Abstract
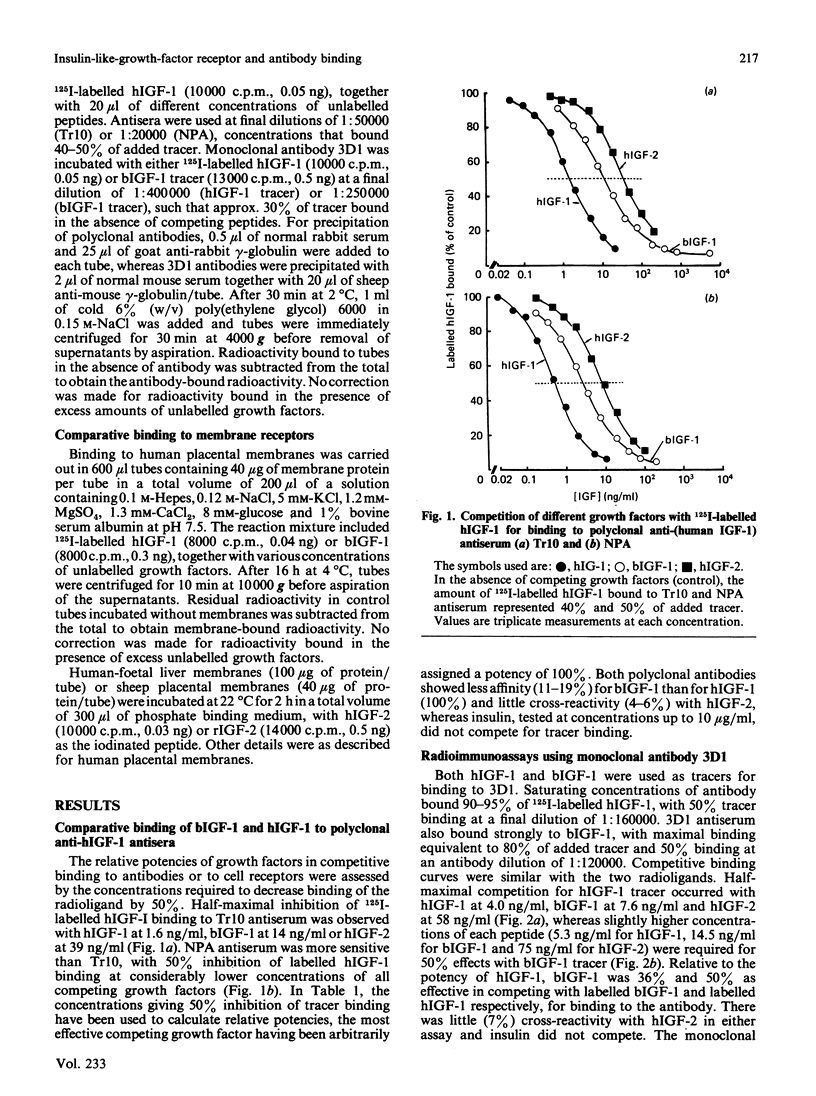
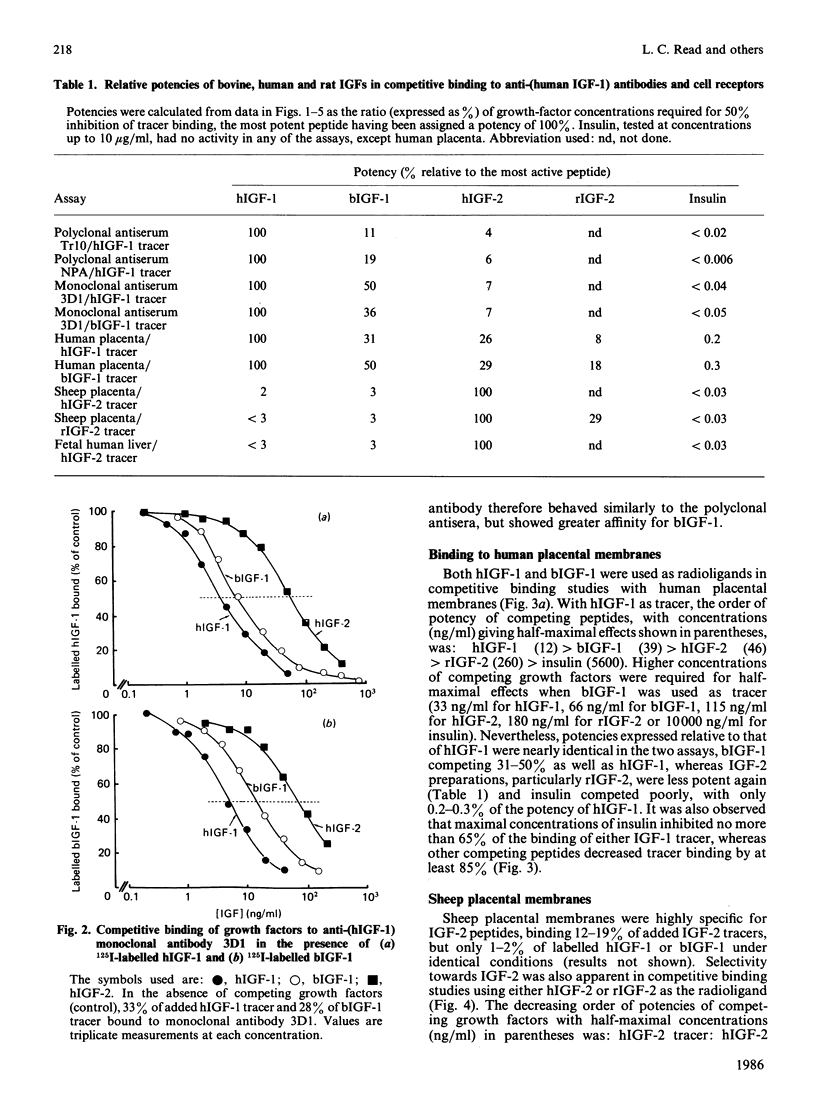
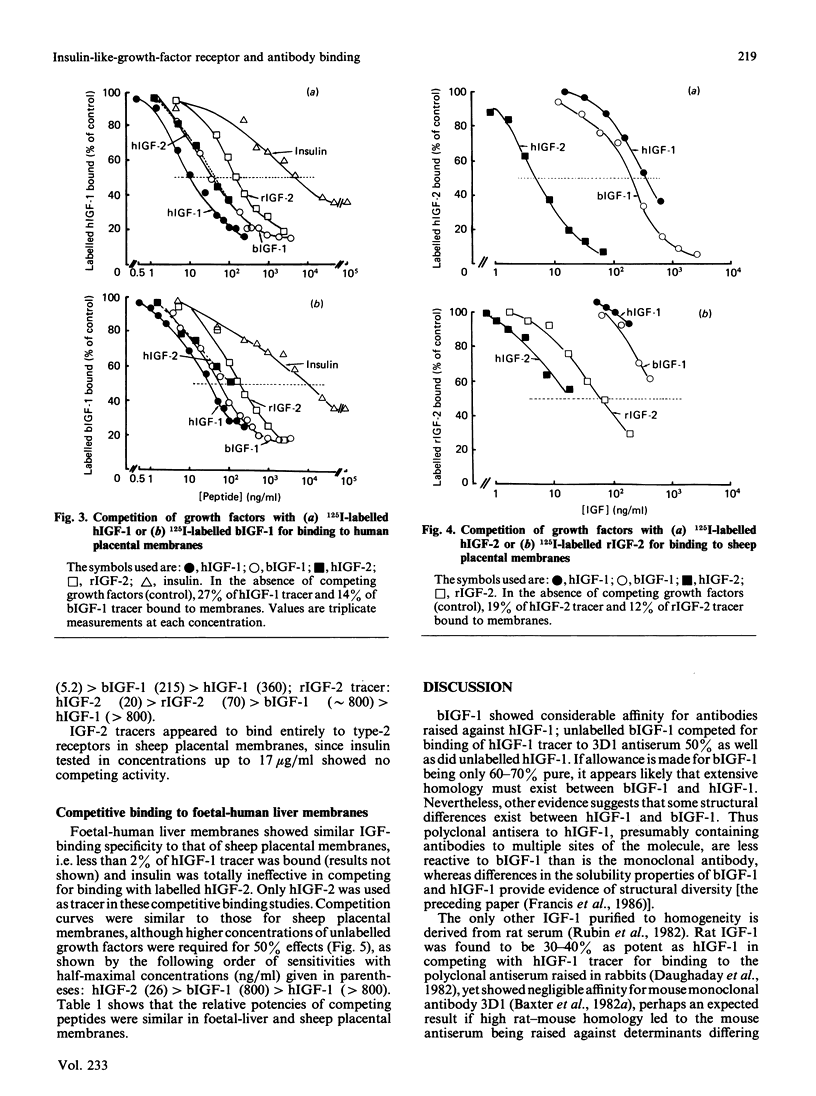
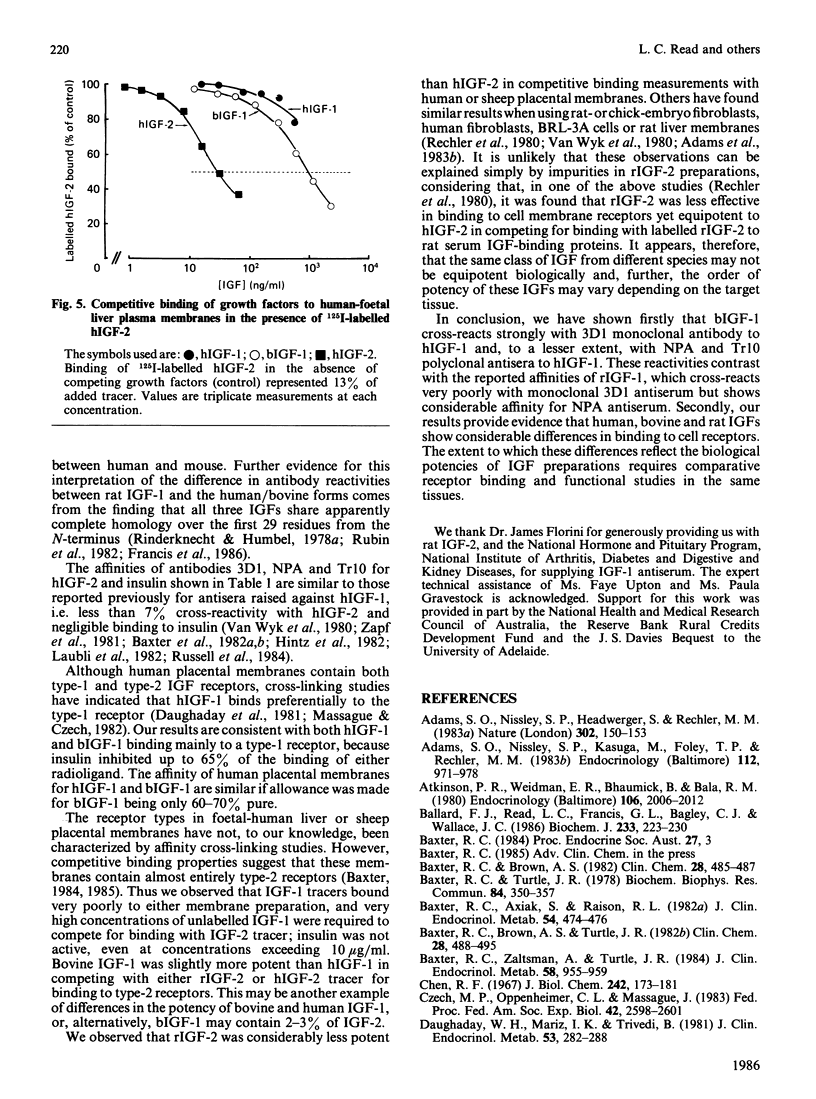
The immunological properties of human, bovine and rat insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and insulin were compared in competitive binding studies with Tr10 and NPA polyclonal antisera raised in rabbits against human IGF-1. Bovine IGF-1 was 11-19% as effective as human IGF-1 in competing for binding with 125I-labelled human IGF-1, whereas IGF-2 reacted poorly and insulin did not compete. Similar competitive binding curves were obtained with the mouse monoclonal anti-(human IGF-1) antibody 3D1, except that bovine IGF-1 showed a severalfold greater affinity for the monoclonal antibody than for either polyclonal antiserum. Membranes isolated from human placenta, sheep placenta and foetal-human liver were used as sources of cellular receptors. In human placental membranes, most of the binding of IGF-1 tracers could be attributed to a type-1 receptor, because insulin inhibited up to 65% of tracer binding. The other two tissues apparently contain only type-2 receptors, as evidenced by the very low potency of bovine or human IGF-1 in competing for binding with IGF-2 tracers and the absence of any competition by insulin. In competition for binding with labelled bovine or human IGF-1 to human placental membranes, bovine IGF-1 had a similar potency to human IGF-1, whereas bovine IGF-1 was more potent in binding studies with tissues rich in type-2 receptors. Rat IGF-2 was considerably less effective than human IGF-2 in competition for receptors on any of the membrane preparations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Handwerger S., Rechler M. M. Developmental patterns of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II synthesis and regulation in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):150–153. doi: 10.1038/302150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Kasuga M., Foley T. P., Jr, Rechler M. M. Receptors for insulin-like growth factors and growth effects of multiplication-stimulating activity (rat