Abstract
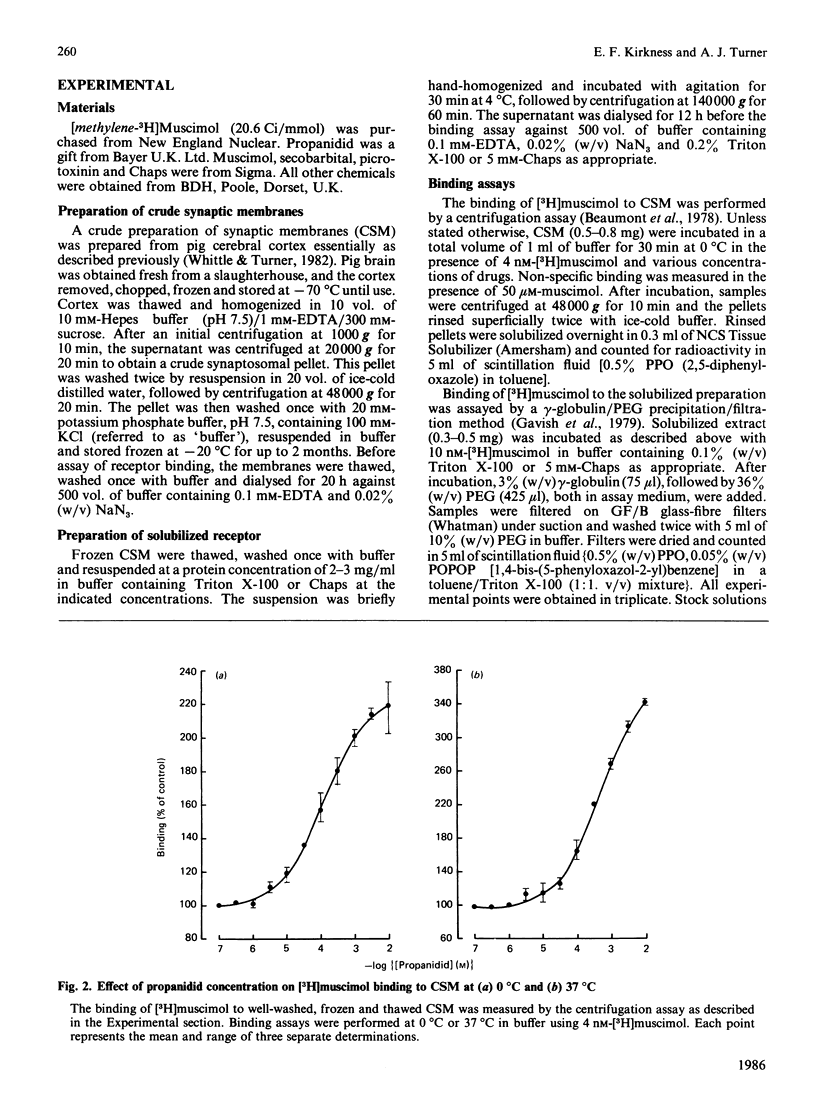
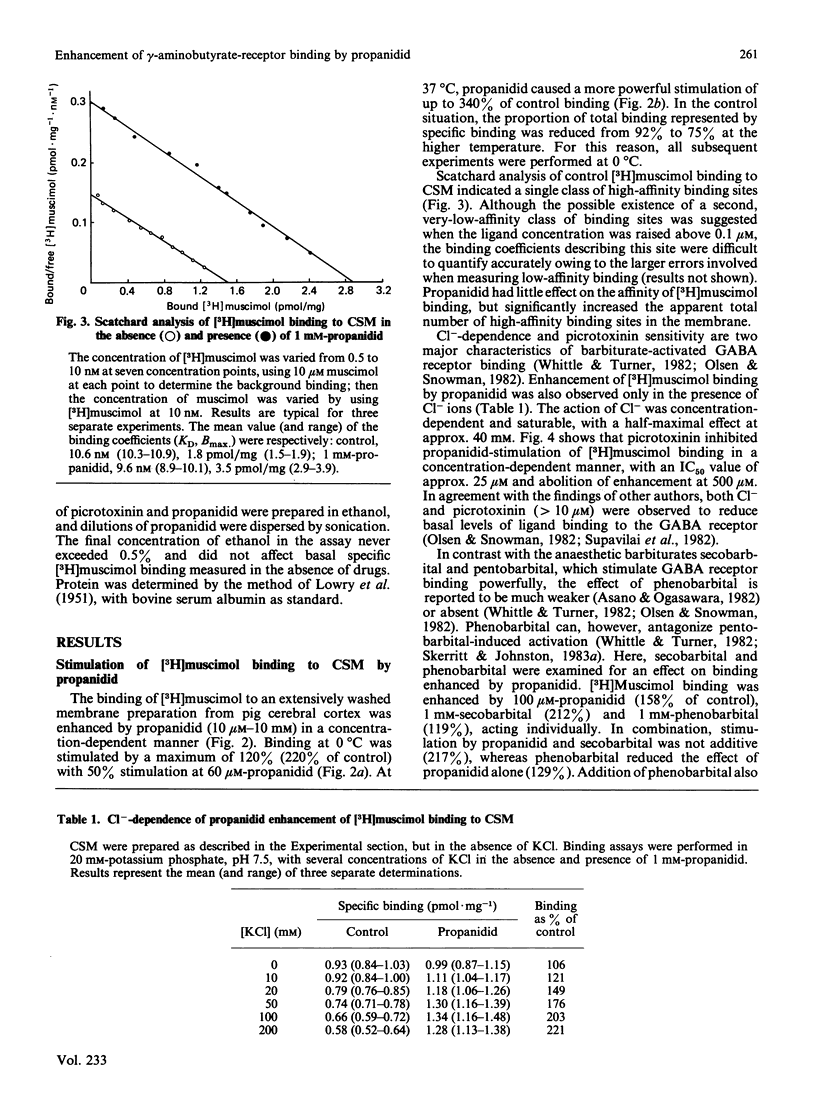
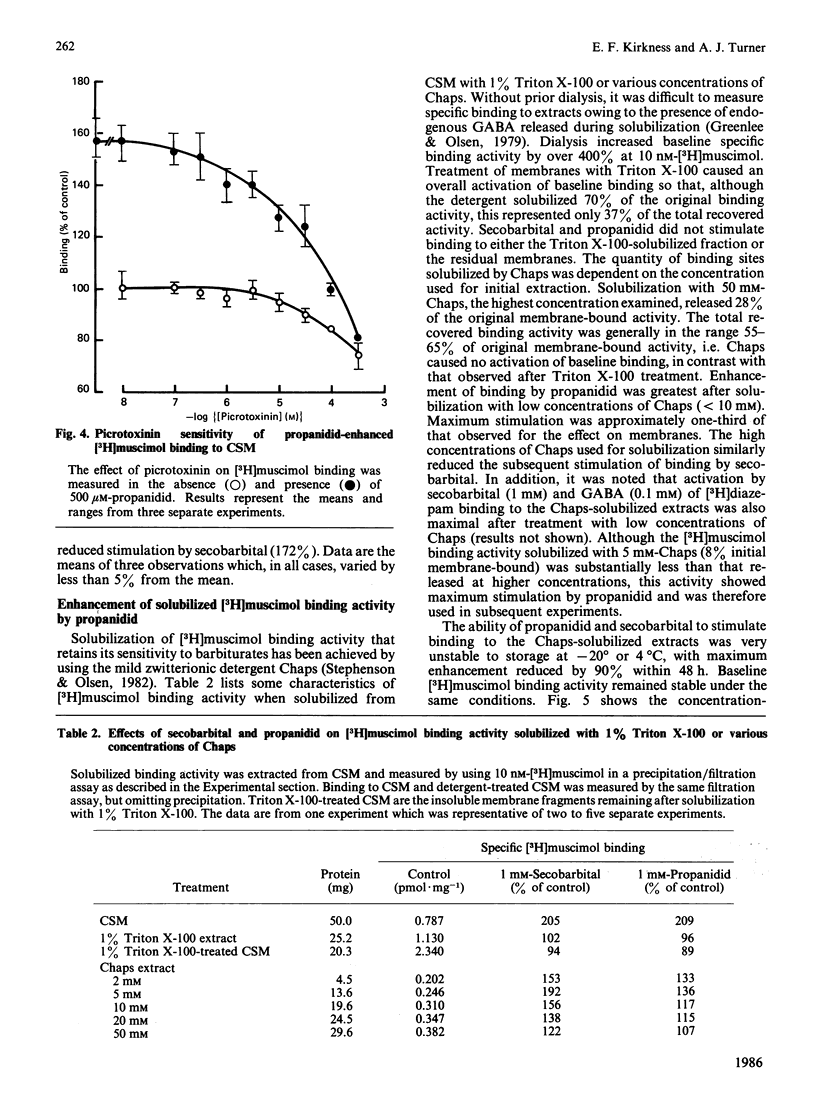
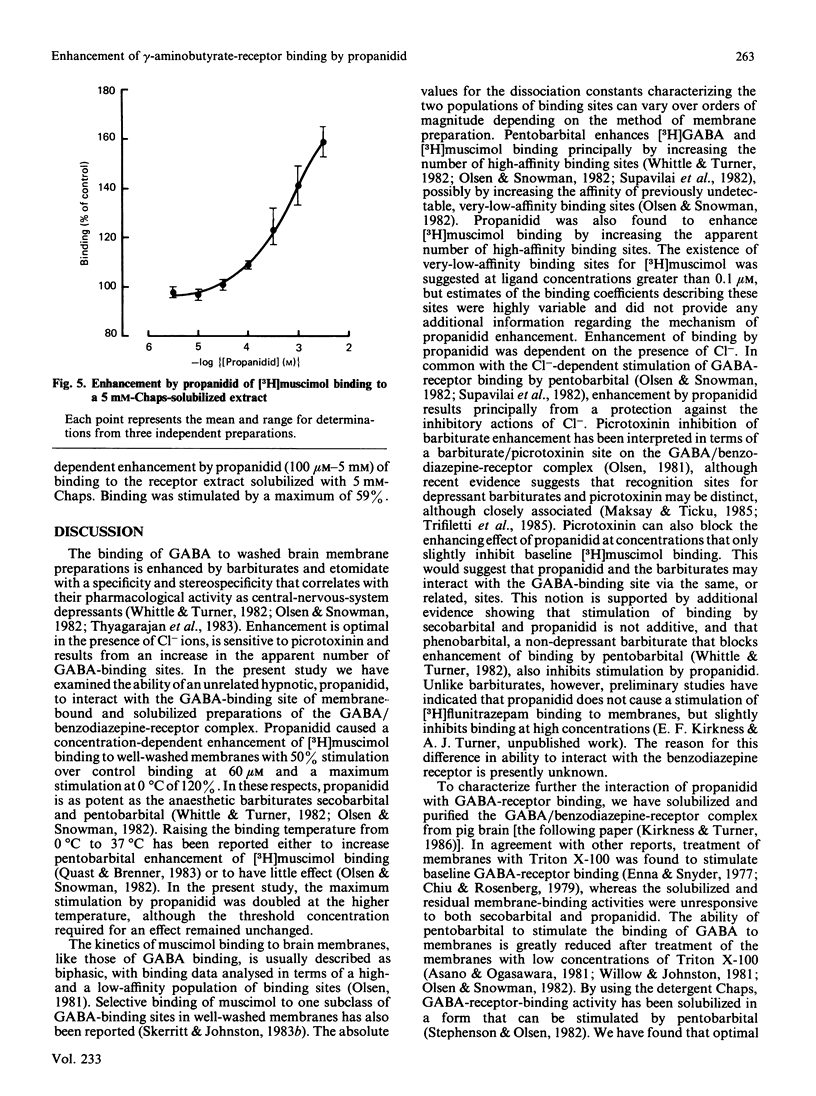
The binding of [3H]muscimol, a gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) receptor agonist, to a membrane preparation from pig cerebral cortex was enhanced by the anaesthetic propanidid in a concentration-dependent manner. At 0 degrees C, binding was stimulated to 220% of control values, with 50% stimulation at 60 microM-propanidid. At 37 degrees C, propanidid caused a more powerful stimulation of [3H]muscimol binding (340% of control values). Propanidid (1 mM) exerted little effect on the affinity of muscimol binding (KD approx. 10 nM), but increased the apparent number of high-affinity binding sites in the membrane by 2-fold. Enhancement of [3H]muscimol binding was observed only in the presence of Cl- ions, half-maximal activation being achieved at approx. 40 mM-Cl-. Picrotoxinin inhibited the stimulation of [3H]muscimol binding by propanidid with an IC50 (concentration causing 50% inhibition) value of approx. 25 microM. The enhancement of [3H]muscimol binding by propanidid was not additive with the enhancement produced by secobarbital. Phenobarbital inhibited the effect of propanidid and secobarbital. The GABA receptor was solubilized with Triton X-100 or with Chaps [3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]propanesulphonate]. Propanidid and secobarbital did not stimulate the binding of [3H]muscimol after solubilization with Triton X-100. However, the receptor could be solubilized by 5 mM-Chaps with retention of the stimulatory effects of propanidid and secobarbital. Unlike barbiturates, propanidid did not stimulate the binding of [3H]flunitrazepam to membranes. It is suggested that the ability to modulate the [3H]muscimol site of the GABA-receptor complex may be a common and perhaps functional characteristic of general anaesthetics.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Chloride-dependent stimulation of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor binding by pentobarbital. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Stimulation of GABA receptor binding by barbiturates. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 5;77(4):355–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton D., Geerts R., Waterkeyn C., Leysen J. E. Etomidate stereospecifically stimulates forebrain, but not cerebellar, 3H-diazepam binding. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2631–2636. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90637-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont K., Chilton W. S., Yamamura H. I., Enna S. J. Muscimol binding in rat brain: association with synaptic GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Rosenberg H. C. Differential effects of triton X-100 on benzodiazepine and GABA binding in a frozen-thawed synaptosomal fraction of rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 1;58(3):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90484-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway C. M., Ellis D. B. Propanidid. Br J Anaesth. 1970 Mar;42(3):249–254. doi: 10.1093/bja/42.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenicke A., Krumey I., Kugler J., Klempa J. Experimental studies of the breakdown of Epontol: determination of propanidid in human serum. Br J Anaesth. 1968 Jun;40(6):415–429. doi: 10.1093/bja/40.6.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Hill R. G. GABA-mimetic action of etomidate. Experientia. 1978 Oct 15;34(10):1325–1327. doi: 10.1007/BF01981448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Chang R. S., Snyder S. H. Solubilization of histamine H-1, GABA and benzodiazepine receptors. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 27;25(9):783–789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Olsen R. W. Solubilization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor protein from mammalian brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Modulation of the GABA receptor complex by a steroid anaesthetic. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 10;323(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Turner A. J. The gamma-aminobutyrate/benzodiazepine receptor from pig brain. Purification and characterization of the receptor complex from cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):265–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2330265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg F., Snowman A., Olsen R. W. Barbiturate receptor sites are coupled to benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7468–7472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg F., Snowman A., Olsen R. W. Perturbation of benzodiazepine receptor binding by pyrazolopyridines involves picrotoxinin/barbiturate receptor sites. J Neurosci. 