Abstract
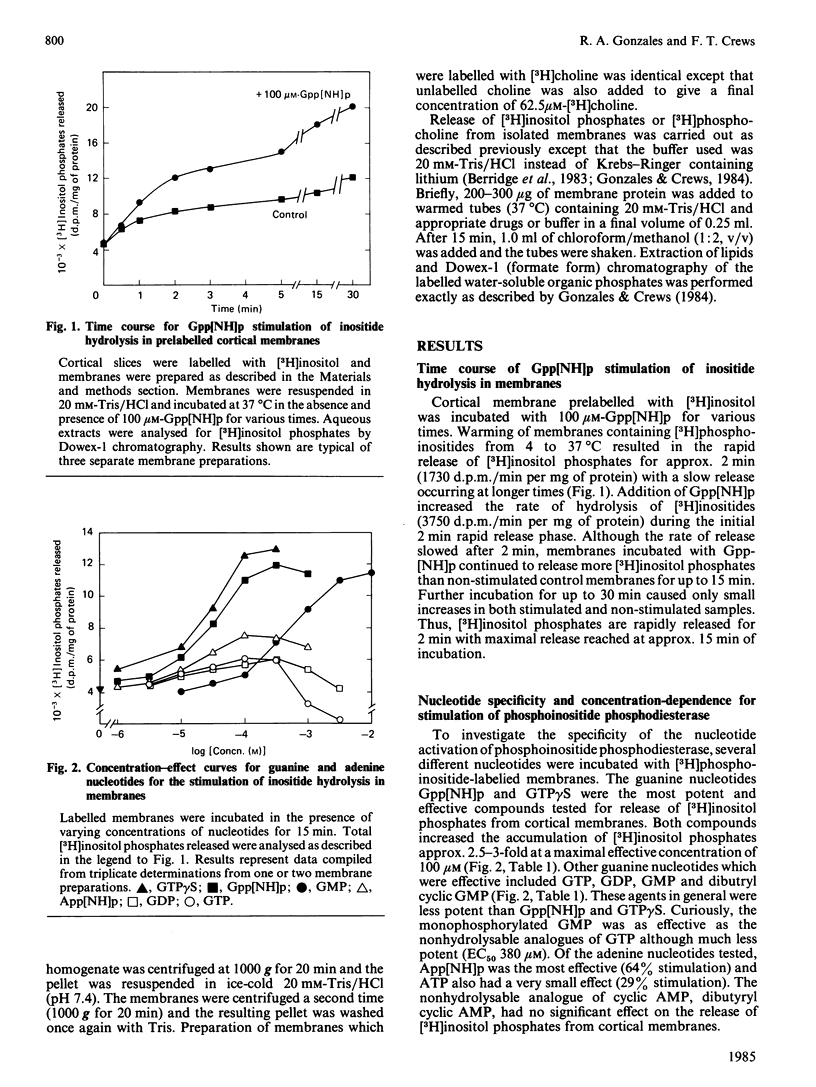
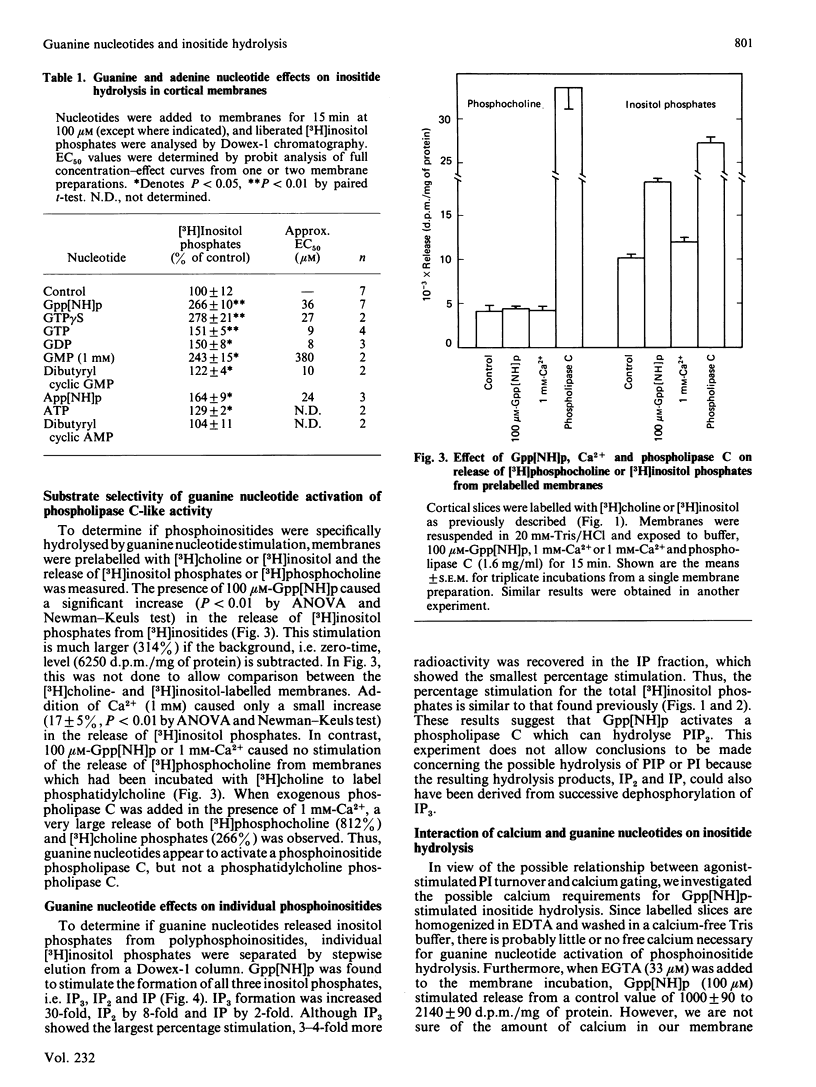
The guanine nucleotides guanosine 5'[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate (Gpp[NH]p), guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]-triphosphate (GTP gamma S), GMP, GDP and GTP stimulated the hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids by a phosphodiesterase in rat cerebral cortical membranes. Addition of 100 microM-Gpp[NH]p to prelabelled membranes caused a rapid accumulation of [3H )inositol phosphates (less than 30 s) for up to 2 min. GTP gamma S and Gpp [NH]p caused a concentration-dependent stimulation of phosphoinositide phosphodiesterase with a maximal stimulation of 2.5-3-fold over control at concentrations of 100 microM. GMP was as effective as the nonhydrolysable analogues, but much less potent (EC50 380 microM). GTP and GDP caused a 50% stimulation of the phospholipase C at 100 microM and at higher concentrations were inhibitory. The adenine nucleotides App[NH]p and ATP also caused small stimulatory effects (64% and 29%). The guanine nucleotide stimulation of inositide hydrolysis in cortical membranes was selective for inositol phospholipids over choline-containing phospholipids. Gpp[NH]p stimulated the production of inositol trisphosphate and inositol bisphosphate as well as inositol monophosphate, indicating that phosphoinositides are substrates for the phosphodiesterase. EGTA (33 microM) did not prevent the guanine nucleotide stimulation of inositide hydrolysis. Calcium addition by itself caused inositide phosphodiesterase activation from 3 to 100 microM which was additive with the Gpp[NH]p stimulation. These data suggest that guanine nucleotides may play a regulatory role in the modulation of the activity of phosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in rat cortical membranes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: I. Receptor characterisation. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1379–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. L., Valdenegro C. A., MacLeod R. M. The inhibition of phosphatidylinositol turnover: a possible postreceptor mechanism for the prolactin secretion-inhibiting effect of dopamine. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):7–14. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin M., Mamrak F., Samaniego S. G. Preparation and properties of a cell-free, hormonally responsive adenylate cyclase from guinea pig brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Jun;22(6):1031–1038. