Abstract
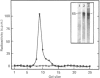
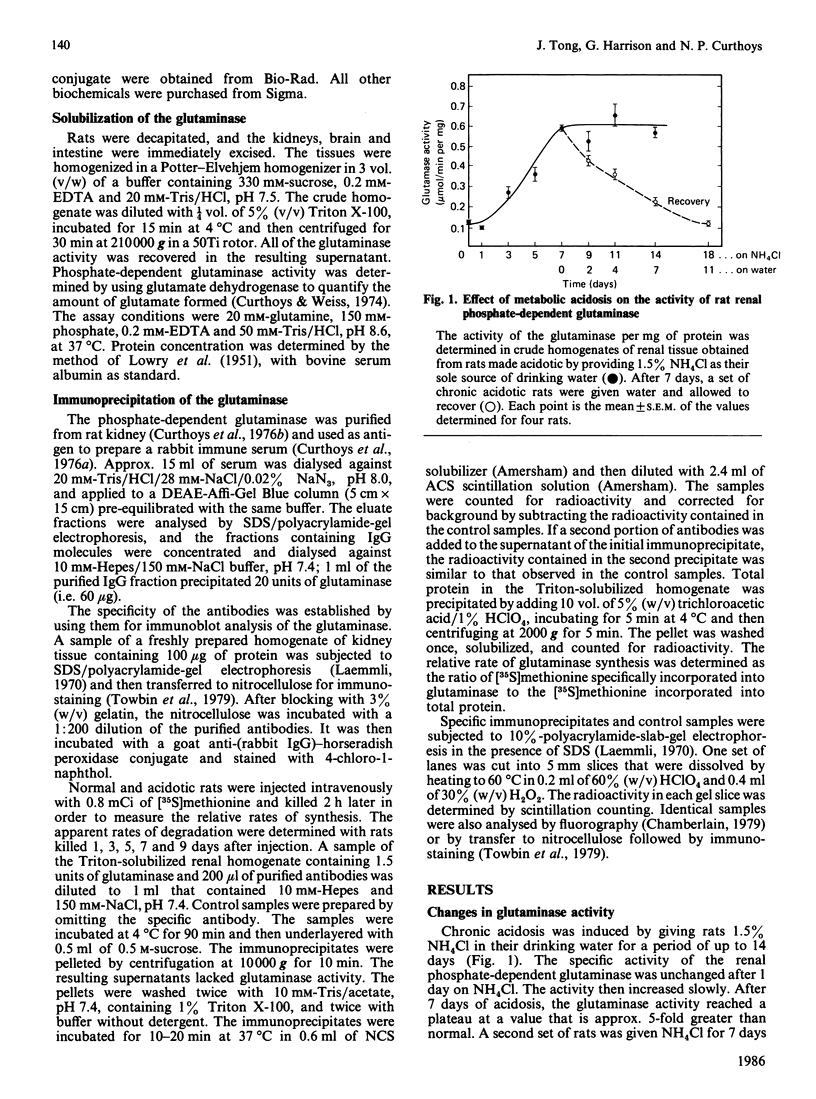
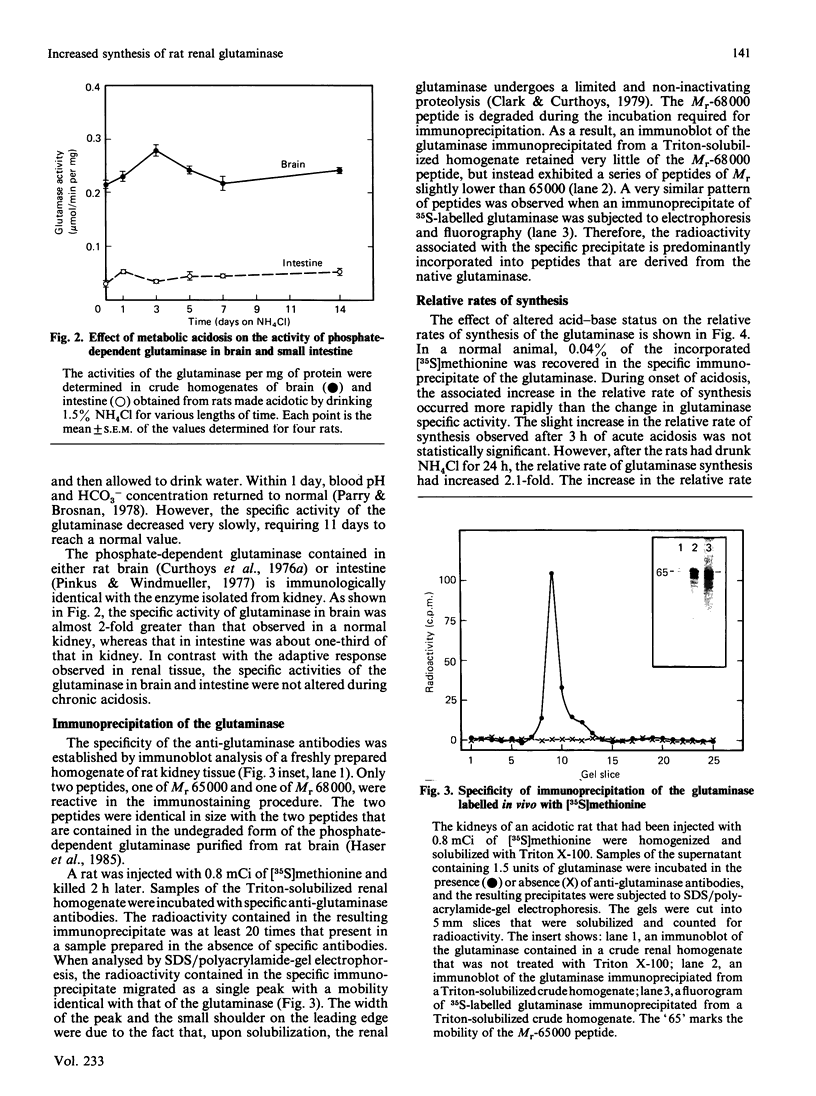
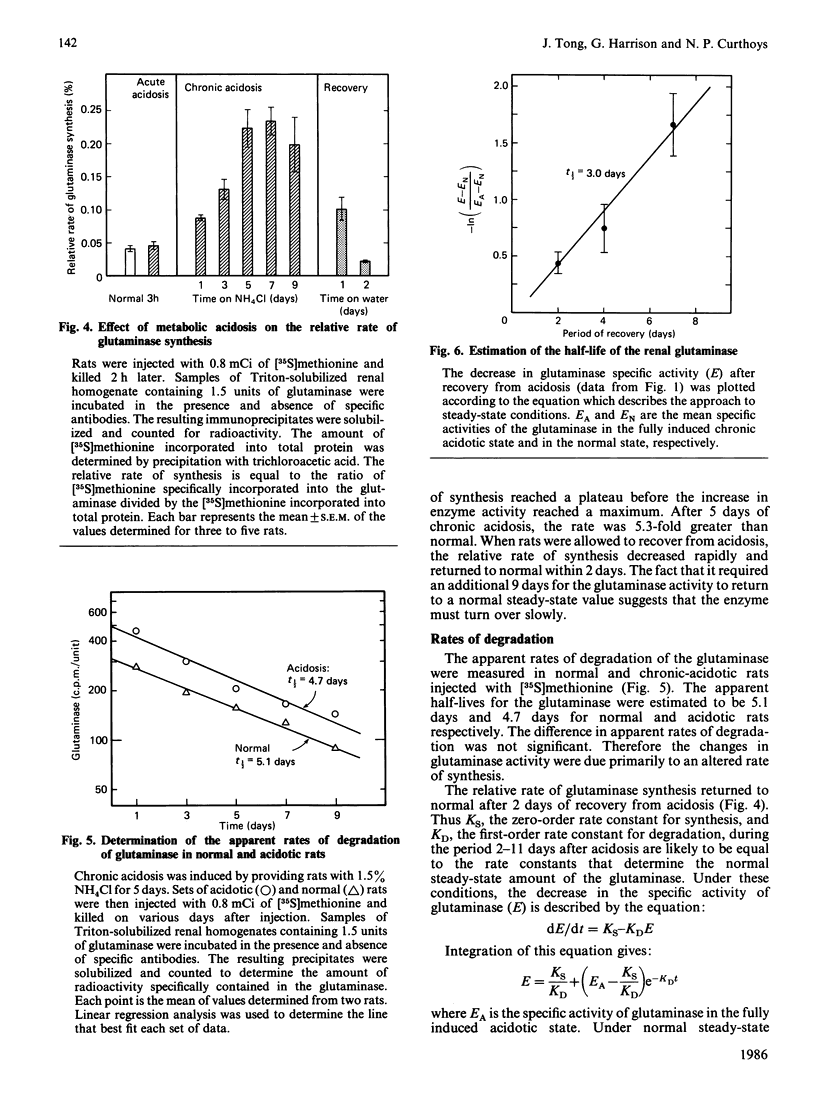
Regulation of the mitochondrial phosphate-dependent glutaminase activity is an essential component in the control of renal ammoniagenesis. Alterations in acid-base balance significantly affect the amount of the glutaminase that is present in rat kidney, but not in brain or small intestine. The relative rates of glutaminase synthesis were determined by comparing the amount of [35S]methionine incorporated into specific immunoprecipitates with that incorporated into total protein. In a normal animal, the rate of glutaminase synthesis constitutes 0.04% of the total protein synthesis. After 7 days of metabolic acidosis, the renal glutaminase activity is increased to a value that is 5-fold greater than normal. During onset of acidosis, the relative rate of synthesis increases more rapidly than the appearance of increased glutaminase activity. The increased rate of synthesis reaches a plateau within 5 days at a value that is 5.3-fold greater than normal. Recovery from chronic acidosis causes a rapid decrease in the relative rate of glutaminase synthesis, but a gradual decrease in glutaminase activity. The former returns to normal within 2 days, whereas the latter requires 11 days. The apparent half-time for glutaminase degradation was found to be 5.1 days and 4.7 days for normal and acidotic rats respectively. These results indicate that the increase in renal glutaminase activity associated with metabolic acidosis is due primarily to an increase in its rate of synthesis. From the decrease in activity that occurs upon recovery from acidosis, the true half-life for the glutaminase was estimated to be 3 days.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleyne G. A., Scullard G. H. Renal metabolic response to acid base changes. I. Enzymatic control of ammoniagenesis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):364–370. doi: 10.1172/JCI105993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd T. A., Goldstein L. Kidney metabolite levels and ammonia production in acute acid-base alterations in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):E289–E295. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.3.E289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch H. B., Narins R. G., Chu C., Fagioli S., Choi S., McCarthy W., Lowry O. H. Distribution along the rat nephron of three enzymes of gluconeogenesis in acidosis and starvation. Am J Physiol. 1978 Sep;235(3):F246–F253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.3.F246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capraro M. A., Hughey R. P. Use of acivicin in the determination of rate constants for turnover of rat renal gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3408–3412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbala M. A., Lamers W. H., Nelson K., Monahan J. E., Yoo-Warren H., Hanson R. W. Rapid changes in the concentration