Abstract
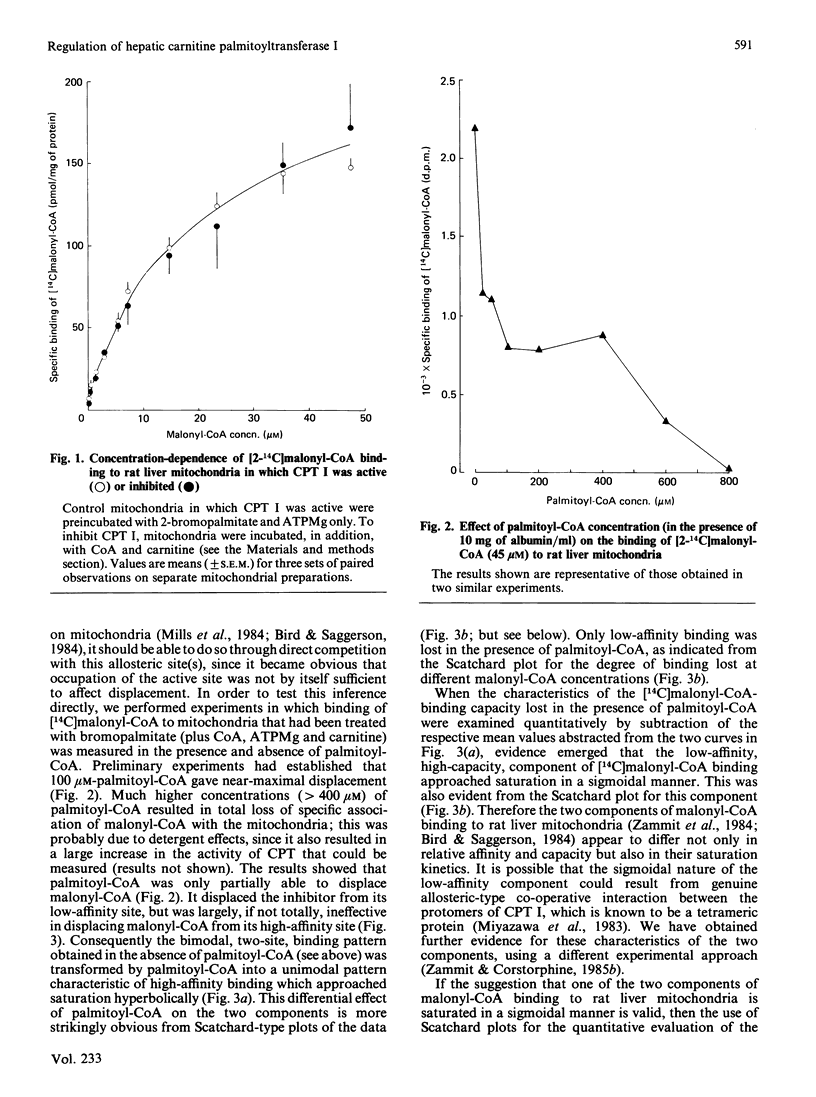
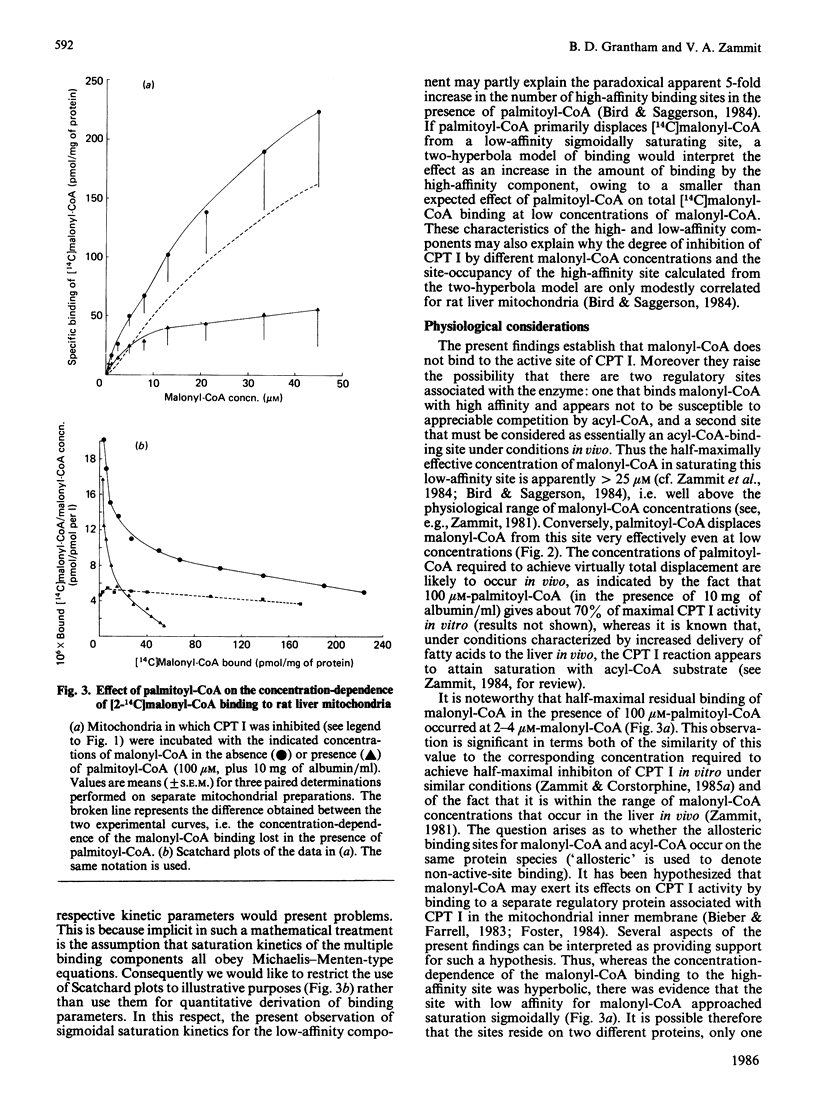
The active site of the overt activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT I) in rat liver mitochondria was blocked by the self-catalysed formation of the S-carboxypalmitoyl-CoA ester of (-)-carnitine, followed by washing of the mitochondria. CPT I activity in treated mitochondria was inhibited by 90-95%. Binding of [14C]malonyl-CoA to these mitochondria was not inhibited as compared with that of control mitochondria. When CPT I activity was inhibited, palmitoyl-CoA could markedly displace [14C]malonyl-CoA binding from the low-affinity site for the inhibitor [Zammit, Corstorphine & Gray (1984) Biochem. J. 222, 335-342], but not from the high-affinity site for malonyl-CoA binding. The saturation characteristics of the malonyl-CoA-binding component lost in the presence of palmitoyl-CoA were sigmoidal, and thus suggestive of co-operative binding at this site. It is suggested that the site hitherto considered to be a low-affinity malonyl-CoA-binding site may be effectively a second, allosteric, acyl-CoA-binding site on CPT I under conditions that prevail in vivo, whereas the high-affinity site for malonyl-CoA may be exclusive to the inhibitor. The possibility that the competitive-type interactions of malonyl-CoA and acyl-CoA on CPT I activity could arise from the effects of separate malonyl-CoA and acyl-CoA allosteric sites is considered. The possible significance of the large difference in the capacity of the two sites and their different saturation kinetics is also discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird M. I., Saggerson E. D. Binding of malonyl-CoA to isolated mitochondria. Evidence for high- and low-affinity sites in liver and heart and relationship to inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):639–647. doi: 10.1042/bj2220639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. F., Tubbs P. K. Conditions for the self-catalysed inactivation of carnitine acetyltransferase. A novel form of enzyme inhibition. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):225–235. doi: 10.1042/bj1110225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. F., Tubbs P. K. Specific inhibition of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation by 2-bromopalmitate and its coenzyme A and carnitine esters. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):55–65. doi: 10.1042/bj1290055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. A. Differences in the sensitivity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase to inhibition by malonyl-CoA are due to differences in Ki values. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12030–12033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fafournoux P., Rémésy C., Demigné C. Control by amino acids of the activity of system A-mediated amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):315–320. doi: 10.1042/bj2310315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiol C. J., Bieber L. L. Sigmoid kinetics of purified beef heart mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Effect of pH and malonyl-CoA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13084–13088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. W. Banting lecture 1984. From glycogen to ketones--and back. Diabetes. 1984 Dec;33(12):1188–1199. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.12.