Abstract
Several alpha-oxohydroxy heteroaromatic chelators have been shown to mobilize iron from horse spleen ferritin. Although the reactions were slow, taking up to 3 days to reach completion, the amounts of iron mobilized were higher than those reported for other chelators. These results increase the prospects for the clinical use of alpha-oxohydroxy chelators in the treatment of iron overload.
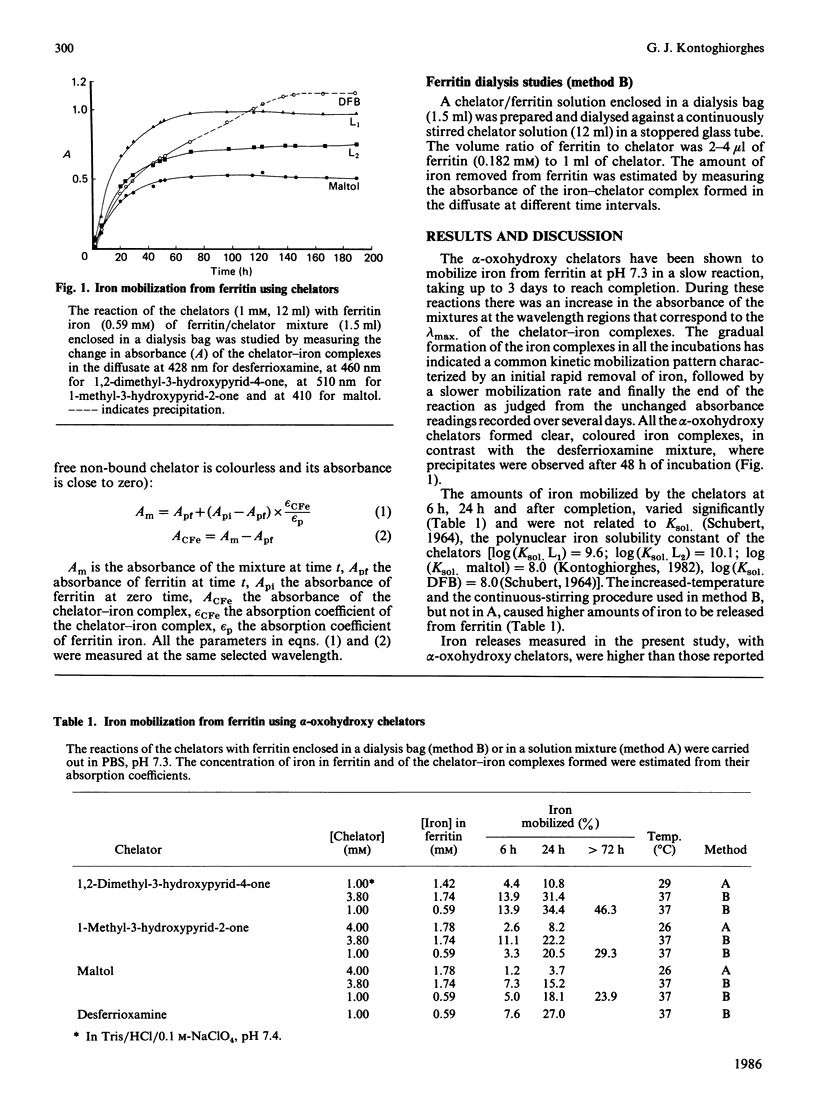
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crichton R. R., Roman F. A mechanism for ferritin-iron oxidation and deposition [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(4):1126–1128. doi: 10.1042/bst0051126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton R. R., Roman F., Roland F. Iron mobilization from ferritin by chelating agents. J Inorg Biochem. 1980 Dec;13(4):305–316. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dognin J., Crichton R. R. Mobilisation of iron from ferritin fractions of defined iron content by biological reductants. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 15;54(2):234–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. M., Hoy T. G., Macara I. G., Hoare R. J. Ferritin iron uptake and release. Structure-function relationships. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):445–451. doi: 10.1042/bj1430445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghes G. J. New orally active iron chelators. Lancet. 1985 Apr 6;1(8432):817–817. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91472-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Linder M. C. Ferritin: structure, biosynthesis, and role in iron metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1978 Apr;58(2):317–396. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L., Multani J. S., Stitt C., Saltman P. The mobilization of iron from ferritin by chelating agents. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):613–616. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirivech S., Frieden E., Osaki S. The release of iron from horse spleen ferritin by reduced flavins. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):311–315. doi: 10.1042/bj1430311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffry A., Harrison P. M. The binding of ferric iron by ferritin. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):709–716. doi: 10.1042/bj1810709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufano T. P., Pecoraro V. L., Raymond K. N. Ferric ion sequestering agents: kinetics of iron release from ferritin to catechoylamides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;668(3):420–428. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasue M., Kawamura N., Sakakibara J. [Syntheses of N-substituted-3-glucosyloxy-2-methyl-4-pyridones and their aglycones]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1970 Oct;90(10):1222–1225. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.90.10_1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


