Abstract
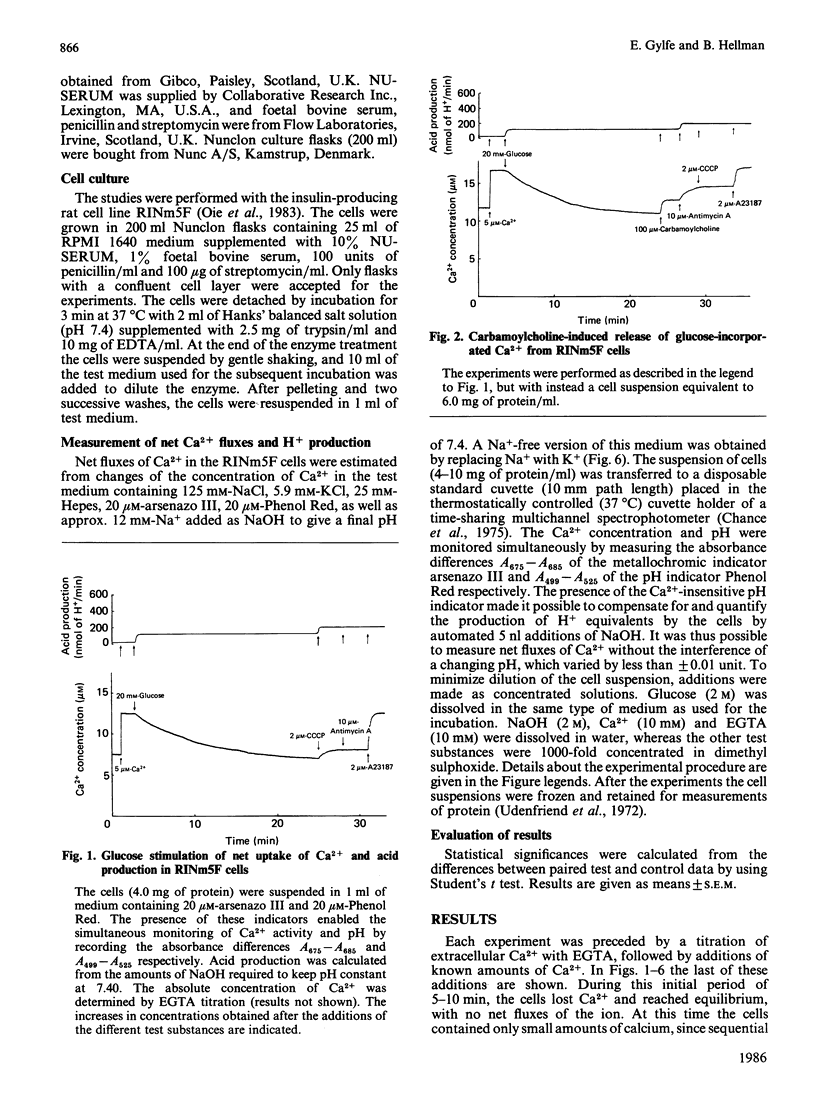
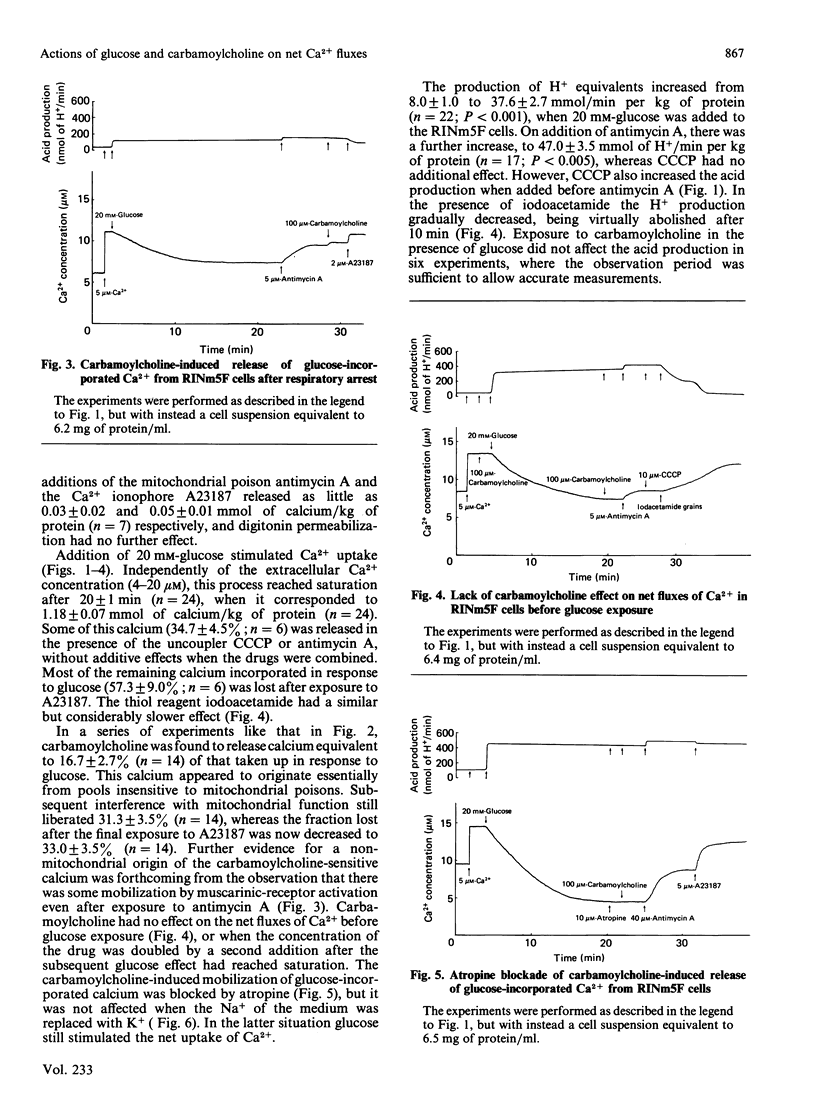
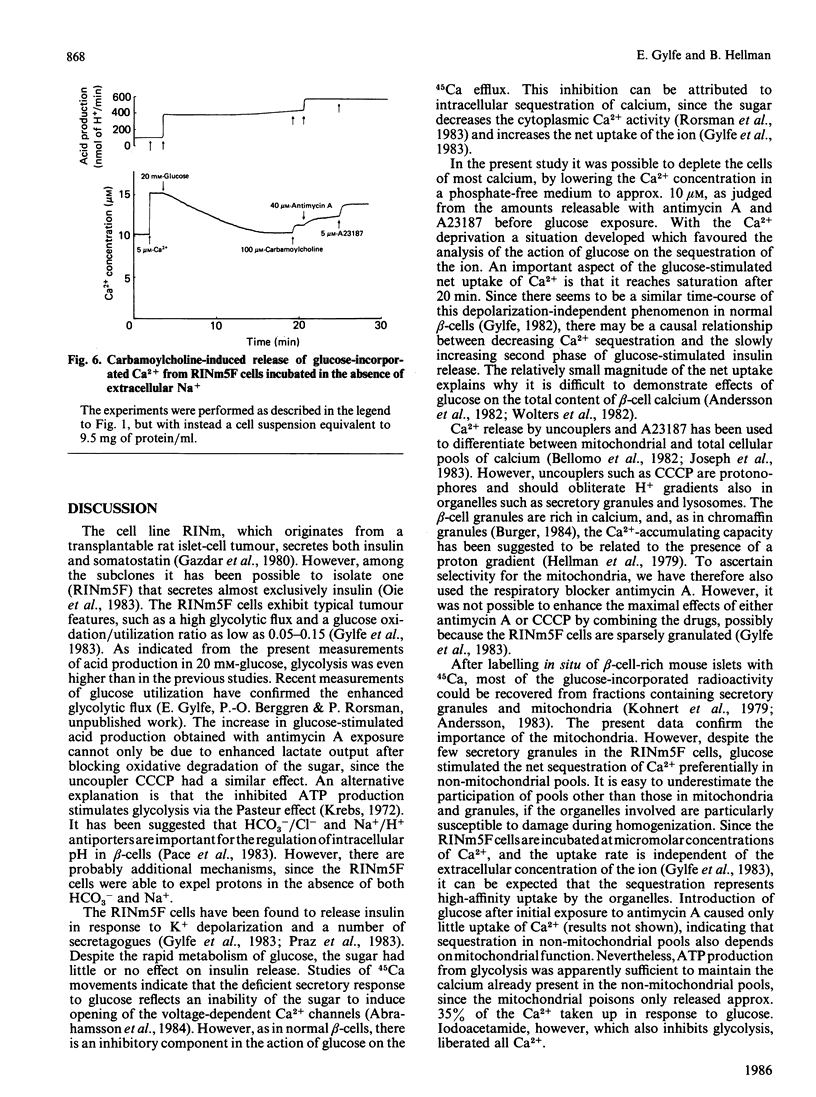
Net fluxes of Ca2+ and acid production were studied in clonal insulin-releasing cells (RINm5F) by using colour indicators and dual-wavelength spectrophotometry. After equilibration with a medium containing 10-20 microM-Ca2+, only minimal amounts of Ca2+ (0.08 mmol/kg of protein) were released from the cells by subsequent additions of the respiratory blocker antimycin A and the Ca2+ ionophore A23187. The presence of 20 mM-glucose resulted in an almost 5-fold increase of the acid production and in a stimulated net uptake of Ca2+. The latter process was independent of the extracellular Ca2+ concentration and reached saturation after 20 +/- 1 min, when it corresponded to 1.18 +/- 0.07 mmol of calcium/kg of protein. Whereas the thiol reagent iodoacetamide suppressed the acid production, interference with mitochondrial function by using antimycin A or the uncoupler carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone had the opposite effect. The latter two drugs induced a selective release of Ca2+ from a pool containing 35% of that taken up during glucose exposure. Most of the remaining Ca2+ was liberated by A23187 or iodoacetamide. Carbamoylcholine was also selective in mobilizing glucose-stimulated calcium, but this calcium (17%) appeared to originate from the pool insensitive to mitochondrial poisons. The action of carbamoylcholine was blocked by atropine and did not depend on the presence of extracellular Na+. The opposite effects of glucose and muscarinic-receptor activation on a non-mitochondrial calcium pool are consistent with participation of the endoplasmic reticulum in the glucose-induced sequestration of Ca2+ in pancreatic beta-cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsson H., Berggren P. O., Hellman B. Mobilization of 45Ca from insulin-producing RINm5F cells attached to microcarriers. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):E719–E725. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.6.E719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T., Berggren P. O., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Amounts and distribution of intracellular magnesium and calcium in pancreatic beta-cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Feb;114(2):235–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb06977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T. Glucose-induced retention of intracellular 45Ca in pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):C343–C347. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.5.C343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo G., Jewell S. A., Thor H., Orrenius S. Regulation of intracellular calcium compartmentation: studies with isolated hepatocytes and t-butyl hydroperoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6842–6846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L., Malaisse W. J. Nutrient and hormone-neurotransmitter stimuli induce hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1814–1820. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L., Malaisse W. J. Stimulation of phosphoinositide breakdown in rat pancreatic islets by glucose and carbamylcholine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 14;116(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90373-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Prentki M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ from permeabilized insulin-secreting cells. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2230467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Legallais V., Sorge J., Graham N. A versatile time-sharing multichannel spectrophotometer, reflectometer, and fluorometer. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jun;66(2):498–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90617-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements R. S., Jr, Rhoten W. B. Phosphoinositide metabolism and insulin secretion from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):684–691. doi: 10.1172/JCI108325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex G., Lernmark A. Effect of D-glucose on the incorporation of 32P into phospholipids of mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80505-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., El Younsi C., Dawson M. C. Inter-relations between the phospholipids of rat pancreatic islets during glucose stimulation, and their response to medium inositol and tetracaine. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagerman E., Idahl L. A., Meissner H. P., Täljedal I. B. Insulin release, cGMP, cAMP, and membrane potential in acetylcholine-stimulated islets. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):E493–E500. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.5.E493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gylfe E., Andersson T., Rorsman P., Abrahamsson H., Arkhammar P., Hellman P., Hellman B., Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F. Depolarization-independent net uptake of calcium into clonal insulin-releasing cells exposed to glucose. Biosci Rep. 1983 Oct;3(10):927–937. doi: 10.1007/BF01140662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gylfe E. Glucose stimulated net uptake of Ca2+ in the pancreatic beta-cell demonstrated with dual wavelength spectrophotometry. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Jan;114(1):149–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb06964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Coll K. E., Cooper R. H., Marks J. S., Williamson J. R. Mechanisms underlying calcium homeostasis in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):731–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Williams R. J., Corkey B. E., Matschinsky F. M., Williamson J. R. The effect of inositol trisphosphate on Ca2+ fluxes in insulin-secreting tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12952–12955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohnert K. D., Hahn H. J., Gylfe E., Borg H., Hellman B. Calcium and pancreatic beta-cell function. 