Abstract
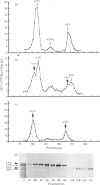
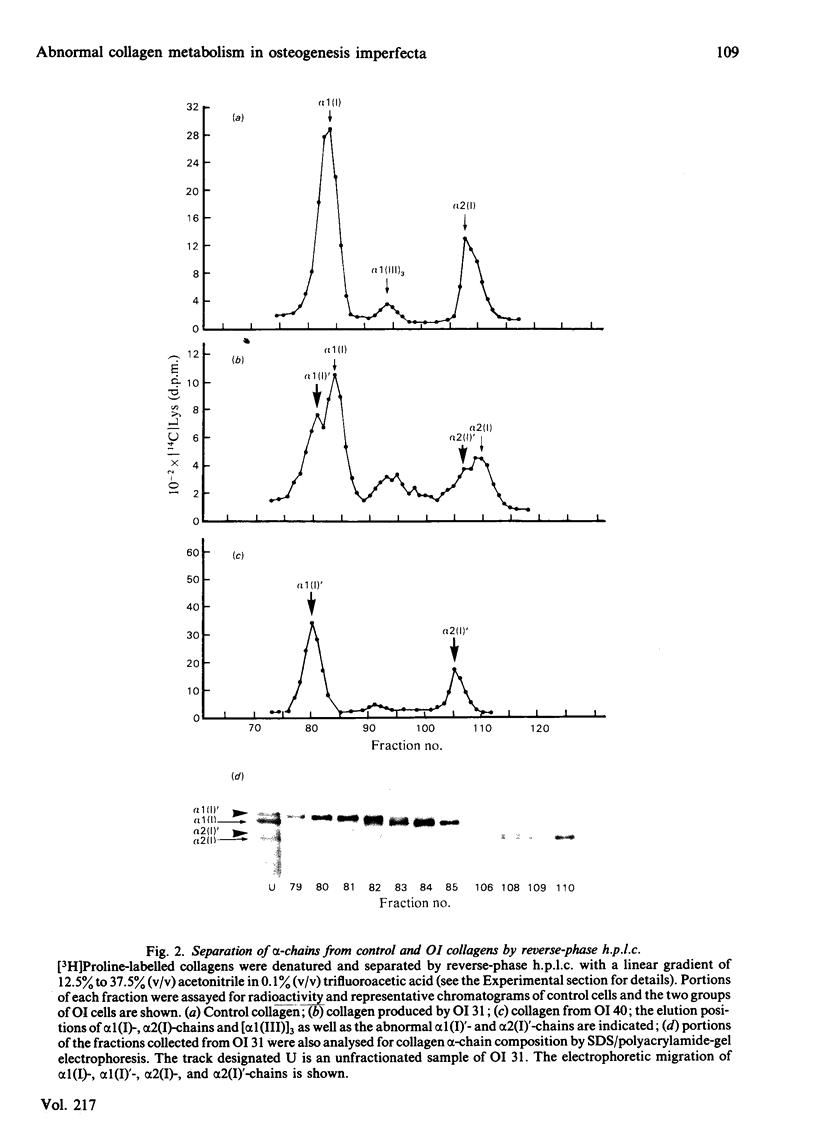
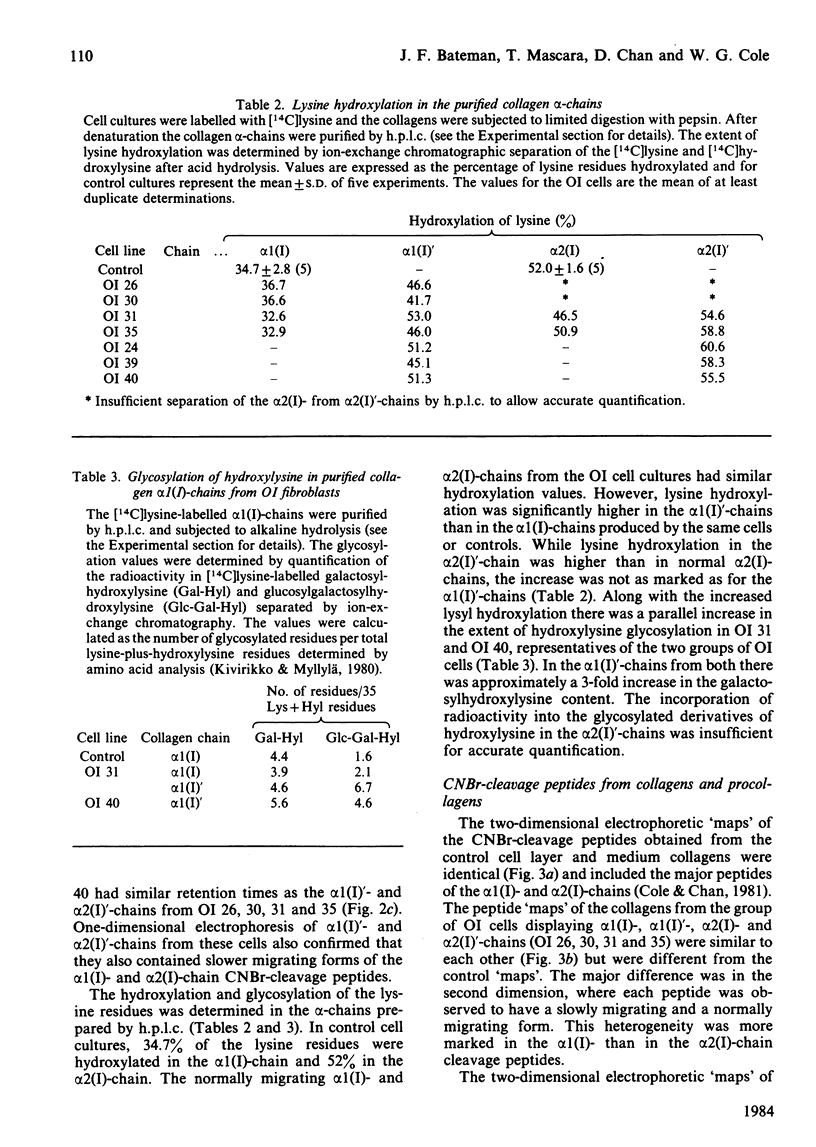
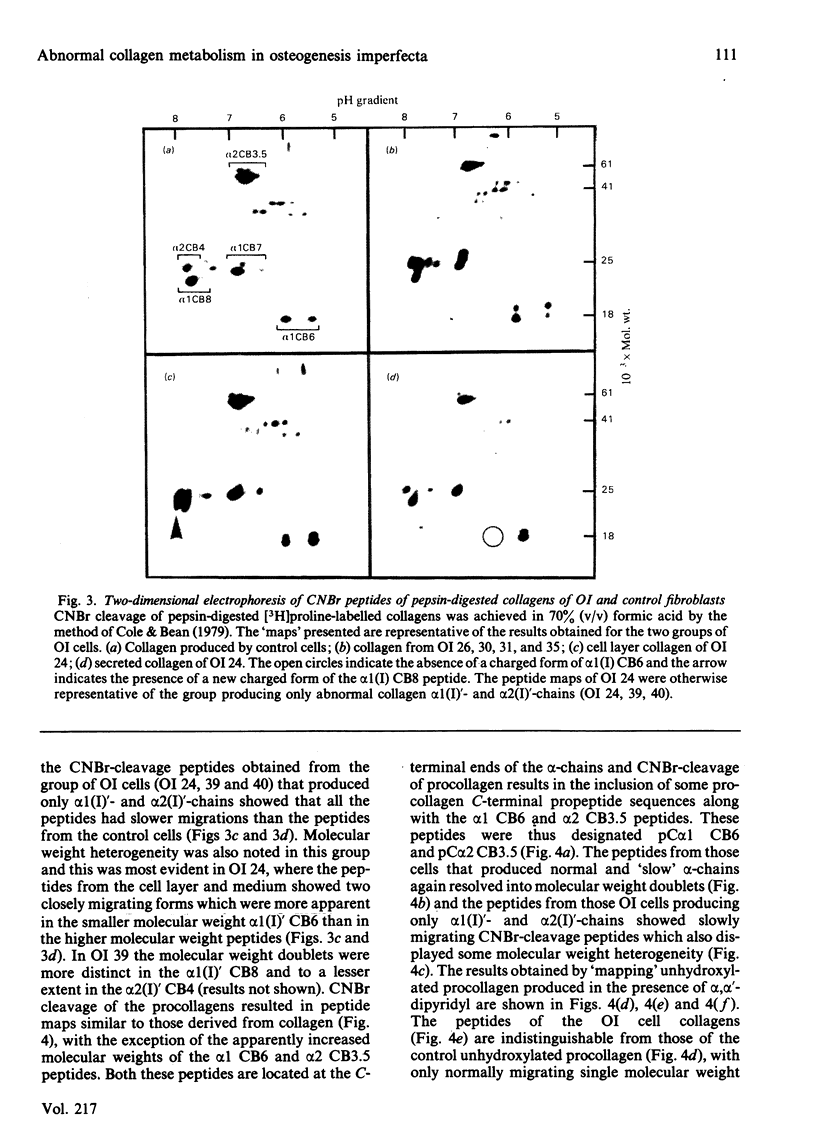
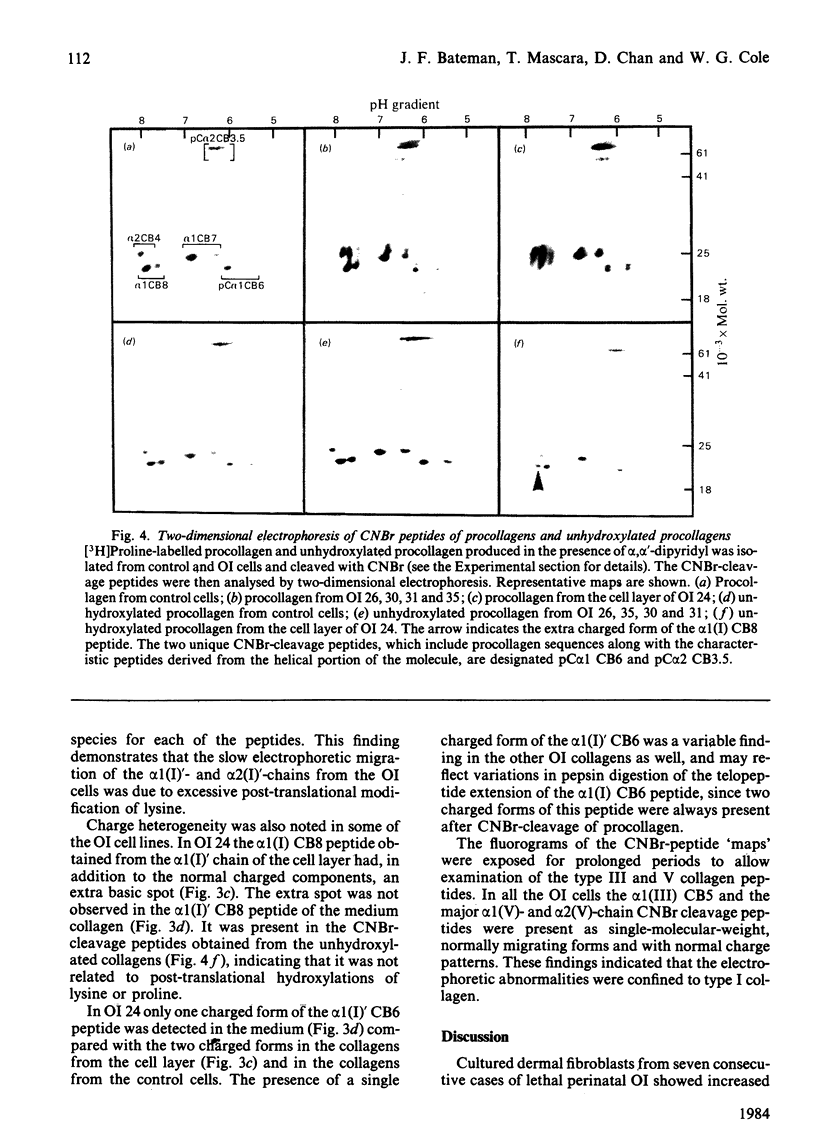
Cultured skin fibroblasts from seven consecutive cases of lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) expressed defects of type I collagen metabolism. The secretion of [14C]proline-labelled collagen by the OI cells was specifically reduced (51-79% of control), and collagen degradation was increased to twice that of control cells in five cases and increased by approx. 30% in the other two cases. Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis revealed that four of the OI cell lines produced two forms of type I collagen consisting of both normally and slowly migrating forms of the alpha 1(I)- and alpha 2(I)-chains. In the other three OI cell lines only the 'slow' alpha (I)'- and alpha 2(I)'-chains were detected. In both groups inhibition of the post-translational modifications of proline and lysine resulted in the production of a single species of type I collagen with normal electrophoretic migration. Proline hydroxylation was normal, but the hydroxylysine contents of alpha 1(I)'- and alpha 2(I)'-chains purified by h.p.l.c. were greater than in control alpha-chains. The glucosylgalactosylhydroxylysine content was increased approx. 3-fold while the galactosylhydroxylysine content was only slightly increased in the alpha 1(I)'-chains relative to control alpha 1(I)-chains. Peptide mapping of the CNBr-cleavage peptides provided evidence that the increased post-translational modifications were distributed throughout the alpha 1(I)'- and alpha 2(I)'-chains. It is postulated that the greater modification of these chains was due to structural defects of the alpha-chains leading to delayed helix formation. The abnormal charge heterogeneity observed in the alpha 1 CB8 peptide of one patient may reflect such a structural defect in the type I collagen molecule.