of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA in rat liver and kidney. Effects of insulin and cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7629–7636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. M., Shapiro R. A., Curthoys N. P. Comparison of the hydrolysis and the covalent binding of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-[6-14C]norleucine by rat renal phosphate-dependent glutaminase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jan;213(1):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90457-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Kuhlenschmidt T., Godfrey S. S., Weiss R. F. Phosphate-dependent glutaminase from rat kidney. Cause of increased activity in response to acidosis and identity with glutaminase from other tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):162–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Lowry O. H. The distribution of glutaminase isoenzymes in the various structures of the nephron in normal, acidotic, and alkalotic rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):162–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Weiss R. F. Regulation of renal ammoniagenesis. Subcellular localization of rat kidney glutaminase isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3261–3266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman A. D., Fuisz R. E., Cahill G. F., Jr Renal gluconeogenesis in acidosis, alkalosis, and potassium deficiency: its possible role in regulation of renal ammonia production. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):612–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI105375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haser W. G., Shapiro R. A., Curthoys N. P. Comparison of the phosphate-dependent glutaminase obtained from rat brain and kidney. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):399–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2290399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughey R. P., Rankin B. B., Curthoys N. P. Acute acidosis and renal arteriovenous differences of glutamine in normal and adrenalectomized rats. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):F199–F204. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.3.F199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W. The regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) synthesis in rat kidney cortex. The role of acid-base balance and glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5596–5603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Hanson R. W. Messenger RNA for renal phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Its translation in a heterologous cell-free system and its regulation by glucocorticoids and by changes in acid-base balance. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8398–8403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARD E., ORLOFF J. Regulation of ammonia excretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jul;182(1):131–138. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.182.