Abstract
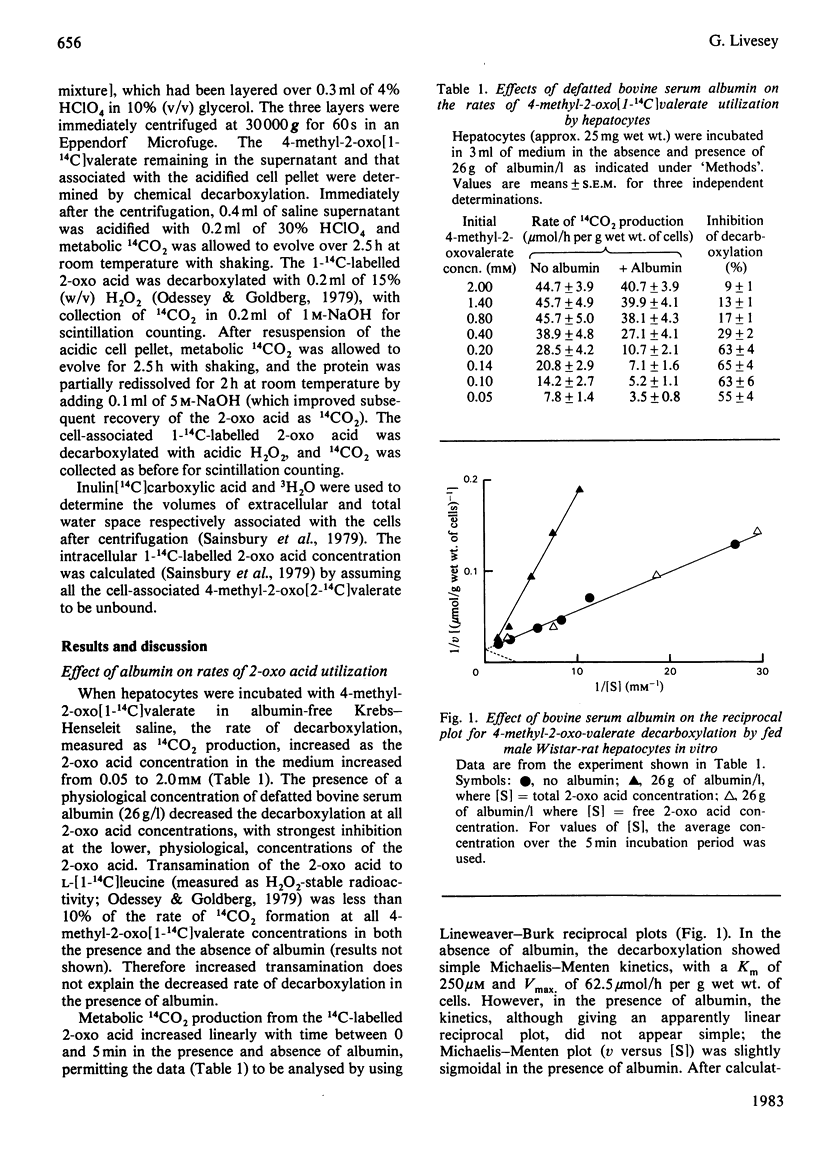
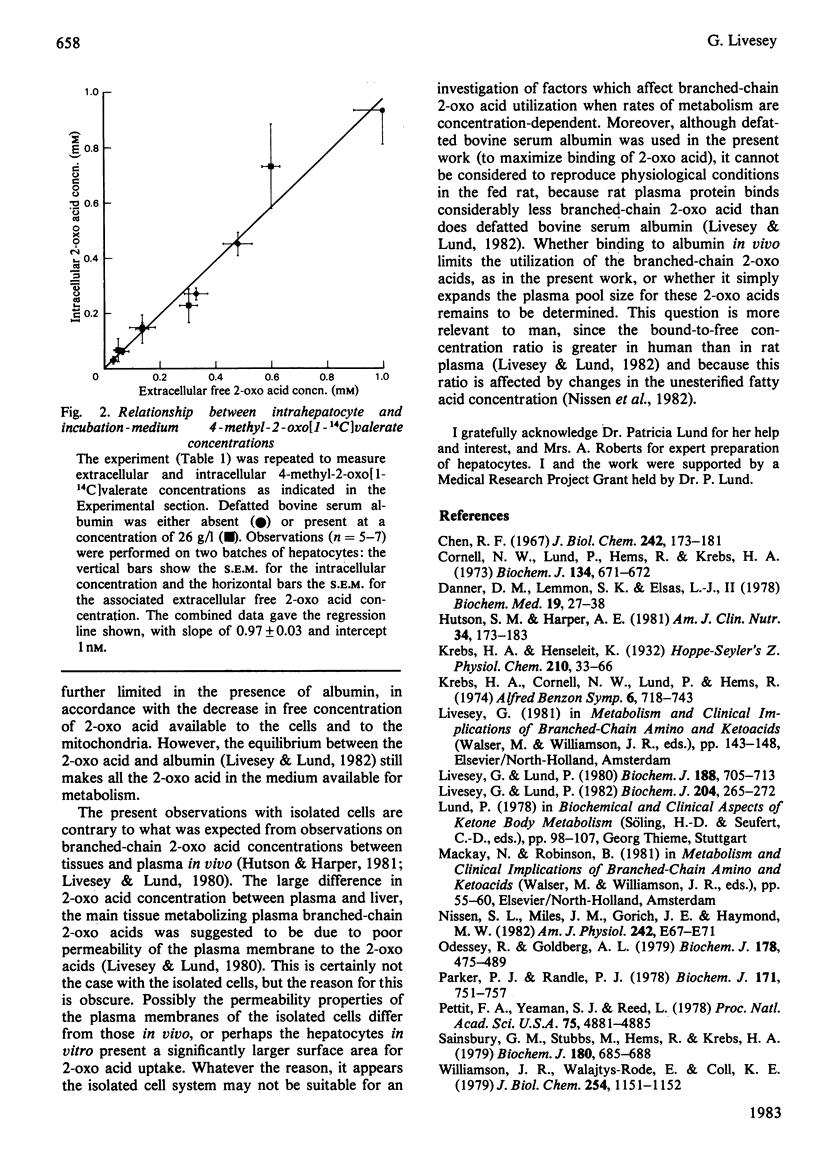
Binding of 4-methyl-2-oxo[1-14C]valerate to defatted bovine serum albumin inhibited the utilization of this 2-oxo acid by fed-rat hepatocytes in vitro. With 0-50g of albumin/l in the presence of 0.05mM 2-oxo acid or on increasing the 2-oxo acid concentration from 0 to 2mM in the presence of 26g of albumin/l, the extent of inhibition was essentially dependent on the change in the free 2-oxo acid concentration. Intrahepatocyte 4-methyl-2-oxo[1-14C]valerate concentrations were similar to extracellular free 2-oxo acid concentrations, suggesting equilibration so that the plasma membrane appears not to be rate-limiting for the utilization of this substrate by the isolated liver cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basner R., Kresse H., von Figura K. N-Acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase from human urine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W., Lund P., Hems R., Krebs H. A. Acceleration of gluconeogenesis from lactate by lysine (Short Communication). Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):671–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1340671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. J., Lemmon S. K., Elsas L. J., 2nd Substrate specificity and stabilization by thiamine pyrophosphate of rat liver branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase. Biochem Med. 1978 Feb;19(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(78)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson S. M., Harper A. E. Blood and tissue branched-chain amino and alpha-keto acid concentrations: effect of diet, starvation, and disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Feb;34(2):173–183. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livesey G., Lund P. Binding of branched-chain 2-oxo acids to bovine serum albumin. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):265–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2040265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livesey G., Lund P. Enzymic determination of branched-chain amino acids and 2-oxoacids in rat tissues. Transfer of 2-oxoacids from skeletal muscle to liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):705–713. doi: 10.1042/bj1880705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen S. L., Miles J. M., Gerich J. E., Haymond M. W. Regulation of alpha-ketoisocaproate binding to albumin in vivo by free fatty acids. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):E67–E71. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.1.E67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odessey R., Goldberg A. L. Leucine degradation in cell-free extracts of skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):475–489. doi: 10.1042/bj1780475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Randle P. J. Partial purification and properties of branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase of ox liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):751–757. doi: 10.1042/bj1710751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Yeaman S. J., Reed L. J. Purification and characterization of branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex of bovine kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4881–4885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury G. M., Stubbs M., Hems R., Krebs H. A. Loss of cell constituents from hepatocytes on centrifugation. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):685–688. doi: 10.1042/bj1800685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