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Baldwin J. M., Allan D. The Ca2+-activated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of human and rabbit neutrophil membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):477–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2210477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Martin M. W., Hughes A. R., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-sensitive, high affinity binding of carbachol to muscarinic cholinergic receptors of 1321N1 astrocytoma cells is insensitive to pertussis toxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;27(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Agranoff B. W. Calcium and the muscarinic synaptosomal phospholipid labeling effect. J Neurochem. 1980 May;34(5):1231–1240. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Reconstitution of resolved muscarinic cholinergic receptors with purified GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3477–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D. Involvement of guanine nucleotide-binding protein in the gating of Ca2+ by receptors. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):64–66. doi: 10.1038/306064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Crews F. T. Characterization of the cholinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain slices. J Neurosci. 1984 Dec;4(12):3120–3127. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-12-03120.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Ferry N., Geynet P., Hanoune J. Hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptors show agonist-specific regulation by guanine nucleotides. Loss of nucleotide effect after adrenalectomy. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11577–11583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. D., Hawthorne J. N., Sykes M., Orlacchio A. A calcium requirement for the phosphatidylinositol response following activation of presynaptic muscarinic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):1143–1147. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne J. N. Is phosphatidylinositol now out of the calcium gate? Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):281–282. doi: 10.1038/295281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Wusteman M., Downes C. P. Muscarinic receptors and hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids in rat cerebral cortex and parotid gland. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: II. Calcium requirement. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1388–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Lin S. H., Fain J. N. Rapid changes in hepatocyte phosphoinositides induced by vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13727–13732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