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., David K. E., Byers P. H. Type I osteogenesis imperfecta: a nonfunctional allele for pro alpha 1 (I) chains of type I procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3838–3842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Peterkofsky B. Mechanisms of Kirsten murine sarcoma virus transformation-induced changes in the collagen phenotype and synthetic rate of BALB 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6028–6032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum B. J., Moss J., Breul S. D., Berg R. A., Crystal R. G. Effect of cyclic AMP on the intracellular degradation of newly synthesized collagen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2843–2847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. A., Schwartz M. L., Crystal R. G. Regulation of the production of secretory proteins: intracellular degradation of newly synthesized "defective" collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4746–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski R. S., Engels C. J. Measurement of intracellular collagen degradation. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 15;116(2):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Barsh G. S., Holbrook K. A. Molecular pathology in inherited disorders of collagen metabolism. Hum Pathol. 1982 Feb;13(2):89–95. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Shapiro J. R., Rowe D. W., David K. E., Holbrook K. A. Abnormal alpha 2-chain in type I collagen from a patient with a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):689–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI110815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chojkier M., Bateman J., Phang J. M., Peterkofsky B. Formation of proline metabolites in chick embryo bone: interference with the measurement of free hydroxyproline by ion-exchange chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chojkier M., Peterkofsky B., Bateman J. New method for determining the extent of proline hydroxylation by measuring changes in the ratio of [4-3H]:[14C]proline in collagenase digests. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 1;108(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. G., Bean D. A. Analysis of collagen cyanogen bromide peptides using electrophoresis in continuous concave gradient polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90642-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. G., Chan D. Analysis of the heterogeneity of human collagens by two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):377–383. doi: 10.1042/bj1970377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., FREEMAN G. Plaque production by the polyoma virus. Virology. 