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Sauer F. Effect of -bromo-palmitate on the oxidation of palmitic acid by rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5862–5867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. E., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Effects of pH on the interaction of substrates and malonyl-CoA with mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):601–608. doi: 10.1042/bj2190601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. E., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Interaction of malonyl-CoA and related compounds with mitochondria from different rat tissues. Relationship between ligand binding and inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):83–91. doi: 10.1042/bj2140083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa S., Ozasa H., Osumi T., Hashimoto T. Purification and properties of carnitine octanoyltransferase and carnitine palmitoyltransferase from rat liver. J Biochem. 1983 Aug;94(2):529–542. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande S. V., Parvin R. Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase catalyzes an equilibrating unidirectional transport as well. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2994–3001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rial E., Nicholls D. G. The regulation of the proton conductance of brown fat mitochondria. Identification of functional and non-functional nucleotide-binding sites. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Carpenter C. A. Effects of fasting and malonyl CoA on the kinetics of carnitine palmitoyltransferase and carnitine octanoyltransferase in intact rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):166–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A., Corstorphine C. G. Altered release of carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity by digitonin from liver mitochondria of rats in different physiological states. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 1;230(2):389–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2300389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A., Corstorphine C. G., Gray S. R. Changes in the ability of malonyl-CoA to inhibit carnitine palmitoyltransferase I activity and to bind to rat liver mitochondria during incubation in vitro. Differences in binding at 0 degree C and 37 degrees C with a fixed concentration of malonyl-CoA. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):335–342. doi: 10.1042/bj2220335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. Regulation of hepatic fatty acid metabolism. The activities of mitochondrial and microsomal acyl-CoA:sn-glycerol 3-phosphate O-acyltransferase and the concentrations of malonyl-CoA, non-esterified and esterified carnitine, glycerol 3-phosphate, ketone bodies and long-chain acyl-CoA esters in livers of fed or starved pregnant, lactating and weaned rats. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):75–83. doi: 10.1042/bj1980075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. The effect of glucagon treatment and starvation of virgin and lactating rats on the rates of oxidation of octanoyl-L-carnitine and octanoate by isolated liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):293–300. doi: 10.1042/bj1900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. Time-dependence of inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I by malonyl-CoA in mitochondria isolated from livers of fed or starved rats. Evidence for transition of the enzyme between states of low and high affinity for malonyl-CoA. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):379–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2180379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


