Abstract
We have determined the DNA sequences encoding 18 S ribosomal RNA in man and in the frog, Xenopus borealis. We have also corrected the Xenopus laevis 18 S sequence: an A residue follows G-684 in the sequence. These and other available data provide a number of representative examples of variation in primary structure and secondary modification of 18 S ribosomal RNA between different groups of vertebrates. First, Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis 18 S ribosomal genes differ from each other by only two base substitutions, and we have found no evidence of intraspecies heterogeneity within the 18 S ribosomal DNA of Xenopus (in contrast to the Xenopus transcribed spacers). Second, the human 18 S sequence differs from that of Xenopus by approx. 6.5%. About 4% of the differences are single base changes; the remainder comprise insertions in the human sequence and other changes affecting several nucleotides. Most of these more extensive changes are clustered in a relatively short region between nucleotides 190 and 280 in the human sequence. Third, the human 18 S sequence differs from non-primate mammalian sequences by only about 1%. Fourth, nearly all of the 47 methyl groups in mammalian 18 S ribosomal RNA can be located in the sequence. The methyl group distribution corresponds closely to that in Xenopus, but there are several extra methyl groups in mammalian 18 S ribosomal RNA. Finally, minor revisions are made to the estimated numbers of pseudouridines in human and Xenopus 18 S ribosomal RNA.
Full text
PDF

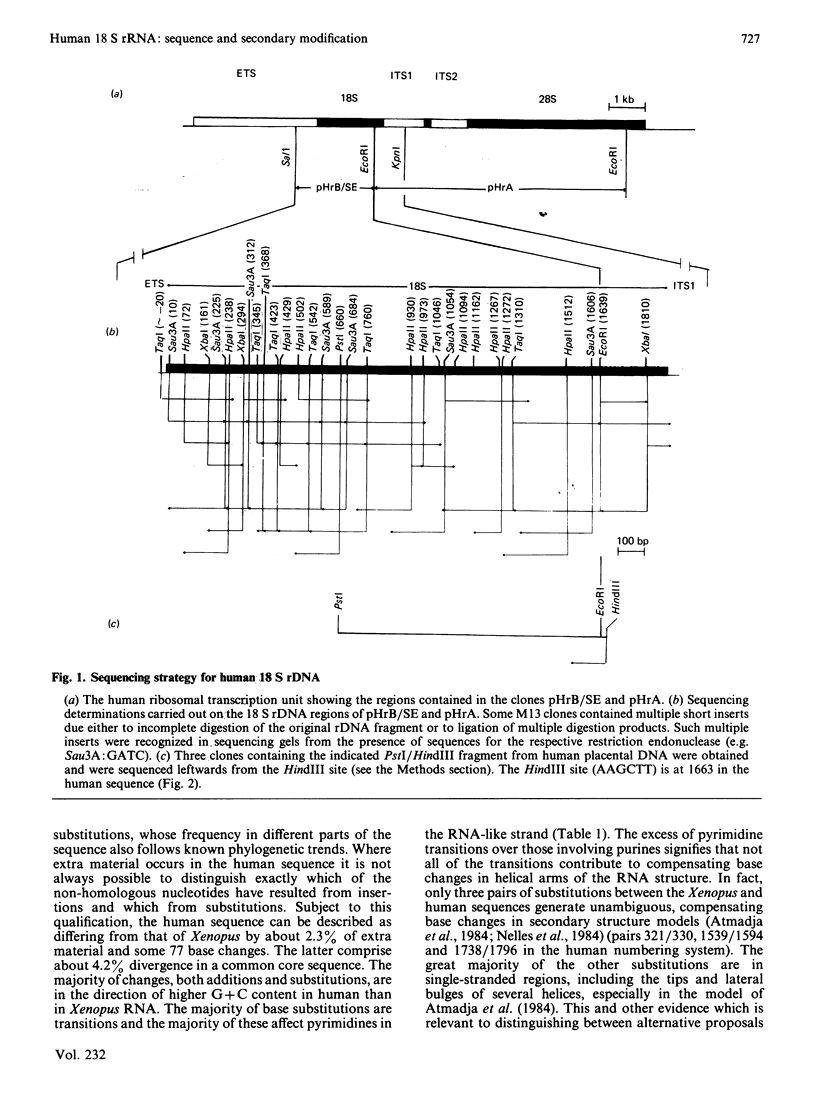

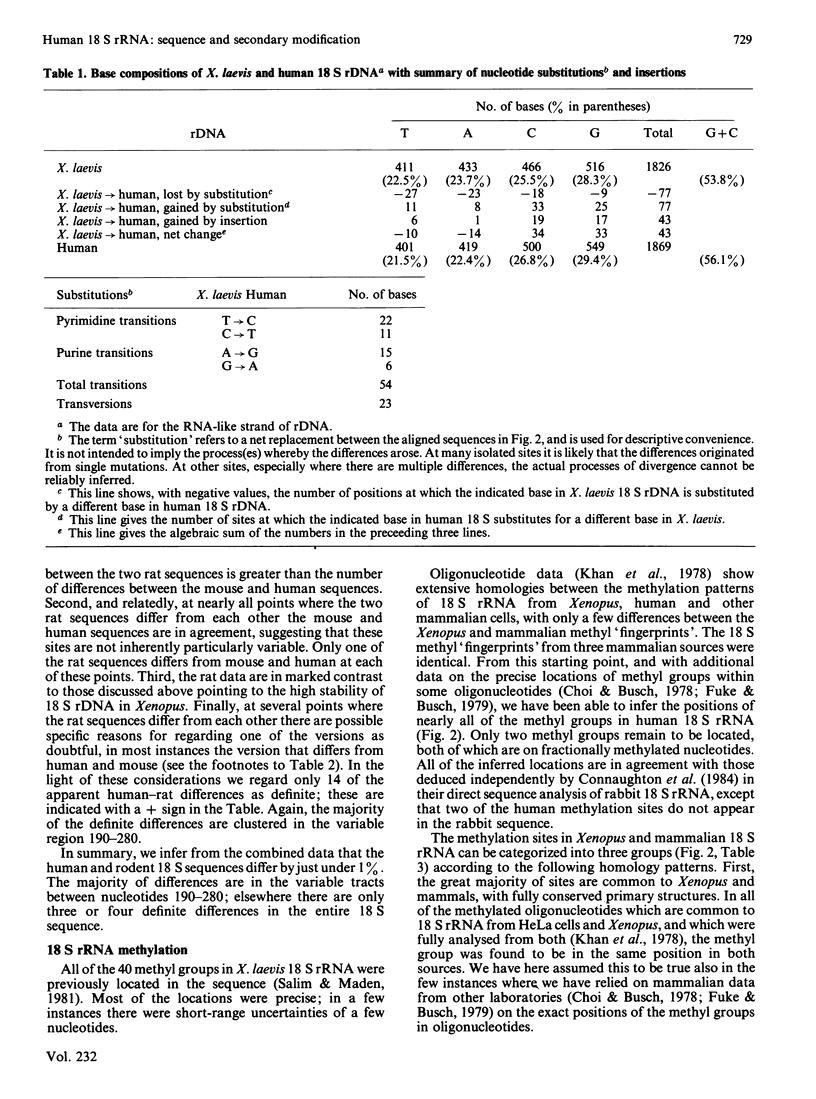
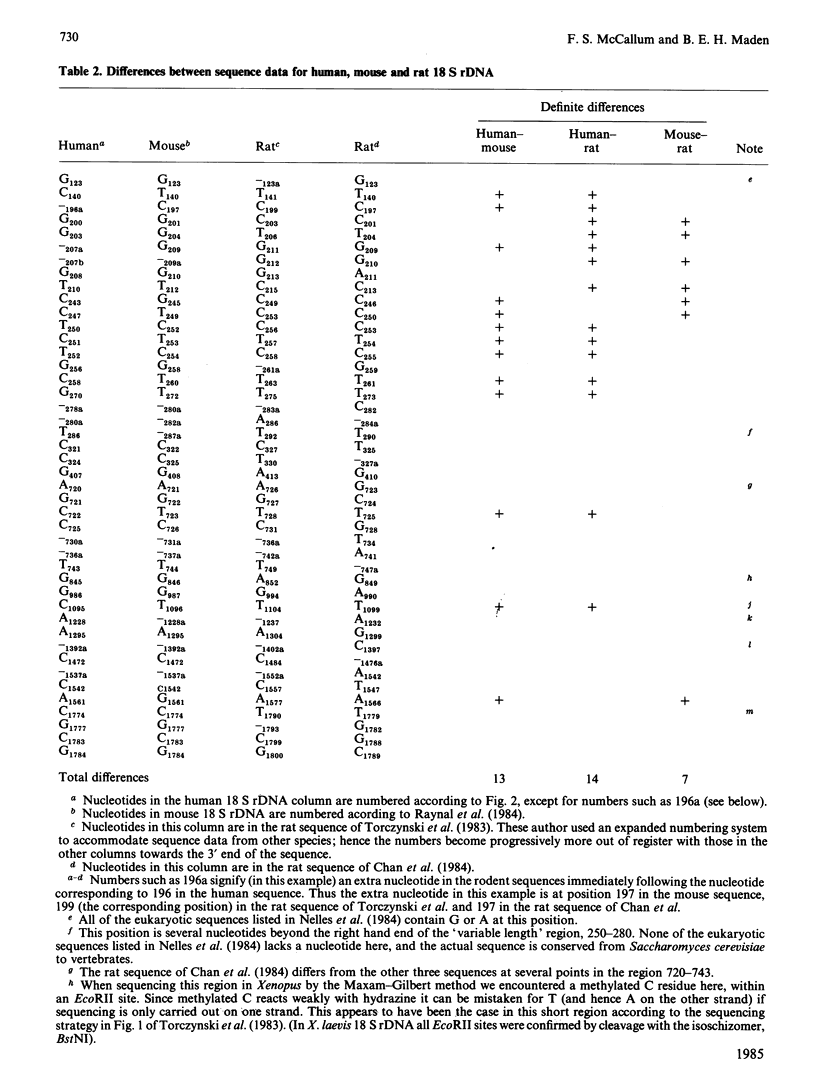
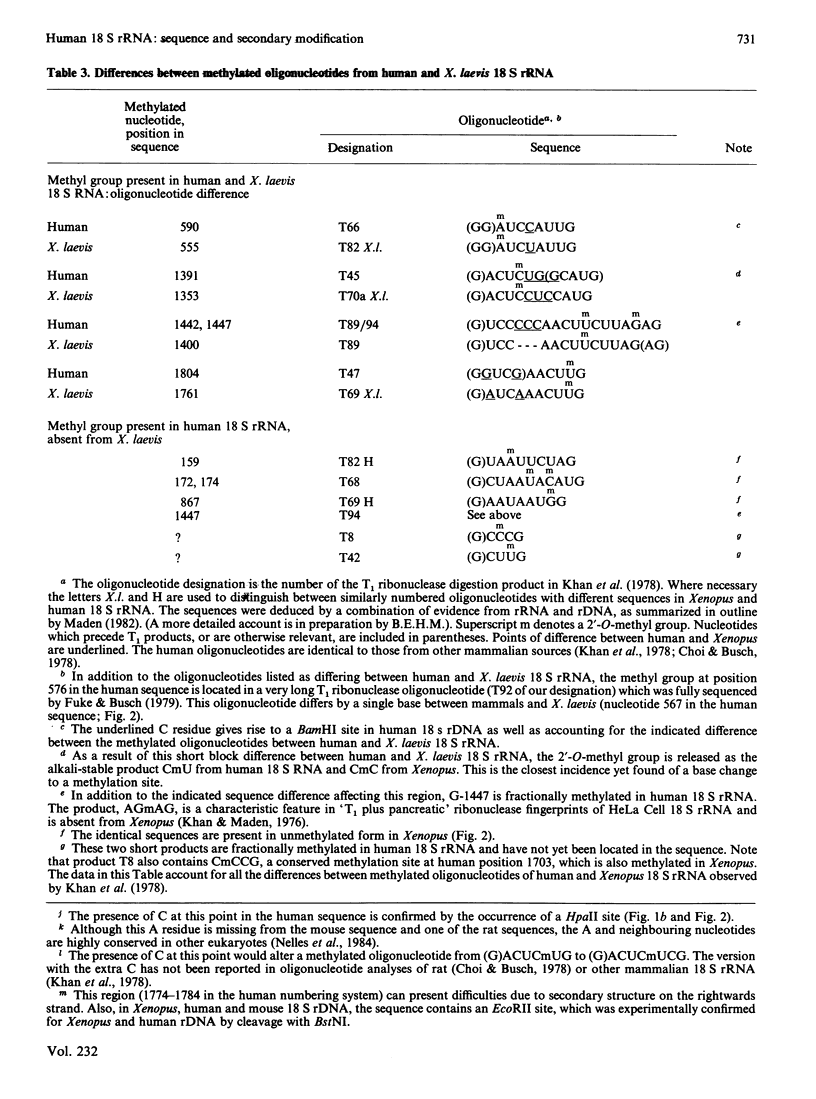