1959 Jul;8(3):396–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z., Bauer E. A., Jeffrey J. J. Human skin collagenase. The role of serum alpha-globulins in the control of activity in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):248–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R. Concepts in collagen biochemistry: evidence that collagenopathies underlie osteogenesis imperfecta. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981 Sep;(159):97–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch E., Krieg T., Remberger K., Fendel H., Bruckner P., Müller P. K. Disorder of collagen metabolism in a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta (lethal type): increased degree of hydroxylation of lysine in collagen types I and III. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;11(1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb01763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myllylä R., Alitalo K., Vaheri A., Kivirikko K. I. Regulation of collagen post-translational modification in transformed human and chick-embryo cells. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 15;196(3):683–692. doi: 10.1042/bj1960683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A. C., Pope F. M., Schloon H. Biochemical heterogeneity of osteogenesis imperfecta: New variant. Lancet. 1979 Jun 2;1(8127):1193–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen A., Anttinen H., Kivirikko K. I. Effect of L-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid on glycosylations of collagen in chick-embryo tendon cells. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):639–645. doi: 10.1042/bj1600639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen A., Anttinen H., Kivirikko K. I. Further studies on the effect of the collagen triple-helix formation on the hydroxylation of lysine and the glycosylations of hydroxylysine in chick-embryo tendon and cartilage cells. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):357–362. doi: 10.1042/bj1660357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen L., Palotie A., Prockop D. J. A defect in the structure of type I procollagen in a patient who had osteogenesis imperfecta: excess mannose in the COOH-terminal propeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6179–6183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A. Abnormal collagen metabolism in cultured cells in osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):586–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell S. R., Fox R., Krane S. M. Human collagens: differences in glycosylated hydroxylysines in skin and bone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope F. M., Nicholls A. C., Eggleton C., Narcissi P., Hey E. N., Parkin J. M. Osteogenesis imperfecta (lethal) bones contain types III and V collagens. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jun;33(6):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.6.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. G., Veis A. The cyanogen bromide peptides of bovine soluble and insoluble collagens. I. Characterization of peptides from soluble type I collagen by sodium dodecylsulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Connect Tissue Res. 1976;4(2):107–116. doi: 10.3109/03008207609152206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Senn A., Danks D. M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):101–116. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Rao V. H., Gitzelmann R. Intracellular degradation of newly synthesized collagen is conformation-dependent. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 12;133(1):142–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80491-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Rubin D., Gross J. Osteogenesis imperfecta congenita: evidence for a generalized molecular disorder of collagen. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Fietzek P. P. A comprehensive approach to the study of collagen primary structure based on high-performance liquid chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(3):491–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]