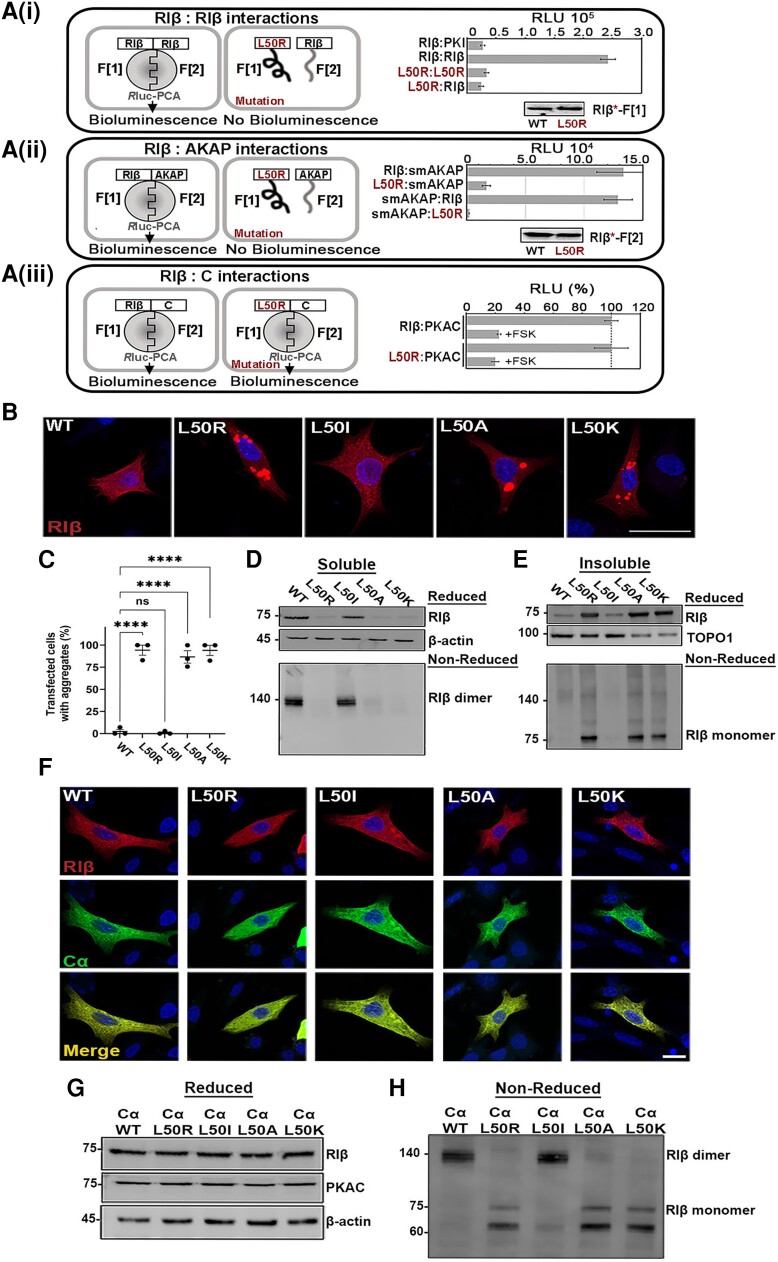
Figure 3.
The RIβ-L50R mutant protein disrupts RIβ:RIβ homo-dimerization, leading to protein aggregation in dissociated cells, but the formation of RIβ:C heterodimers protects against protein aggregation. [A(i)] Schematic illustration of the Renilla luciferase (Rluc) protein-fragment complementation assay (PCA) biosensor strategy used to quantify protein-protein interactions of wild-type (WT) or L50R mutant RIβ hybrid proteins in human embryonic kidney (HEK)293 cells. The two RIβ monomers dimerize, as quantified by a bioluminescence readout, whereas the RIβ-L50R mutant in one or both protomers abolishes dimerization. PKI binding was used as a negative control. Immunoblot of the Rluc-F[1] fused to WT or mutant RIβ using a Rluc-F[1] specific antibodies confirms that the expression levels were the same. [A(ii)] Left: Schematic illustration of RIβ WT or the L50R mutant interacting with an A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) peptide in the Rluc PCA system. Right: The RIβ-L50R mutant disrupts binding to smAKAP. Swapping the tags of the Rluc F[1] or F[2] that were C-terminally fused to RIβ or smAKAP had no effect. Immunoblot confirms that the expression levels of the proteins were the same. The figures are representative of three independent experiments (±standard deviation, technical experiments). [A(iii)] Left: Schematic illustration of RIβ-WT or the L50R mutant with the catalytic subunit (PKAC) in the Rluc PCA. Right: The L50R mutation does not affect RIβ:PKAC complex formation or dissociation of the complex upon forskolin (FSK) treatment. (B) Confocal microscopy images of transiently transfected rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells expressing MKO2-tagged RIβ (WT or mutants). (C) The percentage of transfected cells that contains aggregates. Approximately 70–100 cells in total were counted for each transfection. Each dot represent an independent experiment. (D and E) Cell lysates of transiently transfected cells were divided into soluble (D) and insoluble (E) fractions, which were separated by sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) under reduced conditions (top) or non-reduced conditions (bottom). β-Actin was used as a loading control for the soluble fraction. TOPO1 was used as a loading control for insoluble fraction. (F) Confocal images of PC12 cells co-transfected to express mKO2-tagged RIβ-WT or RIβ-mutants and mCerulean-Ca. Scale bar: 10 µm. (G) Soluble proteins of PC12 cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-RIβ or -Ca antibodies. β-Actin was used as a housekeeping protein loading control for each transfection. (H) The same protein samples as in G were separated by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions and immunoblotted with anti-RIβ antibodies. The position of RIβ monomers and dimers are denoted.