechanisms of protein turnover in cultured cells. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 16;28(11):1195–1208. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arstila A. U., Shelburne J. D., Trump B. F. Studies on cellular autophagocytosis. A histochemical study on sequential alterations of mitochondria in the glucagon-induced autophagic vacuoles of rat liver. Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;27(3):317–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auteri J. S., Okada A., Bochaki V., Dice J. F. Regulation of intracellular protein degradation in IMR-90 human diploid fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):167–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and pyruvate carboxylase in developing rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):866–871. doi: 10.1042/bj1040866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J. Intracellular protein degradation. Essays Biochem. 1977;13:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Wong S. S., Knowles S. E., Partridge N. C., Martin T. J., Wood C. M., Gunn J. M. Insulin inhibition of protein degradation in cell monolayers. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Nov;105(2):335–346. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett K., Ng H., Dale G., Green A., Leonard J. V. Studies on cultured fibroblasts from patients with defects of biotin-dependent carboxylation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1981;4(4):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF02263649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer D. G., Hjelle J. J., Petersen D. R., Malkinson A. M. Calcium-activated proteolytic activity in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1276–1283. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91915-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. S., Ballard F. J. Inhibition of pyruvate carboxylase degradation and total protein breakdown by lysosomotropic agents in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):845–853. doi: 10.1042/bj2100845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. The ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway and mechanisms of energy-dependent intracellular protein degradation. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(1):27–53. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dakshinamurti K., Chalifour L. E. The biotin requirement of HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Jun;107(3):427–438. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041070314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. Liver mitochondria contain an ATP-dependent, vanadate-sensitive pathway for the degradation of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1869–1873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. The ATP-dependent breakdown of proteins in mammalian mitochondria. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Apr;13(2):290–293. doi: 10.1042/bst0130290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer P. W., Goodridge A. G. Coordinate regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase and fatty acid synthetase in liver cells of the developing chick in vivo and in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):332–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Utter M. F. Regulation of the synthesis and degradation of pyruvate carboxylase in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6307–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G., Ahmad P. M., Zegadlo J., Ahmad F. Immunofluorescent localization of acetyl CoA carboxylase, fatty acid synthetase and pyruvate carboxylase during the adipocyte conversion of 3T3 fibroblasts. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1980 May;4(5):497–508. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(80)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisolía S., Timoneda J., Hernández-Yago J., Soler J., De Arriaga M. D., Wallace R. Intracellular degradation of mitochondrial enzymes. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1407–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Heinrich P. C. Cleavage specificity of the serine proteinase from rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 14;85(3):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90647-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare J. F., Hodges R. Turnover of mitochondrial inner membrane proteins in hepatoma monolayer cultures. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3575–3580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare J. F., Hodges R. Turnover of mitochondrial matrix polypeptides in hepatoma monolayer cultures. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12950–12953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopgood M. F., Ballard F. J. Synthesis and degradation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in rat liver and adipose tissue. Changes during a starvation-re-feeding cycle. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):445–453. doi: 10.1042/bj1340445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIVUSALO M., ELORRIAGA C., KAZIRO Y., OCHOA S. Bacterial biotinidase. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:1038–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima K., Tashiro S., Numa S. Acetyl-coenzyme-A carboxylase in cultured hepatocytes. Effects of exogenous fatty acids on the content, synthesis and degradation of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):373–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles S. E., Ballard F. J. Selective control of the degradation of normal and aberrant proteins in Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):609–617. doi: 10.1042/bj1560609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau E. P., Cochran B. C., Munson L., Fall R. R. Bovine kidney 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA carboxylases: each enzyme contains nonidentical subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky N. G., Pedersen P. L. Mitochondrial turnover in animal cells. Half-lives of mitochondria and mitochondrial subfractions of rat liver based on [14C]bicarbonate incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8652–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackall J. C., Lane M. D. Role of pyruvate carboxylase in fatty acid synthesis: alterations during preadipocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):720–725. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackall J. C., Student A. K., Polakis S. E., Lane M. D. Induction of lipogenesis during differentiation in a "preadipocyte" cell line. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6462–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver H. S., Collins A., Tschudy D. P., Rechcigl M., Jr Delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase. II. Induction in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4323–4329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzella L., Sandberg P. O., Glaumann H. Autophagic degradation in rat liver after vinblastine treatment. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Aug;128(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Surmacz C. A. Liver perfusion: an in vitro technique for the study of intracellular protein turnover and its regulation in vivo. Proc Nutr Soc. 1984 Jun;43(2):161–177. doi: 10.1079/pns19840039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Lane M. D. The biotin-dependent enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;35:321–442. doi: 10.1002/9780470122808.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. T., DeMartino G. N., Goldberg A. L. The effect of protease inhibitors and decreased temperature on the degradation of different classes of proteins in cultured hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Dec;101(3):439–457. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Oka T., Schimke R. T. Modulation of ovalbumin synthesis by estradiol-17 beta and actinomycin D as studied in explants of chick oviduct in culture. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):724–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U. Inhibited autophagic degradation of cytoplasm during compensatory growth of liver cells after partial hepatectomy. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1979 Jun 29;30(3):313–333. doi: 10.1007/BF02889111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U., Warmuth-Metz M. Inhibition by insulin of cellular autophagy in proximal tubular cells of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):E109–E114. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.2.E109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Booth G. M. Improved methods for the fluorographic detection of weak beta-emitting radioisotopes in Agarose and acrylamide gel electrophoresis media. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1981 Jun;4(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(81)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S., Dubiel W., Müller M. Characteristics of an ATP-dependent proteolytic system of rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1982 Oct 4;147(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. H., Oei J., Saunders M., Gravel R. [3H]biotin-labeled proteins in cultured human skin fibroblasts from patients with pyruvate carboxylase deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6660–6664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Burgess R. J., Mayer R. J. Protein degradation in rat liver during post-natal development. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):321–330. doi: 10.1042/bj1920321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Grinde B., Solheim A. E. Inhibition of the lysosomal pathway of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes by ammonia, methylamine, chloroquine and leupeptin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):215–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Inhibitors of lysosomal function. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:737–764. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafrir E., Bierman E. L. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity in cultured human fibroblasts. Induction by insulin in relation to cell growth and triacylglycerol metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):432–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton S. A., Hipkiss A. R. Abnormal proteins of shortened length are preferentially degraded in the cytosol of cultured MRC5 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 12;168(1):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80222-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. G., Barden R. E. Biotin enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:385–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]