Abstract
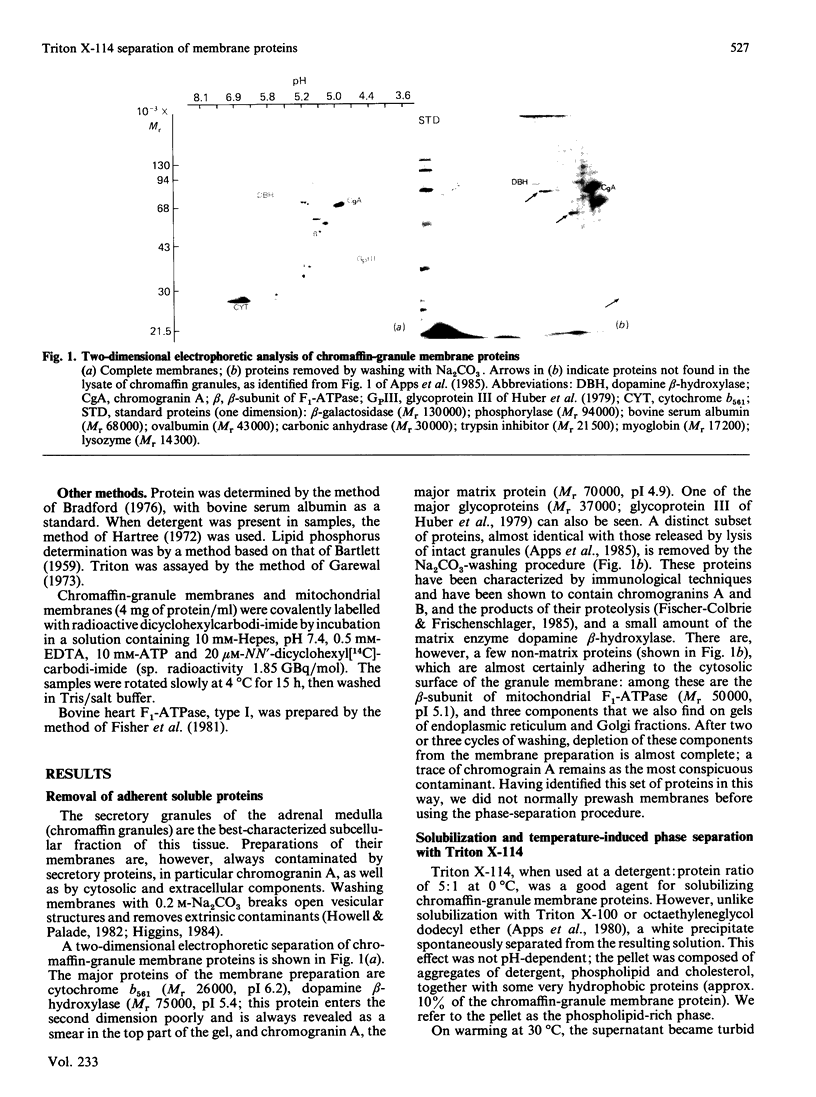
After solubilization with the detergent Triton X-114, membrane proteins may be separated into three groups: if the membrane is sufficiently lipid-rich, one family of hydrophobic constituents separates spontaneously at low temperature; warming at 30 degrees C leads to separation of a detergent-rich phase and an aqueous phase. Using the chromaffin-granule membrane as a model, we found that many intrinsic membrane glycoproteins are found in the latter phase, probably maintained in solution by adherent detergent. They precipitate, however, when this is removed by dialysis, leaving in solution those truly hydrophilic proteins that were originally adhering to the membranes. We have used this method with mitochondria, and with Golgi- and rough-endoplasmic-reticulum-enriched microsomal fractions: it has proved to be a rapid and convenient method for effecting a partial separation of proteins from a variety of different membranes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbs M. T., Phillips J. H. Organisation of the proteins of the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):200–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Phillips J. H., Purves F. C. Glycoproteins of the chromaffin-granule matrix: use of lectin blotting to distinguish several separate classes. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Pryde J. G., Phillips J. H. Cytochrome b561 is identical with chromomembrin B, a major polypeptide of chromaffin granule membranes. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2279–2287. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Pryde J. G., Sutton R. Characterization of detergent-solubilized adenosine triphosphatase of chromaffin granule membranes. Neuroscience. 1983 Jul;9(3):687–700. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Schatz G. An adenosine triphosphatase isolated from chromaffin-granulate membranes is closely similar to F1-adenosine triphosphatase of mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J., Helle K. B., Bock E. Immunochemically identical hydrophilic and amphiphilic forms of the bovine adrenomedullary dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):231–237. doi: 10.1042/bj1810231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cidon S., Ben-David H., Nelson N. ATP-driven proton fluxes across membranes of secretory organelles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11684–11688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., Bienz D., Zahno M. L., Lüscher E. F. Distribution of platelet glycoproteins and phosphoproteins in hydrophobic and hydrophilic phases in Triton X-114 phase partition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 