Abstract
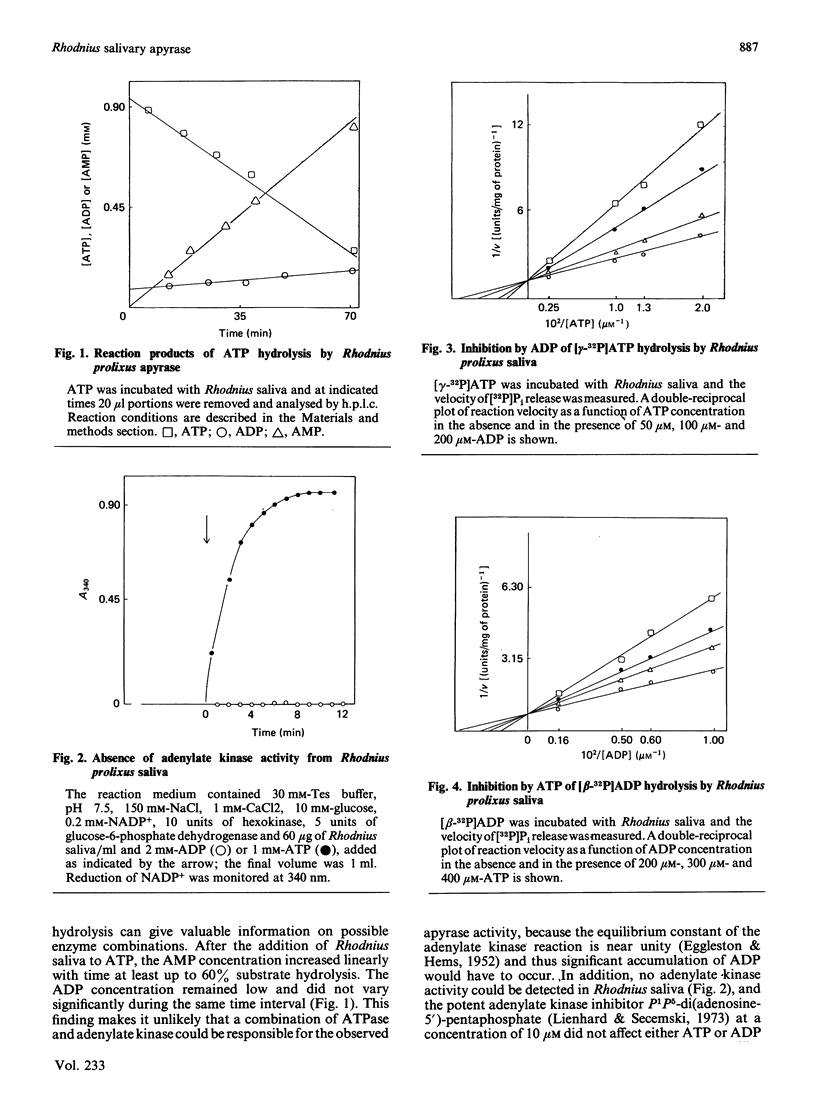
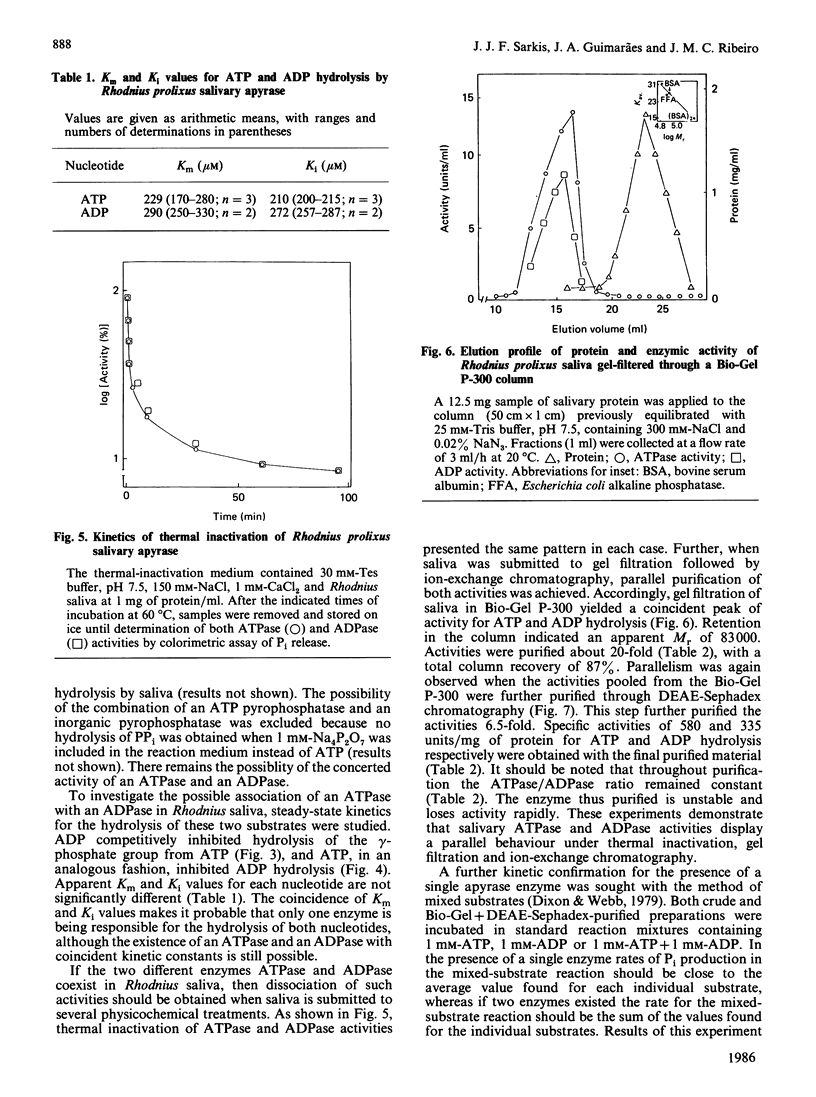
The salivary apyrase activity of the blood-sucking bug Rhodnius prolixus was found to reside in a true apyrase (ATP diphosphohydrolase, EC 3.6.1.5) enzyme. The crude saliva was devoid of 5'-nucleotidase, inorganic pyrophosphatase, phosphatase and adenylate kinase activities. ATP hydrolysis proceeded directly to AMP and Pi without significant accumulation of ADP. Km values for ATP and ADP hydrolysis were 229 and 291 microM respectively. Ki values for ATP and ADP inhibition of ADP and ATP hydrolysis were not different from the Km values, and these experiments indicated competitive inhibition. Activities were purified 126-fold by combined gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography procedures with a yield of 63%. The purified enzyme displayed specific activities of 580 and 335 mumol of Pi released/min per mg of protein for ATP and ADP hydrolysis respectively. The action of the purified enzyme on several phosphate esters indicates that Rhodnius apyrase is a non-specific nucleosidetriphosphate diphosphohydrolase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOCK R. M., LING N. S., MORELL S. A., LIPTON S. H. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of adenosine-5'-triphosphate and related 5'-ribonucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Jun;62(2):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meis L. Phosphorylation of the membranous protein of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Inhibition by Na + and K + . Biochemistry. 1972 Jun 20;11(13):2460–2465. doi: 10.1021/bi00763a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Moraes L. C., Jr, Haddad F., Wanderley E. C., Maciel D. R., Ribeiro J. I. Meningeoma intraventricular. Registro de um caso. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 1980 Sep;38(3):303–307. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x1980000300012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGLESTON L. V., HEMS R. Separation of adenosine phosphates by paper chromotography and the equilibrium constant of the myokinase system. Biochem J. 1952 Sep;52(1):156–160. doi: 10.1042/bj0520156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn J. M., Senior A. E. Evidence that Mg2+- or Ca2+-activated adenosine triphosphatase in rat pancreas is a plasma-membrane ecto-enzyme. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):59–68. doi: 10.1042/bj2140059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa T., Boyer P. D. Occurrence and characteristics of a rapid exchange of phosphate oxygens catalyzed by sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3163–3172. doi: 10.2172/4473783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A. F., Isler R. E., Reece J. F. The common occurrence of ATP diphosphohydrolase in mammalian plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 26;731(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laliberté J. F., St-Jean P., Beaudoin A. R. Kinetic effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on ATP hydrolysis by the purified ATP diphosphohydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3869–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel D., Poirier G. G., Phaneuf S., St-Jean P., Laliberté J. F., Beaudoin A. R. Characterization and purification of a calcium-sensitive ATP diphosphohydrolase from pig pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1227–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Secemski I. I. P 1 ,P 5 -Di(adenosine-5')pentaphosphate, a potent multisubstrate inhibitor of adenylate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):1121–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mant M. J., Parker K. R. Two platelet aggregation inhibitors in tsetse (Glossina) saliva with studies of roles of thrombin and citrate in in vitro platelet aggregation. Br J Haematol. 1981 Aug;48(4):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Wetzel R. Disulfide bond engineered into T4 lysozyme: stabilization of the protein toward thermal inactivation. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.6387910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Garcia E. S. Platelet antiaggregating activity in the salivary secretion of the blood sucking bug Rhodnius prolixus. Experientia. 1981 Apr 15;37(4):384–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01959876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Makoul G. T., Levine J., Robinson D. R., Spielman A. Antihemostatic, antiinflammatory, and immunosuppressive properties of the saliva of a tick, Ixodes dammini. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):332–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Rossignol P. A., Spielman A. Role of mosquito saliva in blood vessel location. J Exp Biol. 1984 Jan;108:1–7. doi: 10.1242/jeb.108.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Sarkis J. J., Rossignol P. A., Spielman A. Salivary apyrase of Aedes aegypti: characterization and secretory fate. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1984;79(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(84)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol P. A., Ribeiro J. M., Spielman A. Increased intradermal probing time in sporozoite-infected mosquitoes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):17–20. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E., Beyer T. A., Oppenheimer C. L., Paulson J. C., Prieels J. P., Rearick J. I., Hill R. L. Purification of mammalian glycosyltransferases. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:458–514. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAVERSO-CORI A., CHAIMOVICH H., CORI O. KINETIC STUDIES AND PROPERTIES OF POTATO APYRASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jan;109:173–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoli L., Marrè E. Purification and characterization of a divalent cation-activated ATP-ADPase from pea stem microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 20;642(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverso-Cori A., Traverso S., Reyes H. Different molecular forms of potato apyrase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Chignard M., Benveniste J. Present concepts on the mechanisms of platelet aggregation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Feb 15;30(4):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


