Abstract
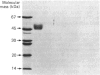
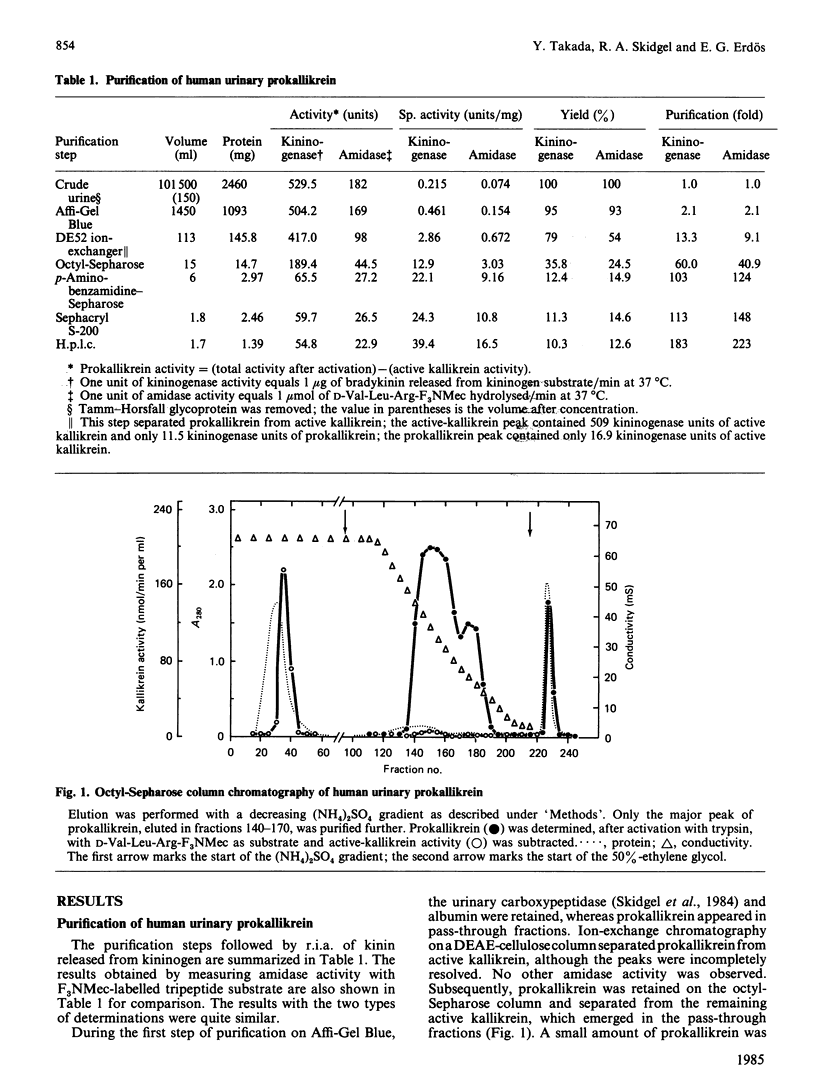
Human urinary active kallikrein and prokallikrein were separated on DEAE-cellulose and octyl-Sepharose columns and both purified to homogeneity by affinity chromatography, gel filtration and hydrophobic h.p.l.c. Prokallikrein was monitored during purification by trypsin activation followed by determination of both amidase and kininogenase activity. After trypsin activation, purified prokallikrein had a specific kininogenase activity of 39.4 micrograms of bradykinin equivalent/min per mg and amidase activity of 16.5 mumol/min per mg with D-Val-Leu-Arg-7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin. Purified active kallikrein had a specific activity of 47 micrograms of bradykinin/min per mg. The molecular mass of prokallikrein was 48 kDa on electrophoresis and 53 kDa on gel filtration whereas active kallikrein gave values of 46 kDa and 53 kDa respectively. Antisera to active and prokallikrein were obtained. In double immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis, antiserum to active kallikrein reacted with active and pro-kallikrein. Antiserum to prokallikrein contained antibodies to determinants not found in active kallikrein, presumably due to the presence of the activation peptide in the proenzyme. Human prokallikrein can be activated by thermolysin, trypsin and human plasma kallikrein. Activation of 50% of the prokallikrein (1.35 microM) was achieved in 30 min with 25 nM-thermolysin, 78 nM-trypsin or 180 nM-human plasma kallikrein. Thus thermolysin was the most effective activator. Thermolysin activated prokallikrein by releasing active kallikrein with N-terminal Ile1-Val2. Thus human tissue (glandular) prokallikrein can be activated by two types of enzymes: serine proteinases, which cleave at the C-terminus of basic amino acids, and by a metalloproteinase that cleaves at the N-terminus of hydrophobic amino acids.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Sato M., Imai Y., Haruyama T., Sato K., Hiwatari M., Kasai Y., Yoshinaga K. Renal kallikrein-kinin: its relation to renal prostaglandins and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone in man. Kidney Int. 1981 Jun;19(6):869–880. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter D. A., Johnston D., Strittmatter W. J. Protease inhibitors implicate metalloendoprotease in synaptic transmission at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthorn J., Imanari T., Yoshida H., Kaizu T., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. Isolation of prokallikrein from human urine. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;120B:575–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch C. B., Strittmatter W. J. Specific blockers of myoblast fusion inhibit a soluble and not the membrane-associated metalloendoprotease in myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5396–5399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa C. D., Caorsi I., Subiabre J., Vío C. P. Immunoreactive kallikrein localization in the rat kidney: an immuno-electron-microscopic study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Jan;32(1):117–121. doi: 10.1177/32.1.6558105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafford J. T., Skidgel R. A., Erdös E. G., Hersh L. B. Human kidney "enkephalinase", a neutral metalloendopeptidase that cleaves active peptides. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3265–3271. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Rosenblatt M., Potts J. T., Jr Parathyroid hormone: biochemical aspects of biosynthesis, secretion, action, and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):985–1053. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. R., Kato J., Erdös E. G., Robinson C. J., Oshima G. Angiotensin i-converting enzyme in the nephron. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 1;18(11):1299–1303. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikekita M., Tsuji T., Yamamoto K., Osawa T., Kizuki K., Moriya H. The carbohydrate moiety of human urinary kallikrein. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1983 Mar;31(3):1052–1058. doi: 10.1248/cpb.31.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai T., Miyazaki H., Hirose S., Hori H., Hayashi T., Kageyama R., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Murakami K. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human renin precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Dunn J. T., Silverberg M. Initiation of contact activation of human plasma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;156:45–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F., Geiger R., Henschen A., Kutzbach C. N-Terminal amino acid sequence of human urinary kallikrein homology with other serine proteases. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Dec;360(12):1947–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren S., Ronne H., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Sequence of an epidermal growth factor-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7780–7784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Stary S. J., Swift G. H. Two similar but nonallelic rat pancreatic trypsinogens. Nucleotide sequences of the cloned cDNAs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9724–9732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Quinto C., Swain W., Pictet R. L., Nikovits W., Rutter W. J. Primary structure of two distinct rat pancreatic preproelastases determined by sequence analysis of the complete cloned messenger ribonucleic acid sequences. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1453–1463. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S. The kallikrein-kinin system and the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:309–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S. The kallikrein-kinin system, renal function and hypertensive diseases. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1980;17:116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morichi S., Sako E., Hasegawa E., Suyama T., Moriya H. Large-scale purification and characterization of human urinary kallikrein. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1984 Mar;32(3):1152–1162. doi: 10.1248/cpb.32.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Takada K., Kimura T. New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy D. I., Strittmatter W. J. Requirement for metalloendoprotease in exocytosis: evidence in mast cells and adrenal chromaffin cells. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):645–656. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., Malik K. U. The renal kallikrein-kinin and prostaglandin systems interaction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:597–609. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Alhenc-Gelas F., White A., Erdös E. G. Activation of membrane-bound kallikrein and renin in the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4975–4978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Shimizu H., Kokubu T. Existence of prokallikrein in the kidney. Its biochemical properties compared to three active glandular kallikreins from the kidney, serum, and urine of the rat. Hypertension. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):205–210. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Ward P., Erdös E. G. Kallikrein and renin in the membrane fractions of the rat kidney. Hypertension. 1980 Jul-Aug;2(4):538–545. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda Y., Takada Y., Erdös E. G. Activation of human and rabbit prokallikrein by serine and metalloproteases. Kidney Int. 1985 Apr;27(4):630–635. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolly H., Lama M. C. Active and inactive kallikrein released by kidney slices from normotensive and hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6 Pt 2):II–35-8. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.6_pt_2.ii-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza N. B., Lieberthal W., Bernard D. B., Levinsky N. G. Antibody that recognizes total human urinary kallikrein: radioimmunological determination of inactive kallikrein. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2361–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito S. F., Orstavik T. B., Scicli A. G., Schork A., Carretero O. A. Role of the autonomic nervous system in the release of rat submandibular gland kallikrein into the circulation. Circ Res. 1983 Jun;52(6):635–641. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.6.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito S. F., Scicli A. G., Kher V., Carretero O. A. Immunoreactive glandular kallikrein in rat plasma: a radioimmunoassay for its determination. Am J Physiol. 