insulin-like growth factor II) in rat embryo fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):971–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkison P. R., Weidman E. R., Bhaumick B., Bala R. M. Release of somatomedin-like activity by cultured WI-38 human fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1980 Jun;106(6):2006–2012. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-6-2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Read L. C., Francis G. L., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Binding properties and biological potencies of insulin-like growth factors in L6 myoblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2330223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Axiak S., Raison R. L. Monoclonal antibody against human somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):474–476. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Brown A. S. Purification of tracer for somatomedin C radioimmunoassay by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):485–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Brown A. S., Turtle J. R. Radioimmunoassay for somatomedin C: comparison with radioreceptor assay in patients with growth-hormone disorders, hypothyroidism, and renal failure. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):488–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Turtle J. R. Regulation of hepatic growth hormone receptors by insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Zaltsman Z., Turtle J. R. Immunoreactive somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein in human milk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Jun;58(6):955–959. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-6-955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Oppenheimer C. L., Massagué J. Interrelationships among receptor structures for insulin and peptide growth factors. Fed Proc. 1983 Jun;42(9):2598–2601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Applewhite G. T., Underwood L. E. Evidence that somatomedin is synthesized by multiple tissues in the fetus. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar 15;75(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Stiles A. D., Underwood L. E. Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Trivedi B. A preferential binding site for insulin-like growth factor II in human and rat placental membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Aug;53(2):282–288. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-2-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Parker K. A., Borowsky S., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Measurement of somatomedin-related peptides in fetal, neonatal, and maternal rat serum by insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I radioimmunoassay, IGF-II radioreceptor assay (RRA), and multiplication-stimulating activity RRA after acid-ethanol extraction. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):575–581. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenmann J. E., Patterson D. F., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I in the dog: a study in different dog breeds and in dogs with growth hormone elevation. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Mar;105(3):294–301. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1050294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Read L. C., Ballard F. J., Bagley C. J., Upton F. M., Gravestock P. M., Wallace J. C. Purification and partial sequence analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 from bovine colostrum. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):207–213. doi: 10.1042/bj2330207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G., Humbel R. Evidence for two species of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF II and "big" IGF II) in human spinal fluid. Endocrinology. 1982 May;110(5):1822–1824. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-5-1822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Seegan G. Characterization of an insulin-like growth factor-I/somatomedin-C radioimmunoassay specific for the C-peptide region. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):927–930. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubli U. K., Baier W., Binz H., Celio M. R., Humbel R. E. Monoclonal antibodies directed to human insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I). Use for radioimmunoassay and immunopurification of IGF. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 22;149(1):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Purification and primary structure of a polypeptide with multiplication-stimulating activity from rat liver cell cultures. Homology with human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6859–6865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Purification and characterization of multiplication-stimulating activity. Insulin-like growth factors purified from rat-liver-cell-conditioned medium. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):387–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Mariz I., Jacobs J. W., Daughaday W. H., Bradshaw R. A. Isolation and partial sequence analysis of rat basic somatomedin. Endocrinology. 1982 Mar;110(3):734–740. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-3-734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. E., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Inhibition of the mitogenic effects of plasma by a monoclonal antibody to somatomedin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2389–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Svoboda M. E., Underwood L. E. Evidence from radioligand assays that somatomedin-C and insulin-like growth factor-I are similar to each other and different from other somatomedins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jan;50(1):206–208. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-1-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. F., Turtle J. R. Purification of the insulin receptor from human placental membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 28;579(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. M., Hintz R. L. Inter-species comparison of somatomedin structure using immunological probes. J Endocrinol. 1982 Oct;95(1):59–64. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0950059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