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atmadja J., Brimacombe R., Maden B. E. Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA: experimental determination of secondary structural elements, and locations of methyl groups in the secondary structure model. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2649–2667. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand R. C., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J., Maden B. E. Biosynthesis of a hypermodified nucleotide in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis 17S and HeLa-cell 18S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):71–77. doi: 10.1042/bj1690071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Gutell R., Noller H. F., Wool I. G. The nucleotide sequence of a rat 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene and a proposal for the secondary structure of 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. C., Busch H. Modified nucleotides in T1 RNase oligonucleotides of 18S ribosomal RNA of the Novikoff hepatoma. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2551–2560. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton J. F., Rairkar A., Lockard R. E., Kumar A. Primary structure of rabbit 18S ribosomal RNA determined by direct RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4731–4745. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eladari M. E., Galibert F. Sequence determination of 5'-terminal and 3'-terminal T1 oligonucleotides of 18-S ribosomal RNA of a mouse cell line (L 5178 Y). Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rushford C. L., Dorney D. J., Wilson G. N., Schmickel R. D. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: molecular analysis of cloned fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuke M., Busch H. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of large T1 ribonuclease fragments of 18S ribosomal RNA of rat and chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1131–1135. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong J. C., Forbes J., Robertson M., Maden B. E. The external transcribed spacer and preceding region of Xenopus borealis rDNA: comparison with the corresponding region of Xenopus laevis rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8183–8196. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong J. C., Maden B. E. Patterns of major divergence between the internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA in Xenopus borealis and Xenopus laevis, and of minimal divergence within ribosomal coding regions. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):443–448. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01442.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
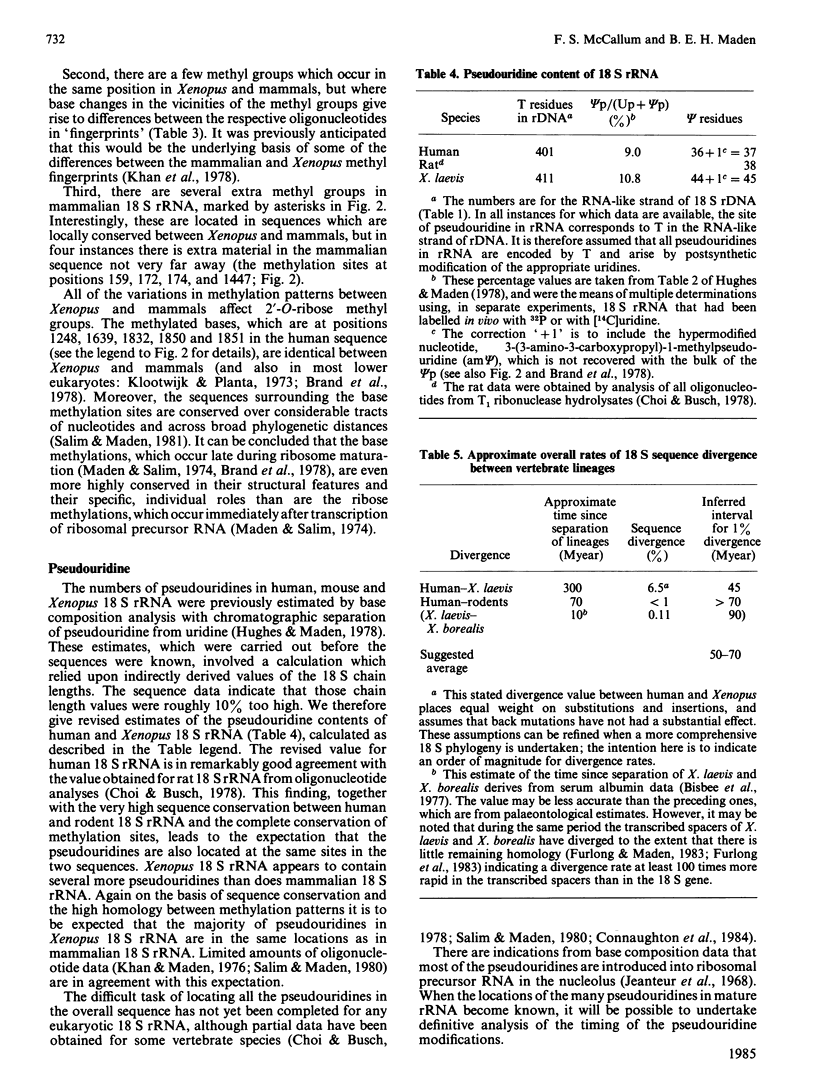
- Hughes D. G., Maden B. E. The pseudouridine contents of the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of three vertebrate species. Numerical correspondence between pseudouridine residues and 2'-O-methyl groups is not always conserved. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):781–786. doi: 10.1042/bj1710781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanteur P., Amaldi F., Attardi G. Partial sequence analysis of ribosomal RNA from HeLa cells. II. Evidence for sequences of non-ribosmal type in 45 and 32 s ribosomal RNA precursors. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):757–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. S., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequences within the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of HeLa cells, Xenopus laevis and chick embryo fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 25;101(2):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. S., Salim M., Maden B. E. Extensive homologies between the methylated nucleotide sequences in several vertebrate ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):531–542. doi: 10.1042/bj1690531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Analysis of the methylation sites in yeast ribosomal RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):325–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Forbes J. M., Stewart M. A., Eason R. 18S coding sequences in amplified ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes are highly homogeneous, unmethylated, and lack major open reading frames. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):597–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Salim M. The methylated nucleotide sequences in HELA cell ribosomal RNA and its precursors. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):133–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelles L., Fang B. L., Volckaert G., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Nucleotide sequence of a crustacean 18S ribosomal RNA gene and secondary structure of eukaryotic small subunit ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8749–8768. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal F., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 18 S rRNA gene: comparison with other available homologs. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 27;167(2):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence encoding the 5' end of Xenopus laevis 18S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2871–2884. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Hall L. M., Maden B. E. Multiple heterogeneities in the transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):629–646. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torczynski R., Bollon A. P., Fuke M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the rat 18S ribosomal RNA gene and comparison with the respective yeast and frog genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4879–4890. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vass J. K., Maden B. E. Studies on the conformation of the 3' terminus of 18-S rRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):241–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M. H., Jr, Soeiro R., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The effects of methionine deprivation on ribosome synthesis in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1527–1534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Soeiro R. Nascent ribosomes from HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1984–1990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of RNA: processing of HeLa ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Hollar B. A., Waterson J. R., Schmickel R. D. Molecular analysis of cloned human 18S ribosomal DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5367–5371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