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan D. J., Lotspeich W. D. Factors affecting the deamidation of glutamine by kidney mitochondria of normal and acidotic rats. Enzymologia. 1968 Aug 31;35(2):82–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. M., Brosnan J. T. Glutamine metabolism in the kidney during induction of, and recovery from, metabolic acidosis in the rat. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):387–396. doi: 10.1042/bj1740387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus L. M., Windmueller H. G. Phosphate-dependent glutaminase of small intestine: localization and role in intestinal glutamine metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):506–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of renal ammoniagenesis. Purification and characterization of phosphate-dependent glutaminase from rat kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 May;174(1):82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolwerth A. C., LaNoue K. F. Control of ammoniagenesis by alpha-ketoglutarate in rat kidney mitochondria. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):F399–F408. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.4.F399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolwerth A. C., Nazar B. L., LaNoue K. F. Glutamate dehydrogenase activation and ammonia formation by rat kidney mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6177–6183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröck H., Goldstein L. Interorgan relationships for glutamine metabolism in normal and acidotic rats. Am J Physiol. 1981 May;240(5):E519–E525. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.5.E519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyama S., Saeki T., Katunuma N. Comparison of properties and inducibility of glutamate dehydrogenases in rat kidney and liver. J Biochem. 1973 Jan;73(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. A., Clark V. M., Curthoys N. P. Covalent interaction of L-2-amino-4-oxo-5-chloropentanoic acid with rat renal phosphate-dependent glutaminase. Evidence for a specific glutamate binding site and of subunit heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):7086–7090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires E. J., Hall D. E., Brosnan J. T. Arteriovenous differences for amino acids and lactate across kidneys of normal and acidotic rats. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):125–128. doi: 10.1042/bj1600125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannen R. L. Ammonia metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1978 Oct;235(4):F265–F277. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.4.F265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinay P., Allignet E., Pichette C., Watford M., Lemieux G., Gougoux A. Changes in renal metabolite profile and ammoniagenesis during acute and chronic metabolic acidosis in dog and rat. Kidney Int. 1980 Mar;17(3):312–325. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]