1981 May;1(5):471–477. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-05-00471.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maksay G., Ticku M. K. Dissociation of [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate binding differentiates convulsant and depressant drugs that modulate GABAergic transmission. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):480–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mernoff S. T., Cherwinski H. M., Becker J. W., de Blas A. L. Solubilization of brain benzodiazepine receptors with a zwitterionic detergent: optimal preservation of their functional interaction with the GABA receptors. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):752–758. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. GABA-benzodiazepine-barbiturate receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Snowman A. M. Chloride-dependent enhancement by barbiturates of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1812–1823. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01812.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Placheta P., Karobath M. In vitro modulation by SQ 20009 and SQ 65396 of GABA receptor binding in rat CNS membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 21;62(2-3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Brenner O. Modulation of [3H]muscimol binding in rat cerebellar and cerebral cortical membranes by picrotoxin, pentobarbitone, and etomidate. J Neurochem. 1983 Aug;41(2):418–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. H. Physical mechanisms of anesthesia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1979;19:159–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.19.040179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerritt J. H., Johnston G. A. Diazepam stimulates the binding of GABA and muscimol but not THIP to rat brain membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 8;38(3):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerritt J. H., Johnston G. A. Interactions of some anaesthetic, convulsant, and anticonvulsant drugs at GABA-benzodiazepine receptor-ionophore complexes in rat brain synaptosomal membranes. Neurochem Res. 1983 Oct;8(10):1351–1362. doi: 10.1007/BF00964003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A., Olsen R. W. Solubilization by CHAPS detergent of barbiturate-enhanced benzodiazepine-GABA receptor complex. J Neurochem. 1982 Dec;39(6):1579–1586. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Study R. E., Barker J. L. Diazepam and (--)-pentobarbital: fluctuation analysis reveals different mechanisms for potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in cultured central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7180–7184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyagarajan R., Ramanjaneyulu R., Ticku M. K. Enhancement of diazepam and gamma-aminobutyric acid binding by (+)etomidate and pentobarbital. J Neurochem. 1983 Aug;41(2):578–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifiletti R. R., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Barbiturate recognition site on the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex is distinct from the picrotoxinin/TBPS recognition site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 13;106(2):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90737-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Whittle S. R. Biochemical dissection of the gamma-aminobutyrate synapse. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):29–41. doi: 10.1042/bj2090029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle S. R., Turner A. J. Differential effects of sedative and anticonvulsant barbiturates on specific [3H]GABA binding to membrane preparations from rat brain cortex. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 15;31(18):2891–2895. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M. A comparison of the actions of pentobarbitone and etomidate on [3H]GABA binding to crude synaptosomal rat brain membranes. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 14;220(2):427–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M., Johnston G. A. Dual action of pentobarbitone on GABA binding: role of binding site integrity. J Neurochem. 1981 Nov;37(5):1291–1294. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


