Abstract
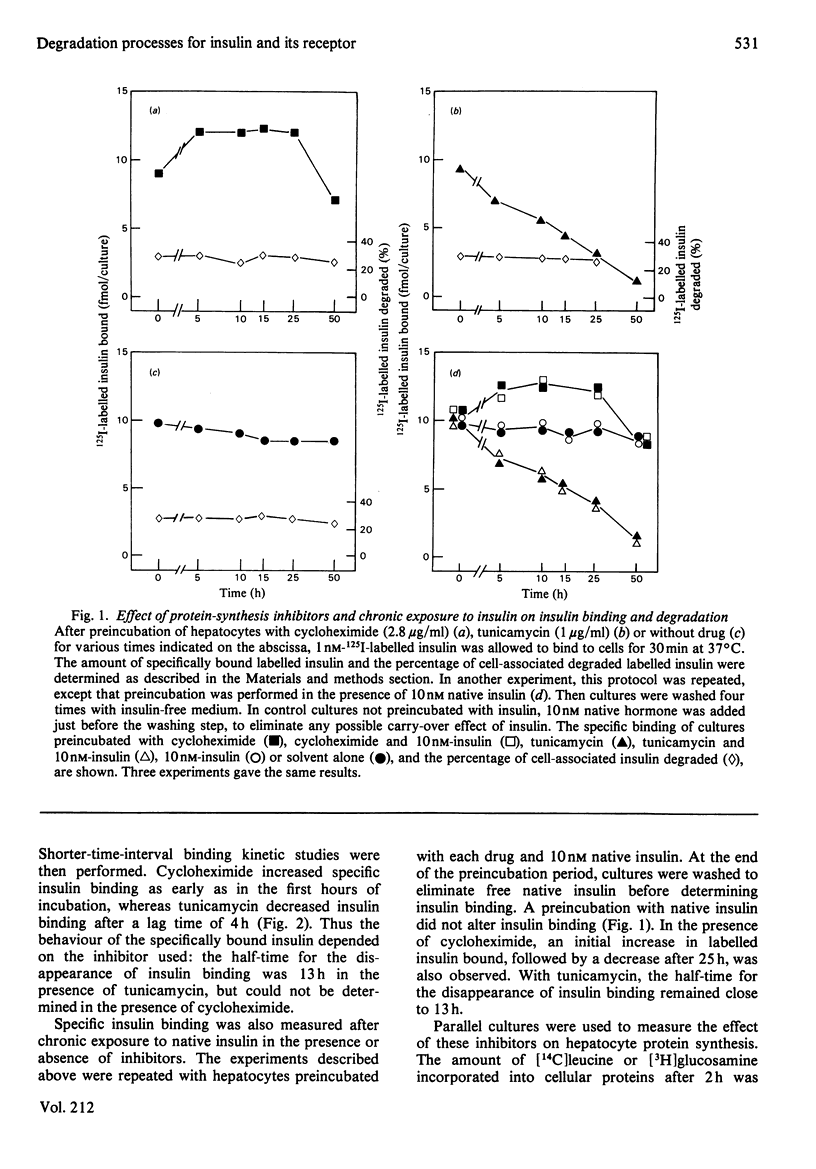
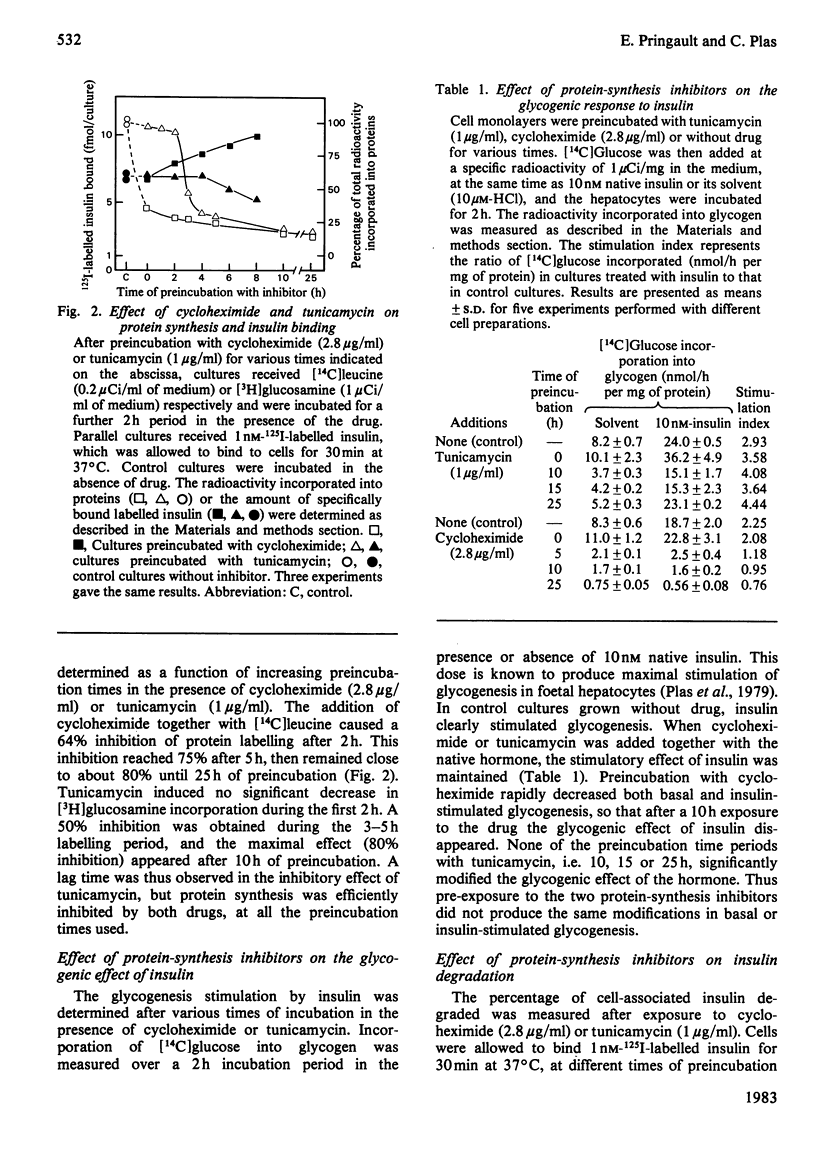
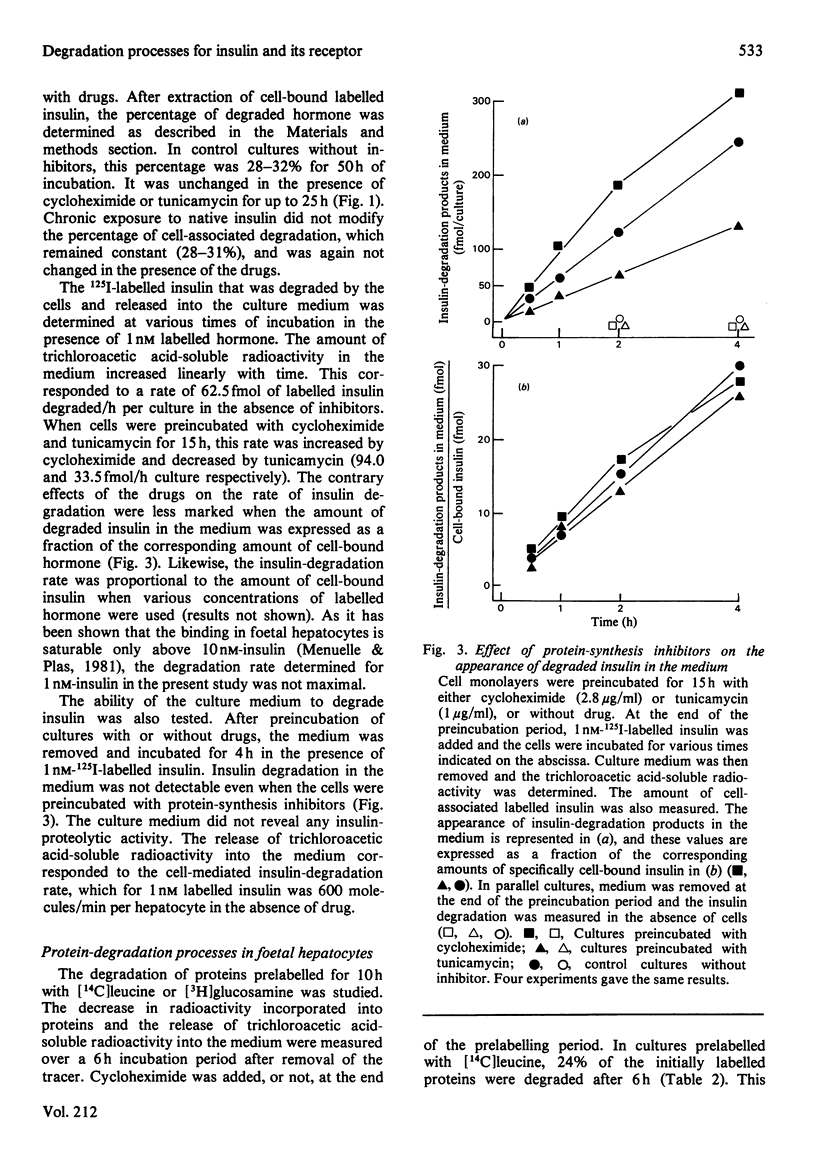
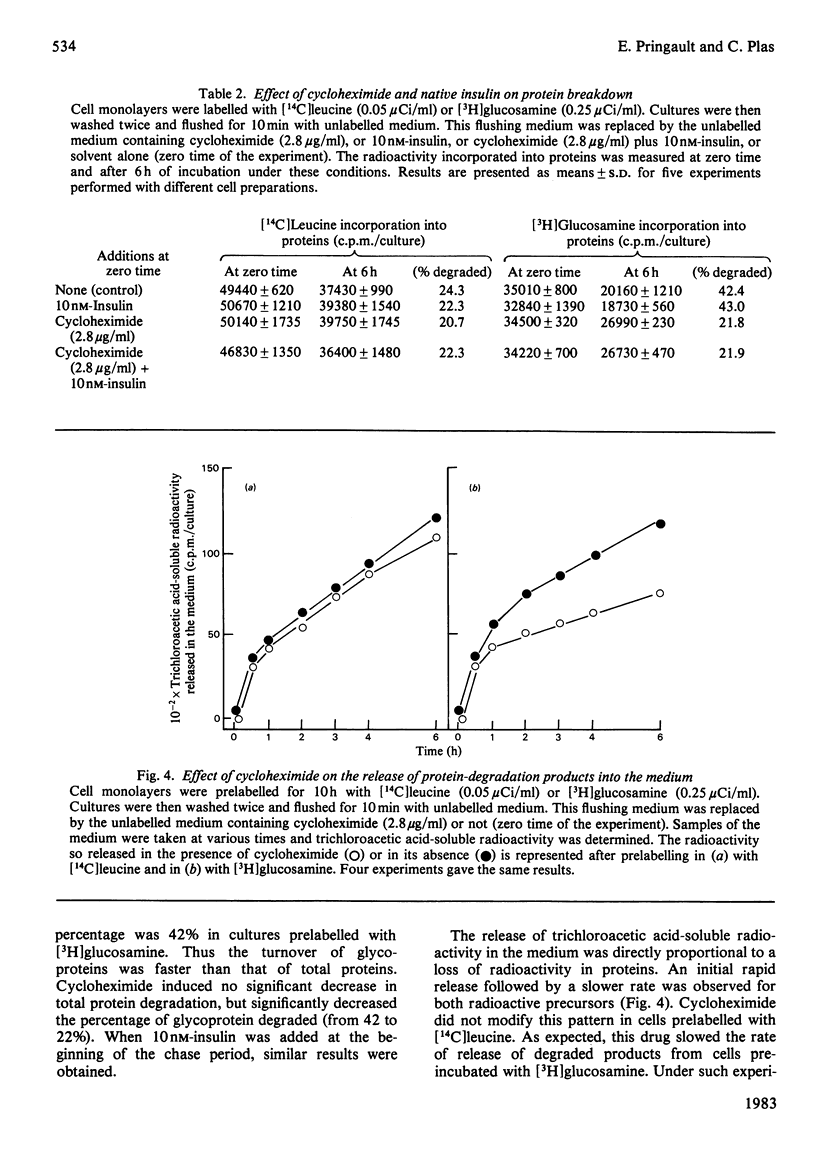
Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin were studied in cultured foetal hepatocytes after exposure to the protein-synthesis inhibitors tunicamycin and cycloheximide. Tunicamycin (1 microgram/ml) induced a steady decrease of insulin binding, which was decreased by 50% after 13 h. As the total number of binding sites per hepatocyte was 20000, the rate of the receptor degradation could not exceed 13 sites/min per hepatocyte. Cycloheximide (2.8 micrograms/ml) increased insulin binding by 30% within 6 h, an effect that persisted for up to 25 h. This drug had a specific inhibitory effect on the degradation of proteins prelabelled for 10 h with [14C]glucosamine, without affecting the degradation of total proteins. Chronic exposure to 10 nM-insulin neither decreased insulin binding nor modified the effect of the drugs. The absence of down-regulation of insulin receptors cannot be attributed to rapid receptor biosynthesis in foetal hepatocytes. Cellular insulin degradation, which is exclusively receptor-mediated, was determined by two different parameters. First, the rate of release of degraded insulin into the medium was 600 molecules/min per hepatocyte with 1 nM labelled hormone, and increased (preincubation with cycloheximide) or decreased (tunicamycin) as a function of the amount of cell-bound insulin. Secondly, the percentage of cell-bound insulin degraded was not changed by the presence of protein-synthesis inhibitors (25-30%). The stability of insulin degradation suggested that this process was dependent on long-life proteinase systems. Such differences in degradation rates and cycloheximide sensitivity imply that hormone- and receptor-degradation processes utilize distinct pathways.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge S., Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Hanson H. Metabolism of insulin and glucagon. Glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase from microsomes of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Sikstrom R., Hand A. R., Posner B. I. Binding and uptake of 125I-insulin into rat liver hepatocytes and endothelium. An in vivo radioautographic study. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):427–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Guzelian P. S., Small M. E. Down regulation of insulin receptors in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes in monolayer. Endocrinology. 1978 Aug;103(2):548–553. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-2-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Amatruda J. M. Functional relationships between insulin binding, action, and degradation. A reassessment. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10052–10055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Barazzone P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Intracellular localization of 125I-labeled insulin in hepatocytes from intact rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Lysosomal association of internalized 125I-insulin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Direct demonstration by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1249–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI109420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Krug F., Cuatrecasas P. Inhibitors of glucagon inactivation. Effect on glucagon--receptor interactions and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Lopez S., Burlet H. Ligand-induced translocation of insulin receptors in intact rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10852–10860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Willeput J., Huet de Froberville A. Receptor-mediated internalisation of insulin in intact rat liver. A biochemical study. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):338–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Stentz F. B., Heinemann M., Kitabchi A. E. Initial site of insulin cleavage by insulin protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):635–639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duksin D., Bornstein P. Changes in surface properties of normal and transformed cells caused by tunicamycin, an inhibitor of protein glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS V. J., BRYANT J. C., KERR H. A., SCHILLING E. L. CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIA FOR CULTIVATION OF LONG-TERM CELL STRAINS FROM FOUR MAMMALIAN SPECIES. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Dec;36:439–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Carpentier J. L., Le Cam A., Thamm P., Saunders D., Brandenburg D., Orci L., Freychet P. Biochemical and morphological evidence that the insulin receptor is internalized with insulin in hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):82–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D. Interaction of insulin, polypeptide hormones, and growth factors with intracellular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Livingston J. N. An evaluation of the importance of lysosomal and neutral cytosol proteases in insulin degradation by adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1981 Mar;108(3):953–961. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-3-953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P. O., Orci L. Internalization of polypeptide hormones: mechanism, intracellular localization and significance. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Direct demonstration of glycosylation of insulin receptor subunits by biosynthetic and external labeling: evidence for heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4791–4795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille M. B., Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T., Fell H. B. Microassay for cathepsin D shows an unexpected effedt of cycloheximide on limb-bone rudiments in organ culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):470–472. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Ji T. H., Miller B., Steiner D. F. Photoaffinity labeling of the insulin receptor in H4 hepatoma cells: lack of cellular receptor processing. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. The subunit structure of rat liver insulin receptor. Antibodies directed against the insulin-binding subunit. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6937–6940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. Polypeptide-binding membrane receptors: analysis and classification. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):14–20. doi: 10.1126/science.6259730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Hedo J. A., Van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M. Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Peptide hormone-induced receptor mobility, aggregation, and internalization. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 9;305(2):77–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107093050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmakos F. C., Roth J. Insulin-induced loss of the insulin receptor in IM-9 lymphocytes. A biological process mediated through the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9860–9869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Lane M. D. Evidence for different pathways for the degradation of insulin and insulin receptor in the chick liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1372–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M., Lane M. D. On the mechanism of ligand-induced down-regulation of insulin receptor level in the liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1689–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Jeanrenaud B., Freychet P. Insulin binding and effects in isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):E348–E358. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.4.E348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menuelle P., Plas C. Relationship between insulin binding and glycogenesis in cultured fetal hepatocytes. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):647–653. doi: 10.1007/BF00257435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:239–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Bretscher M. S. Membrane recycling by coated vesicles. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:85–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Chapeville F., Jacquot R. Development of glycogen storage ability under cortisol control in primary cultures of rat fetal hepatocytes. Dev Biol. 1973 May;32(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Desbuquois B. Receptor-mediated insulin degradation and insulin-stimulated glycogenesis in cultured foetal hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):333–341. doi: 10.1042/bj2020333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Menuelle P., Moncany M. L., Fulchignoni-Lataud M. C. Time dependence of the glycogenic effect of insulin in cultured fetal hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):705–712. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Nunez J. Role of cortisol on the glycogenolytic effect of glucagon and on the glycogenic response to insulin in fetal hepatocyte culture. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1431–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Ronnett G. V., Lane M. D. Role of glycosylation and protein synthesis in insulin receptor metabolism by 3T3-L1 mouse adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2908–2912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Chia G. H., Fung C., Rubin C. S. Tunicamycin-mediated depletion of insulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Apr;99(1):37–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Retention and degradation of 125I-insulin by perfused livers from diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):885–896. doi: 10.1172/JCI108365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Nafz M. A., Chandler M. L. Interaction of insulin analogs, glucagon, growth hormone, vasopressin, oxytocin, and scrambled forms of ribonuclease and lysozyme with glytathione-insulin transhydrogenase (thiol: protein-disulfide oxidoreductase): dependence upon conformation. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2115–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


