Abstract
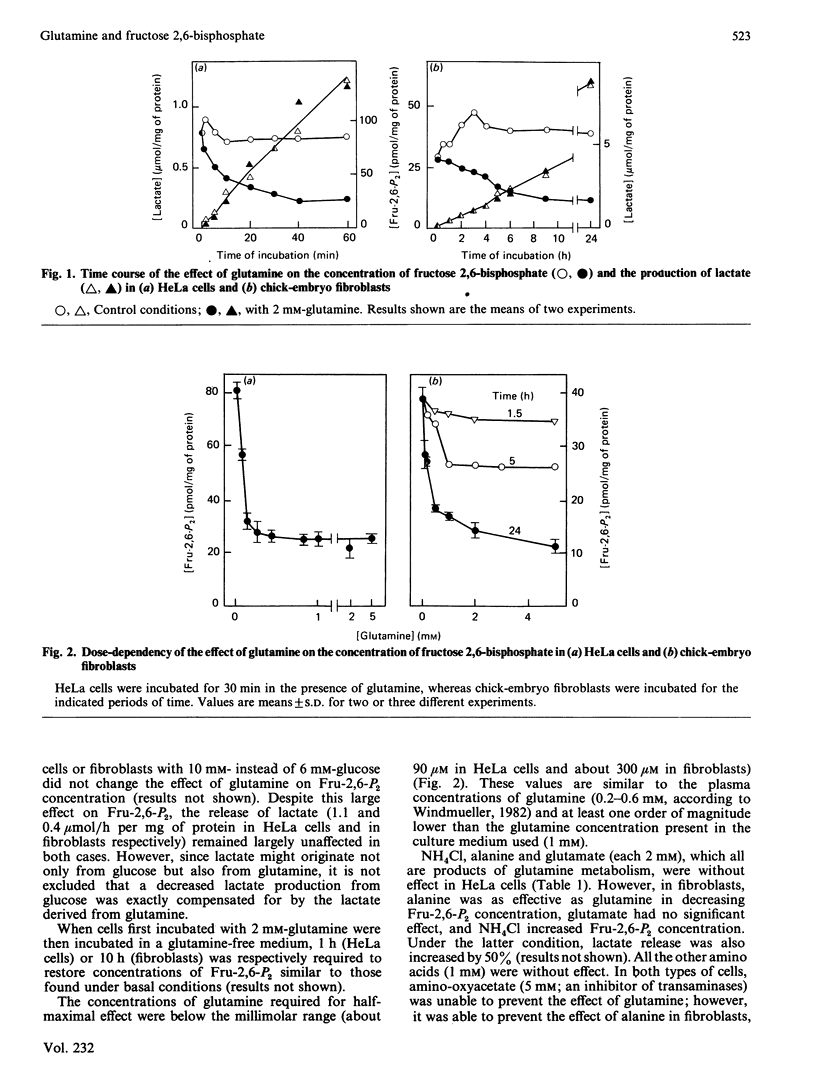
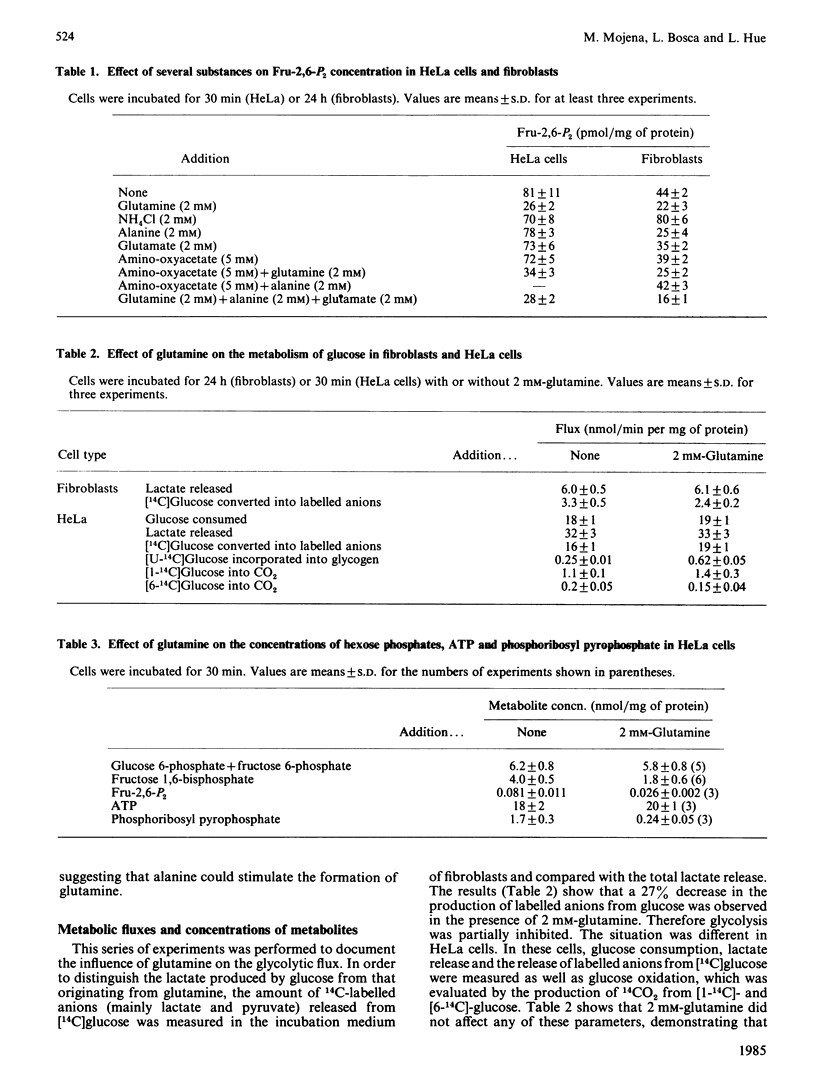
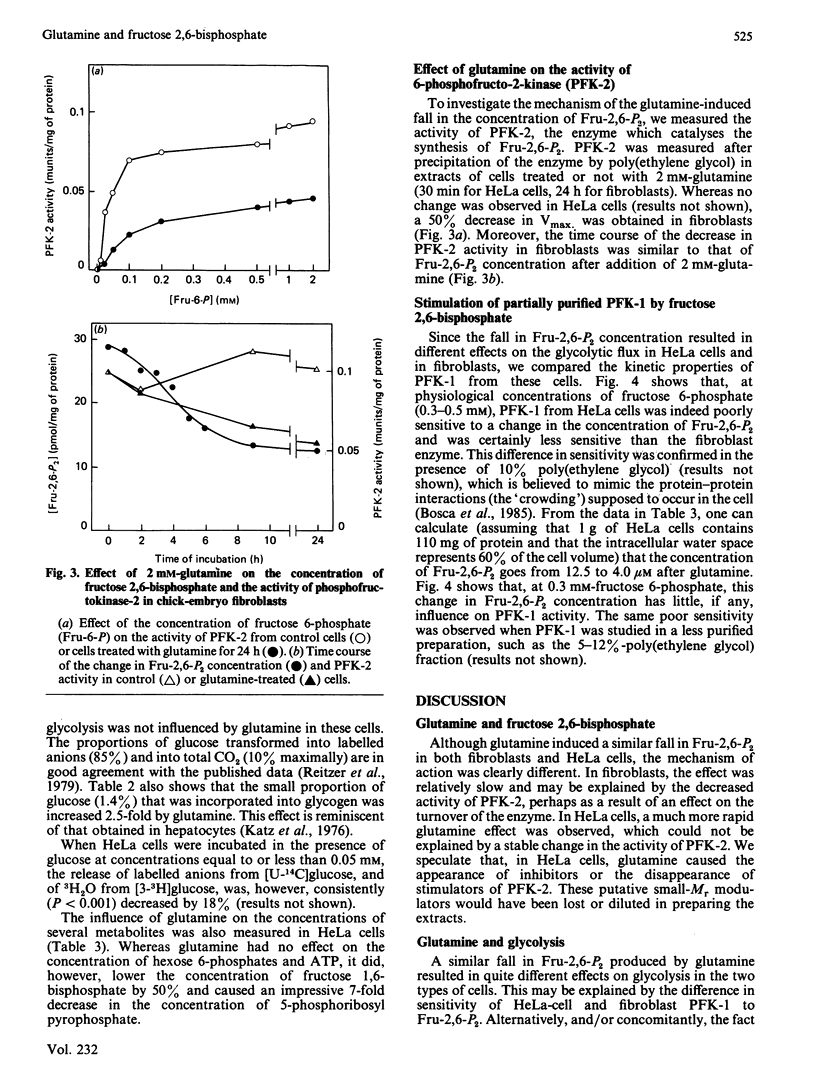
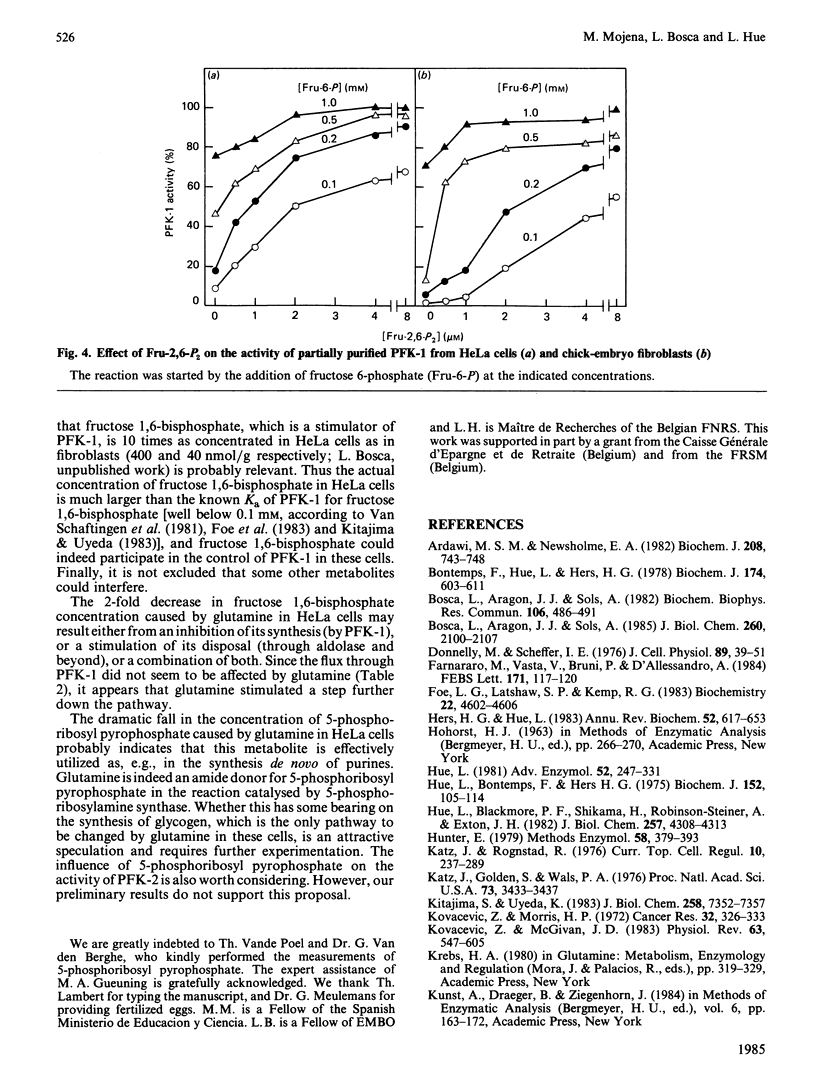
Glutamine caused a dose-dependent decrease in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate concentration in both HeLa cells and chick-embryo fibroblasts. The effect was complete within 15 min in HeLa cells, but required more than 9 h in the fibroblasts. Half-maximal effects were obtained with 0.1-0.3 mM-glutamine. In chick-embryo fibroblasts, but not in HeLa cells, glutamine induced a time-dependent decrease in the activity of phosphofructokinase-2, which correlated with the decrease in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Glutamine decreased the glycolytic flux by about 25% only in chick-embryo fibroblasts. The difference in glycolytic response between the two types of cells might correspond to a difference in the sensitivity of phosphofructokinase-1 for fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. In HeLa cells, glutamine caused a 2-3-fold stimulation of the synthesis of glycogen, a 50% decrease in the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and a more than 80% decrease in the concentration of 5-phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate; the concentrations of hexose 6-phosphates and ATP were not affected.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardawi M. S., Newsholme E. A. Maximum activities of some enzymes of glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle and ketone-body and glutamine utilization pathways in lymphocytes of the rat. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):743–748. doi: 10.1042/bj2080743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bontemps F., Hue L., Hers H. G. Phosphorylation of glucose in isolated rat hepatocytes. Sigmoidal kinetics explained by the activity of glucokinase alone. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):603–611. doi: 10.1042/bj1740603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscá L., Aragón J. J., Sols A. Modulation of muscle phosphofructokinase at physiological concentration of enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2100–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscá L., Aragón J. J., Sols A. Specific activation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and inhibition by P-enolpyruvate of ascites tumor phosphofructokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):486–491. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly M., Scheffler I. E. Energy metabolism in respiration-deficient and wild type Chinese hamster fibroblasts in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Sep;89(1):39–51. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnararo M., Vasta V., Bruni P., D'Alessandro A. The effect of insulin on Fru-2,6-P2 levels in human fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jun 4;171(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe L. G., Latshaw S. P., Kemp R. G. Binding of hexose bisphosphates to muscle phosphofructokinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4601–4606. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Hue L. Gluconeogenesis and related aspects of glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:617–653. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Blackmore P. F., Shikama H., Robinson-Steiner A., Exton J. H. Regulation of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate content in rat hepatocytes, perfused hearts, and perfused hindlimbs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4308–4313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Bontemps F., Hers H. The effects of glucose and of potassium ions on the interconversion of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase and of glycogen synthetase in isolated rat liver preparations. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;152(1):105–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1520105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L. The role of futile cycles in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1981;52:247–331. doi: 10.1002/9780470122976.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. Biological techniques for avian sarcoma viruses. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:379–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Golden S., Wals P. A. Stimulation of hepatic glycogen synthesis by amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rognstad R. Futile cycles in the metabolism of glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:237–289. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima S., Uyeda K. A binding study of the interaction of beta-D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate with phosphofructokinase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7352–7357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacevic Z., McGivan J. D. Mitochondrial metabolism of glutamine and glutamate and its physiological significance. Physiol Rev. 1983 Apr;63(2):547–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.2.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacević Z., Morris H. P. The role of glutamine in the oxidative metabolism of malignant cells. Cancer Res. 1972 Feb;32(2):326–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minatogawa Y., Hue L. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in rat skeletal muscle during contraction. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):73–79. doi: 10.1042/bj2230073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreadith R. W., Lehninger A. L. The pathways of glutamate and glutamine oxidation by tumor cell mitochondria. Role of mitochondrial NAD(P)+-dependent malic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6215–6221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEPTUNE E. M., Jr RESPIRATION AND OXIDATION OF VARIOUS SUBSTRATES BY ILEUM IN VITRO. Am J Physiol. 1965 Aug;209:329–332. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G. Hexose transport in undifferentiated and differentiated BALB/c 3T3 preadipose cells: effects 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and insulin. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jan;110(1):63–71. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S., Rost J., Schultze M. Glutamine and glutamate as respiratory substrates of rabbit reticulocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):166–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Wice B. M., Kennell D. Evidence that glutamine, not sugar, is the major energy source for cultured HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2669–2676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh V. N., Singh M., August J. T., Horecker B. L. Alterations in glucose metabolism in chick-embryo cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus: intracellular levels of glycolytic intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4129–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Study of the fructose 6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bi-phosphate cycle in the liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):263–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1920263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Jett M. F., Hue L., Hers H. G. Control of liver 6-phosphofructokinase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and other effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3483–3486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M. F., Van den Berghe G., Hers H. G. Metabolism of hypoxanthine in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):145–155. doi: 10.1042/bj2220145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watford M., Lund P., Krebs H. A. Isolation and metabolic characteristics of rat and chicken enterocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):589–596. doi: 10.1042/bj1780589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G. Glutamine utilization by the small intestine. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1982;53:201–237. doi: 10.1002/9780470122983.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Spaeth A. E. Uptake and metabolism of plasma glutamine by the small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5070–5079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielke H. R., Zielke C. L., Ozand P. T. Glutamine: a major energy source for cultured mammalian cells. Fed Proc. 1984 Jan;43(1):121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