1982 Apr;242(4):H602–H610. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.242.4.H602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalekamp M. A., Derkx F. H. Plasma kallikrein and plasmin as activators of prorenin: links between the renin-angiotensin system and other proteolytic systems in plasma. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Jul;61(1):15–21. doi: 10.1042/cs0610015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Malfroy B., De La Baume S. Biological inactivation of enkephalins and the role of enkephalin-dipeptidyl-carboxypeptidase ("enkephalinase") as neuropeptidase. Life Sci. 1981 Oct 26;29(17):1715–1740. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Gandolfi R., Carretero O. A. Site of formation of kinins in the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):F36–F40. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.1.F36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki T., Nakajima T., Erdös E. G. Colon kallikrein, its relation to the plasma enzyme. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 May 1;21(9):1227–1235. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. R., ole-MoiYoi O., Austen K. F., Spragg J. Active site radioimmunoassay for human urokallikrein and demonstration by radioimmunoassay of a latent form of the enzyme. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1551–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Davis R. M., Erdös E. G. Purification of a human urinary carboxypeptidase (kininase) distinct from carboxypeptidases A, B, or N. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):520–531. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spragg J. Characterization of purified human latent kallikrein. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;156:393–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Dagorn J. C., Ashley P. L., Cummings S. W., MacDonald R. J. Rat pancreatic kallikrein mRNA: nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the encoded preproenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7263–7267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaoka M., Akiyama H., Ito K., Okamura H., Morimoto S. Isolation of inactive kallikrein from rat urine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 15;109(3):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vio C. P., Churchill L., Rabito S. F., Terragno A., Carretero O. A., Terragno N. A. Renal kallikrein in venous effluent of filtering and non-filtering isolated kidneys. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;156(Pt B):897–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vio C. P., Roblero J. S., Croxatto H. R. Dexamethasone, aldosterone and kallikrein release by isolated rat kidney. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Aug;61(2):241–243. doi: 10.1042/cs0610241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., VOGEL R. [On the excretion of kallikrein in urine after experimental kidney injury]. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Jun 1;126:171–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., VOGEL R. [On the release of a kallikrein-like substance by extracts of various organs]. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1961 May 1;131:257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Erdös E. G., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Reynolds R. C. Isolation of membrane-bound renal enzymes that metabolize kinins and angiotensins. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1570643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Erdös E. G. Isolation of membrane-bound renal kallikrein and kininase. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1510755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Erdös E. G. Kallikrein and prekallikrein of the isolated basolateral membrane of rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1982 Oct;22(4):331–337. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Schulz W. W., Page D. S., Erdös E. G. Kallikrein and prekallikrein on the basolateral membrane of rat kidney tubules. Hypertension. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6 Pt 2):II–59-64. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.6_pt_2.ii-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]