6. Glucose and intracellular 45Ca distribution. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Dec;16(3):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A. The Pasteur effect and the relations between respiration and fermentation. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G. Identification and metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in isolated islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):101–106. doi: 10.1042/bj2160101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Morgan N. G., Rumford G. M., Prince C. A. Effect of glucose on polyphosphoinositide metabolism in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):483–489. doi: 10.1042/bj2270483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nenquin M., Awouters P., Mathot F., Henquin J. C. Distinct effects of acetylcholine and glucose on 45calcium and 86rubidium efflux from mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Weir G. C., Baylin S. B. Clonal analysis of insulin and somatostatin secretion and L-dopa decarboxylase expression by a rat islet cell tumor. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):1070–1075. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T., Smith J. S. Stimulus-secretion coupling in beta-cells: modulation by pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):E3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.1.E3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praz G. A., Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Strauss A. J., Renold A. E. Regulation of immunoreactive-insulin release from a rat cell line (RINm5F). Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):345–352. doi: 10.1042/bj2100345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Berggren P. O., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Reduction of the cytosolic calcium activity in clonal insulin-releasing cells exposed to glucose. Biosci Rep. 1983 Oct;3(10):939–946. doi: 10.1007/BF01140663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Siegel E. G., Sharp G. W. Dependency of acetylcholine-induced insulin release on Ca++ uptake by rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):924–929. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters G. H., Wiegman J. B., Konijnendijk W. The effect of glucose stimulation on 45calcium uptake of rat pancreatic islets and their total calcium content as measured by a fluorometric micro-method. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):122–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00254841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


