Abstract
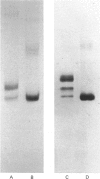
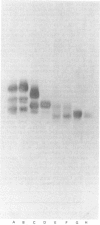
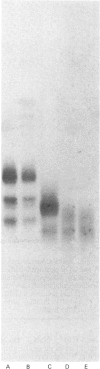
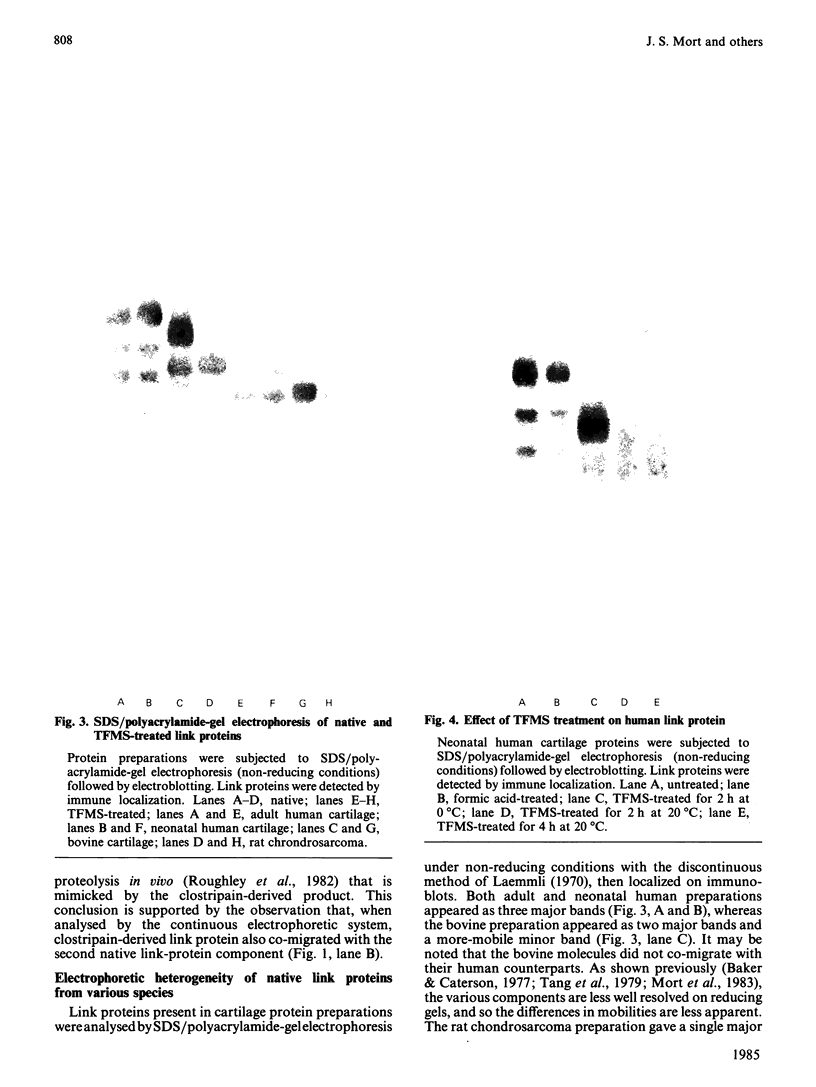
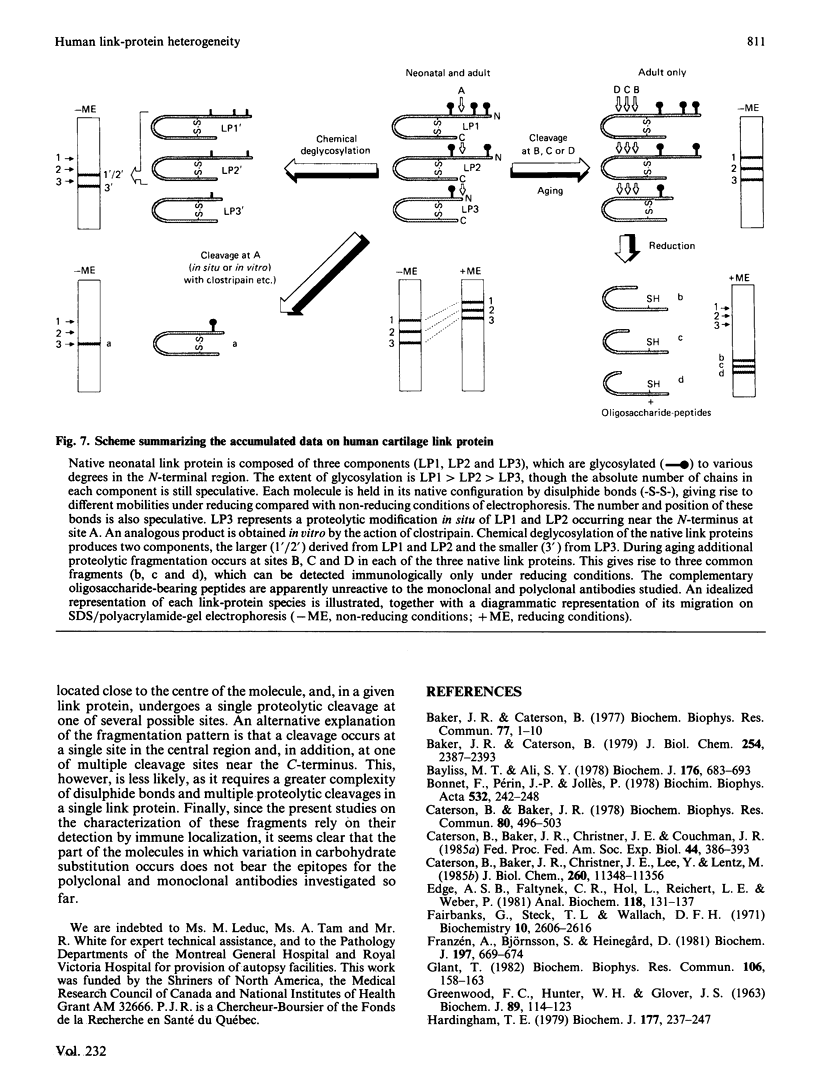
Human articular-cartilage link proteins are resolved into three components by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, indicative of three different structures. The action of the proteinase clostripain yields a single link-protein component with electrophoretic properties analogous to those of the smallest (most mobile) native link protein, suggesting that this link protein may be derived naturally from one or both of the larger molecules by proteolytic cleavage in situ. Upon chemical deglycosylation of native link protein two components are resolved, suggesting that two of the link proteins differ only in their degree and/or type of oligosaccharide substitution. This pattern is compatible with a proteolytic origin for the smallest link protein. During aging further proteolytic fragmentation occurs, though it is only apparent on reduction of disulphide bonds. This fragmentation occurs at identical sites in all three native link proteins, indicating the existence of a large region common to all the link proteins, which appears to consist predominantly of the C-terminal half of the molecules. These observations are compatible with the variation in oligosaccharide and proteolytic heterogeneity occurring at the N-terminus of the link proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. R., Caterson B. The isolation and characterization of the link proteins from proteoglycan aggregates of bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2387–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J., Caterson B. The purification and cyanogen bromide cleavage of the 'link proteins' from cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. T., Ali S. Y. Age-related changes in the composition and structure of human articular-cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):683–693. doi: 10.1042/bj1760683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Périn J. P., Jollès P. Isolation and chemical characterization of two distinct "link proteins" from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 15;532(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90578-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. R., Christner J. E., Lee Y., Lentz M. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for determining the microheterogeneity of the link proteins of cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11348–11356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. The interaction of link proteins with proteoglycan monomers in the absence of hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R., Couchman J. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against connective tissue proteoglycans. Fed Proc. 1985 Feb;44(2):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregate formation. Role of link protein. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1970669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glant T. T. Concanavalin A-binding link protein in the proteoglycan aggregate of hyaline cartilage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 14;106(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Glédic S., Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Jollès P. Identity of the protein cores of the two link proteins from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Localization of their sugar moieties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14759–14761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., Fellini S. A., Kimura J. H., Stevens R. L., Hascall V. C. Formation of proteoglycan aggregates in rat chondrosarcoma chondrocyte cultures treated with tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12280–12286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Poole A. R., Roughley P. J. Age-related changes in the structure of proteoglycan link proteins present in normal human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):269–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2140269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal S., Strider W., Margolis R., Gallo G., Lee-Huang S. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from human chondrosarcomas. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1279–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. P., Mason R. M. Proteoglycan aggregates in adult human costal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):512–526. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Reiner A., Mort J. S., Tang L. H., Choi H. U., Rosenberg L. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C. Cartilage link proteins. Biochemical and immunochemical studies of isolation and heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14849–14856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Reiner A., Tang L. H., Rosenberg L. Proteoglycans from bovine nasal cartilage. Immunochemical studies of link protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9295–9305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Jollès P. Comparative studies on human and bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex components. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Nov 1;21(2):71–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00240278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Pizon V., Jollès J., Jollès P. Structural data concerning the link proteins from bovine nasal cartilage proteolycan complex. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The heterogeneity of link proteins isolated from human articular cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J. Age-related changes in the structure of the proteoglycan subunits from human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The inability to prepare high-buoyant-density proteoglycan aggregates from extracts of normal adult human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):637–644. doi: 10.1042/bj2210637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu J., Towle C. A., Treadwell B. V. Characterisation of human articular cartilage link proteins from normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Apr;41(2):164–167. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang L. H., Rosenberg L., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Proteoglycans from bovine nasal cartilage. Properties of a soluble form of link protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10523–10531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]