19;778(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong L. T., Fleming P. J. The asymmetric orientation of cytochrome b561 in bovine chromaffin granule membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jan;228(1):332–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan R. W. Hydrophile-lipophile balance and critical micelle concentration as key factors influencing surfactant disruption of mitochondrial membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4442–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Frischenschlager I. Immunological characterization of secretory proteins of chromaffin granules: chromogranins A, chromogranins B, and enkephalin-containing peptides. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1854–1861. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Schachinger M., Zangerle R., Winkler H. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase and other glycoproteins from the soluble content and the membranes of adrenal chromaffin granules: isolation and carbohydrate analysis. J Neurochem. 1982 Mar;38(3):725–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Liang A. M., Sundstrom G. C. Selective disaggregation of the H+-translocating ATPase. Isolation of two discrete complexes of the rutamycin-insensitive ATPase differing in mitochondrial membrane-binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):707–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garewal H. S. A procedure for the estimation of microgram quantities of triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
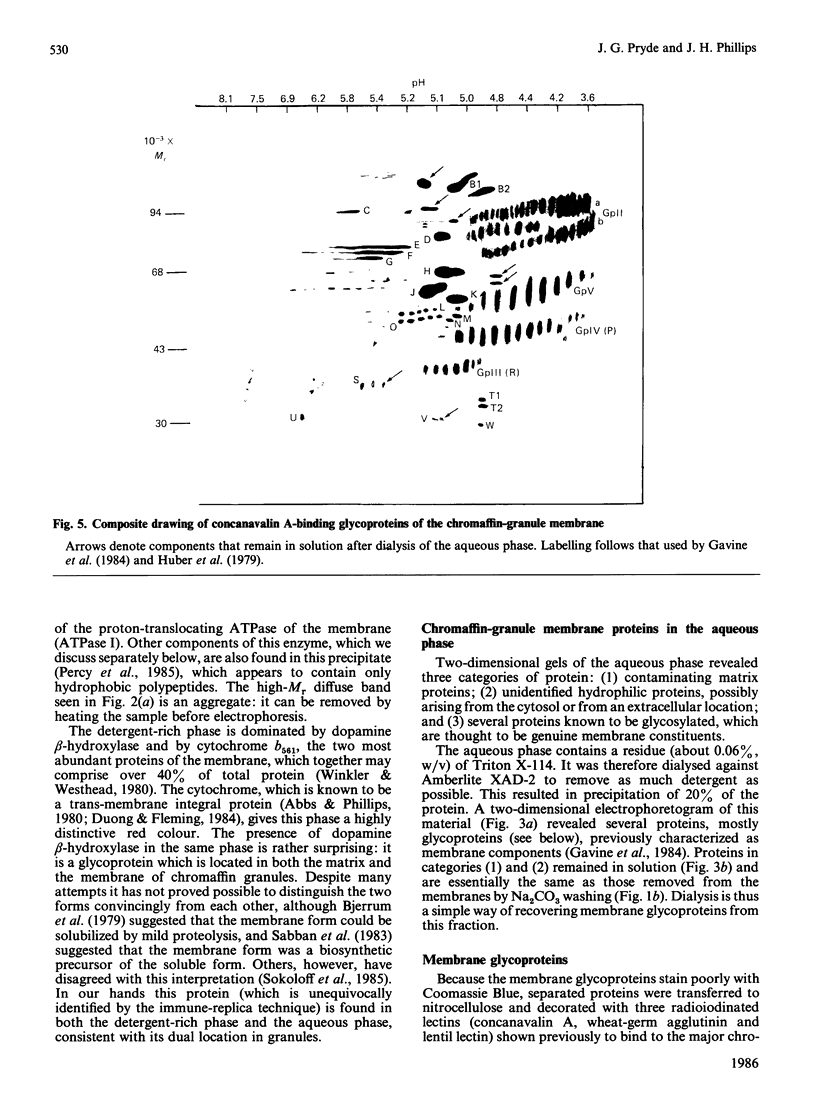
- Gavine F. S., Pryde J. G., Deane D. L., Apps D. K. Glycoproteins of the chromaffin granule membrane: separation by two-dimensional electrophoresis and identification by lectin binding. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1243–1252. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A. The transverse distribution of phospholipids in the membranes of Golgi subfractions of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):261–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2190261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houstek J., Pavelka S., Kopecký J., Drahota Z., Palmieri F. Is the mitochondrial dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-reactive protein of Mr 33 000 identical with the phosphate transport protein? FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80682-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Hepatic Golgi fractions resolved into membrane and content subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):822–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber E., König P., Schuler G., Aberer W., Plattner H., Winkler H. Characterization and topography of the glycoproteins of adrenal chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):35–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchel P. W., Campbell D. G., Barclay A. N., Williams A. F. Molecular weights of the Thy-1 glycoproteins from rat thymus and brain in the presence and absence of deoxycholate. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 1;169(2):411–417. doi: 10.1042/bj1690411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Singer S. J. Anomalous interaction of the acetylcholine receptor protein with the nonionic detergent Triton X-114. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pember S. O., Heyl B. L., Kinkade J. M., Jr, Lambeth J. D. Cytochrome b558 from (bovine) granulocytes. Partial purification from Triton X-114 extracts and properties of the isolated cytochrome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10590–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy J. M., Pryde J. G., Apps D. K. Isolation of ATPase I, the proton pump of chromaffin-granule membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):557–564. doi: 10.1042/bj2310557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E. L., Greene L. A., Goldstein M. Mechanism of biosynthesis of soluble and membrane-bound forms of dopamine beta-hydroxylase in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7812–7818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satre M., Bof M., Issartel J. P., Vignais P. V. Chemical modification of F1-ATPase by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide: application to analysis of the stoichiometry of subunits in Escherichia coli F1. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4772–4776. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
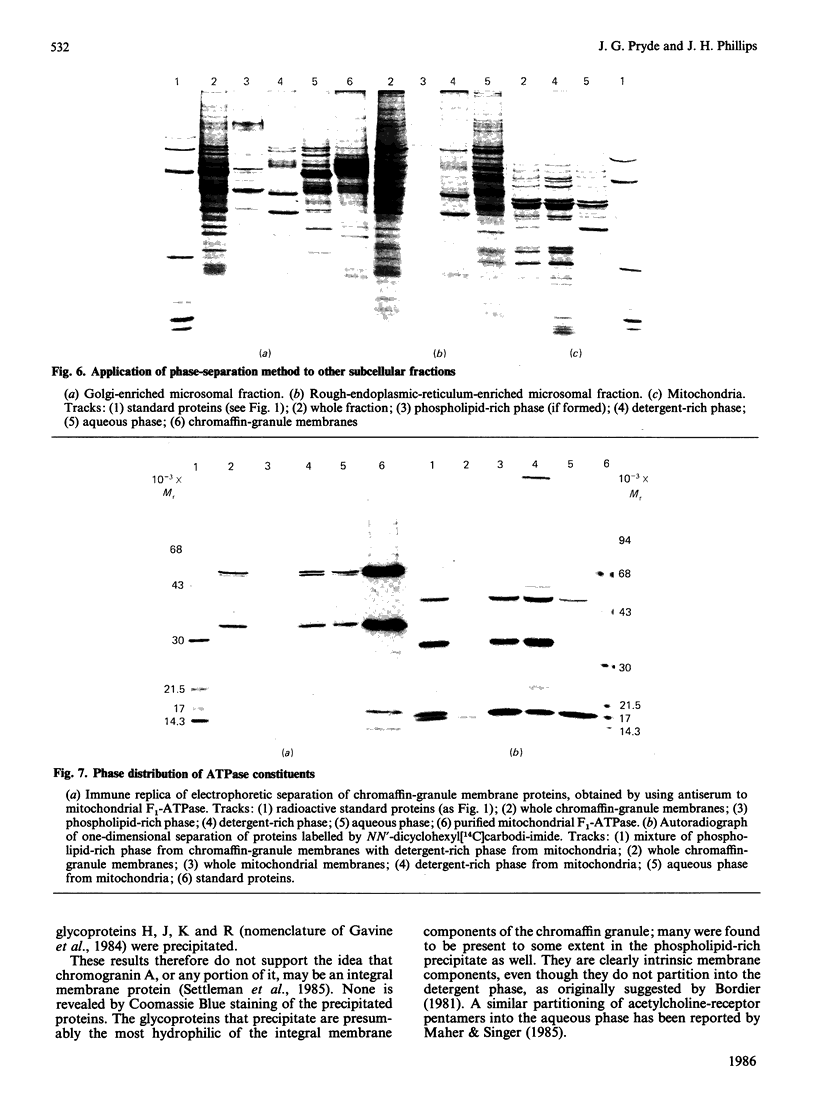
- Settleman J., Nolan J., Angeletti R. H. Chromogranin, an integral membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1641–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff R. L., Frigon R. P., O'Connor D. T. Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase: structural comparisons of membrane-bound versus soluble forms from adrenal medulla and pheochromocytoma. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):411–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Apps D. K. Isolation of a DCCD-binding protein from bovine chromaffin-granule membranes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80675-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Westhead E. The molecular organization of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1980;5(11):1803–1823. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]