Abstract
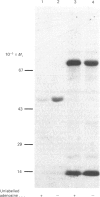
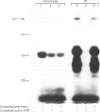
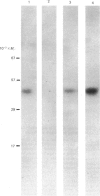
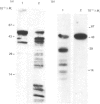
S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (AdoHcyase) has previously been identified as a cytoplasmic adenosine and cyclic AMP binding protein. In order to examine the relationship between the adenosine and cyclic AMP binding sites on this enzyme we have explored the use of 8-azido analogues of adenosine and cyclic AMP as photoaffinity reagents for covalently labelling AdoHcyase purified from human placenta. 8-Azidoadenosine (8-N3-Ado), like adenosine, inactivated AdoHcyase, and the rate of inactivation was greatly increased by periodate oxidation. In addition, 8-N3-Ado was found to participate in the first step in the catalytic mechanism for AdoHcyase, resulting in conversion of enzyme-bound NAD+ to NADH, although it was not a substrate for the full enzyme-catalysed reaction. Radioactively labelled 8-N3-Ado, its periodate-oxidized derivative and 8-azidoadenosine 3', 5'-phosphate (8-N3-cAMP) bound specifically to adenosine binding sites on AdoHcyase and, after irradiation, became covalently linked to the enzyme. Photoaffinity-labelled enzyme could be precipitated by monoclonal antibody to human AdoHcyase. Two observations suggested that cyclic AMP and adenosine bind to the same sites on AdoHcyase. First cyclic AMP and adenosine each blocked binding of both radioactively labelled 8-N3-Ado and 8-N3-cAMP, and second, digestion with V8 proteinase generated identical patterns of peptides from AdoHcyase that had been photolabelled with [32P]8-N3-cAMP and [3H]8-N3-Ado. Binding sites for cyclic AMP on AdoHcyase were found to differ functionally and structurally from cyclic AMP binding sites on the R1 regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles R. H., Fish S., Lapinskas B. S-Adenosylhomocysteinase: mechanism of inactivation by 2'-deoxyadenosine and interaction with other nucleosides. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5557–5562. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. K., Guranowski A., Segall J. E. Irreversible inhibition of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by nucleoside analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Mar;207(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Cuzin F. Covalent affinity labeling by periodate-oxidized [alpha-32P]ATP of the large-T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6300–6305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LA HABA G., CANTONI G. L. The enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine from adenosine and homocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):603–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills W. L., Goodwin C. D., Lincoln T. M., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Corbin J. D., Krebs E. G. Purification of cyclic nucleotide receptor proteins by cyclic nucleotide affinity chromatography. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:199–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskeland S. O., Ueland P. M. Binding proteins for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in bovine adrenal cortex. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):561–573. doi: 10.1042/bj1650561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D. Regulatory mechanisms in the control of protein kinases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Feb;12(2):133–186. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi T., Fujioka M. Inactivation of rat liver S-adenosylhomocysteinase by iodoacetamide. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4171–4176. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES R. E., ROBINS R. K. PURINE NUCLEOSIDES. IX. THE SYNTHESIS OF 9-BETA-D-RIBOFURANOSYL URIC ACID AND OTHER RELATED 8-SUBSTITUTED PURINE RIBONUCLEOSIDES. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Apr 20;87:1772–1776. doi: 10.1021/ja01086a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helland S., Ueland P. M. The relation between the functions of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine as inactivator and substrate of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):758–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Aiyar V. N., Premakumar R., Small W. C. S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase from human placenta. Affinity purification and characterization. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):43–52. doi: 10.1042/bj2300043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S. Apparent suicide inactivation of human lymphoblast S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by 2'-deoxyadenosine and adenine arabinoside. A basis for direct toxic effects of analogs of adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):22–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Francke U. The human genes for S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and adenosine deaminase are syntenic on chromosome 20. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):739–742. doi: 10.1126/science.7079734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kredich N. M., Koller C. A., Mitchell B. S., Kurtzberg J., Kinney T. R., Falletta J. M. S-adenosylhomocysteine catabolism and basis for acquired resistance during treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with 2'-deoxycoformycin alone and in combination with 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3451–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kredich N. M., Ownby D. R., Ownby H., Buckley R. In vivo inactivation of erythrocyte S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by 2'-deoxyadenosine in adenosine deaminase-deficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):807–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI109367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Krodich N. M. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase is an adenosine-binding protein: a target for adenosine toxicity. Science. 1978 Nov 17;202(4369):757–760. doi: 10.1126/science.715439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kurtzberg J., Harden E., Moore J. O., Whang-Peng J., Haynes B. F. Conversion of a stem cell leukemia from a T-lymphoid to a myeloid phenotype induced by the adenosine deaminase inhibitor 2'-deoxycoformycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman R. J., Guitton M. C., Véron M. Purification of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase from Dictyostelium discoideum: reversible inactivation by cAMP and 2'-deoxyadenosine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman R. J., Veron M. S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase from Dictyostelium discoideum is inactivated by cAMP and reactivated by NAD+. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 9;165(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Hershfield M. S. S-adenosylhomocysteine toxicity in normal and adenosine kinase-deficient lymphoblasts of human origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2450–2454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Martin D. V., Jr Role of S-adenosylhomocysteine in adenosinemediated toxicity in cultured mouse T lymphoma cells. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):931–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandler R., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H., Kammer G. M., Rudolph S. A. Abnormal adenosine-induced immunosuppression and cAMP metabolism in T lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell B. S., Koller C. A., Heyn R. Inhibition of adenosine deaminase activity results in cytotoxicity to T lymphoblasts in vivo. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):556–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Suh E. J., Hershfield M. S. Regional localization of the human genes for S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (cen----q131) and adenosine deaminase (q131----qter) on chromosome 20. Hum Genet. 1984;66(4):292–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00287630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A. Ligand binding to the adenine analogue binding protein of the rabbit erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):367–375. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. L., Abeles R. H. Mechanism for enzymatic thioether formation. Mechanism of action of S-adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5817–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. L., Abeles R. H. The mechanism of action of S-adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1217–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip T., Lenoir G., Rolland M. O., Philip I., Hamet M., Lauras B., Fraisse J. Regional assignment of the ADA locus on 20q13.2 leads to qter by gene dosage studies. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(2-3):187–189. doi: 10.1159/000131481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Haley B. E. Photoaffinity labeling of nucleotide binding sites with 8-azidopurine analogs: techniques and applications. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:613–633. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblit P. D., Levy D. Photoaffinity labeling of the adenosine transport system in adipocyte plasma membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 1;204(1):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K. Cyclic nucleotide control of protein kinases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:233–288. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60602-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Corbin J. D. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-binding proteins in bovine and rat tissues. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):423–437. doi: 10.1042/bj1590423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Creagan R. P., Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of a gene for adenosine deaminase to human chromosome 20. Hum Hered. 1974;24(1):1–11. doi: 10.1159/000152631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Doskeland S. O. An adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-adenosine binding protein from mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):677–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Døskeland S. O. An adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-adenosine binding protein from mouse liver. A study on its interaction with adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1667–1676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Helland S. Binding of adenosine to intracellular S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):747–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M. Pharmacological and biochemical aspects of S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Sep;34(3):223–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh K. C., Tao M. Purification and characterization of adenosine-adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate binding protein factors from rabbit erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 3;13(25):5220–5226. doi: 10.1021/bi00722a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]