Abstract
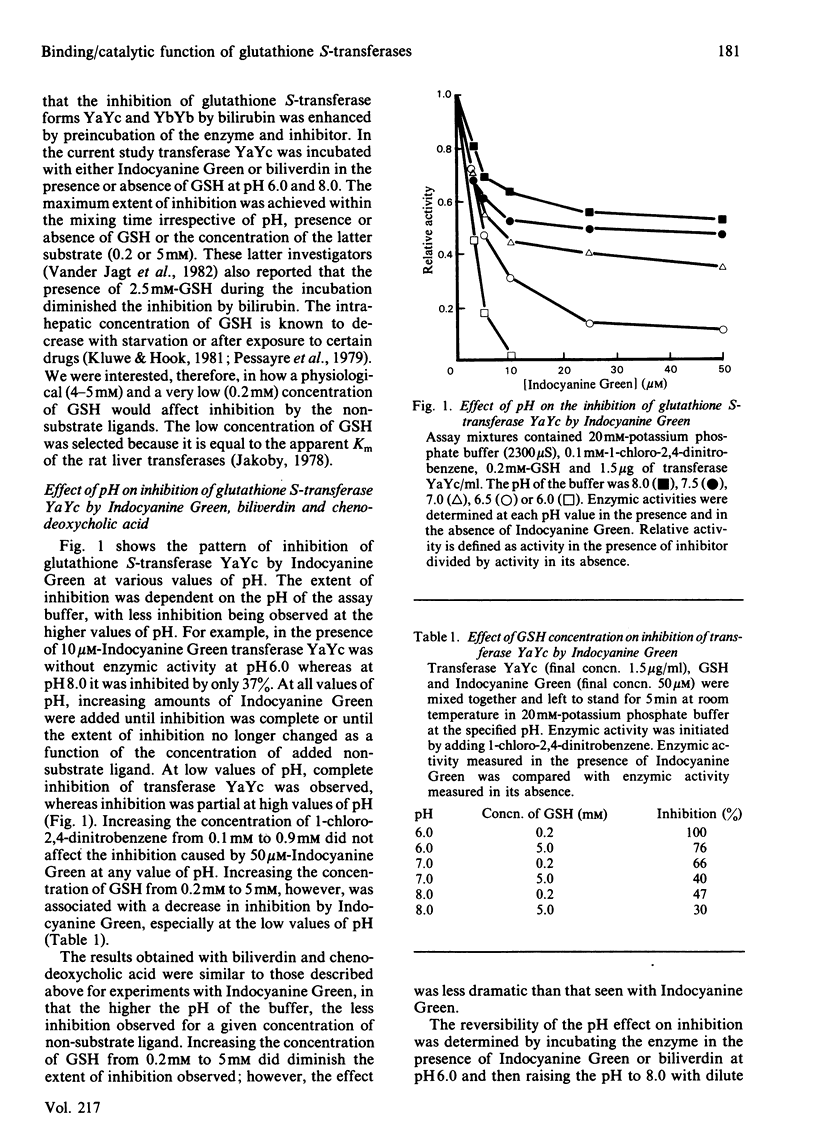
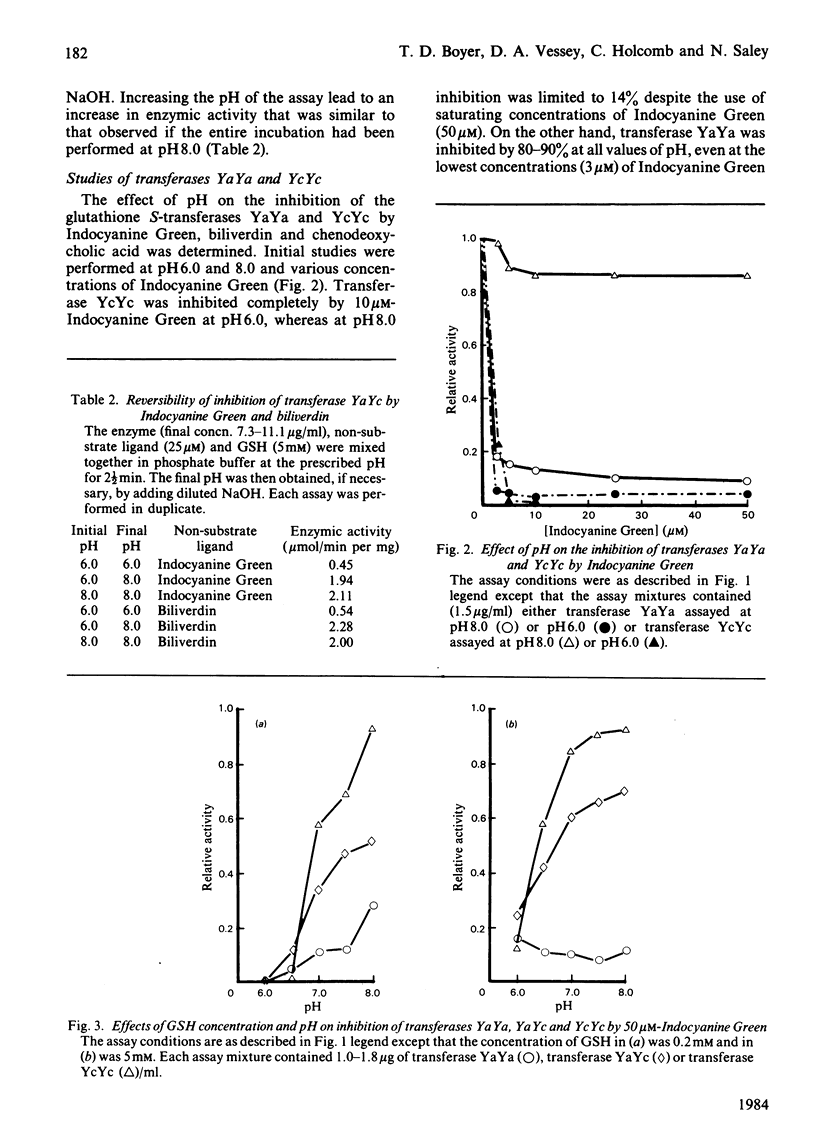
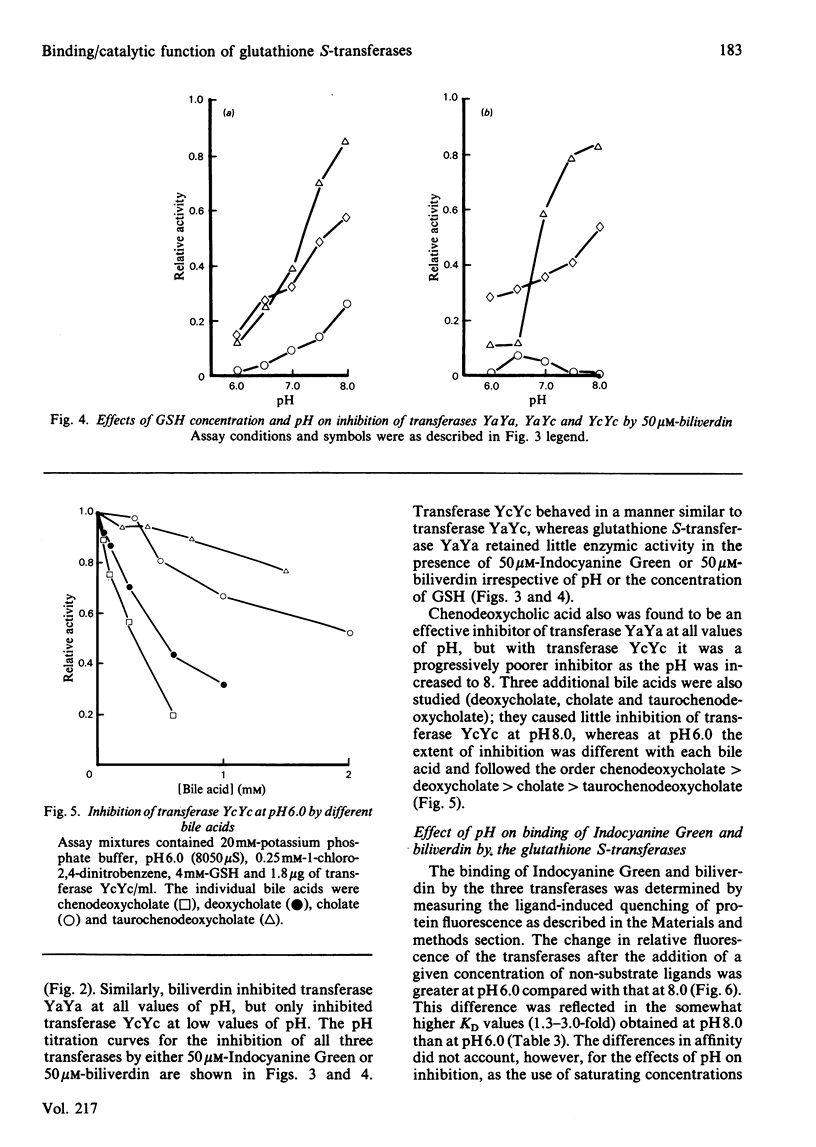
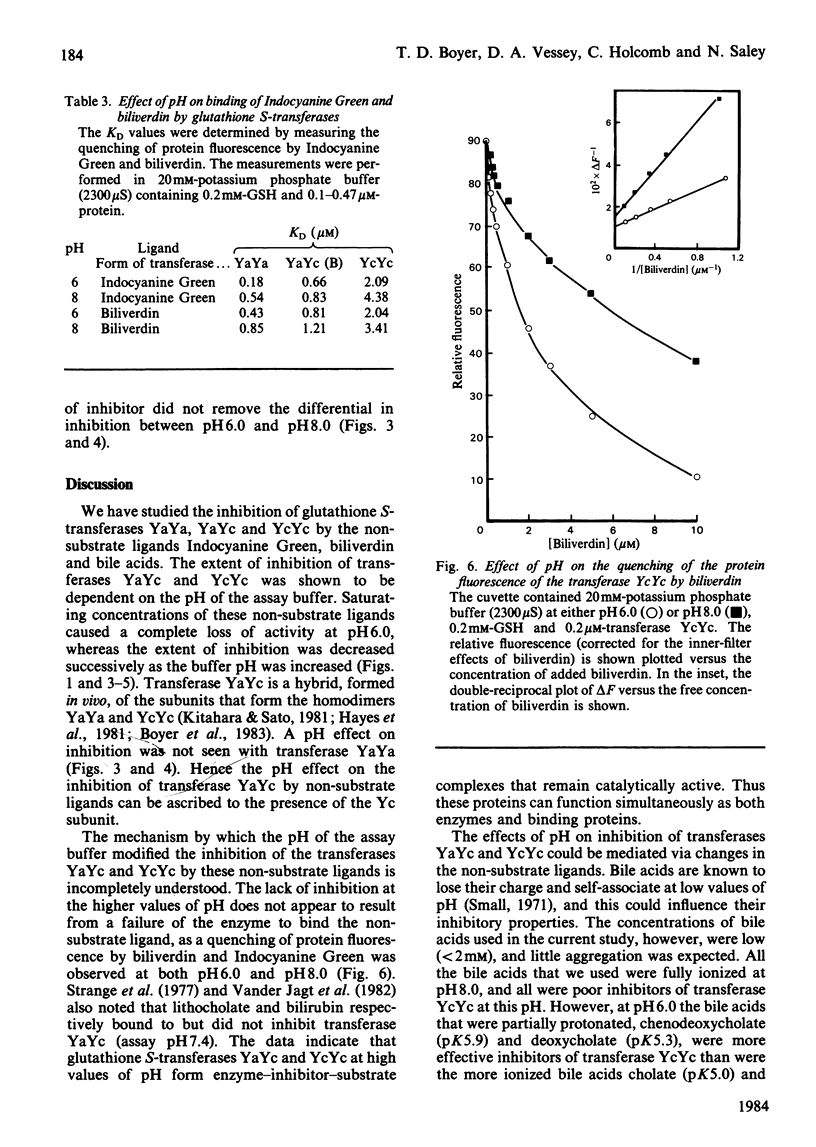
The dimeric enzyme glutathione S-transferase B is composed of two dissimilar subunits, referred to as Ya and Yc. Transferase B (YaYc) and two other transferases that are homodimers of the individual Ya and Yc subunits were purified from rat liver. Inhibition of these three enzymes by Indocyanine Green, biliverdin and several bile acids was investigated at different values of pH (range 6.0-8.0). Indocyanine Green, biliverdin and chenodeoxycholate were found to be effective inhibitors of transferases YaYc and YcYc at low (pH 6.0) but not high (pH 8.0) values of pH. Between these extremes of pH intermediate degrees of inhibition were observed. Cholate and taurochenodeoxycholate, however, were ineffective inhibitors of transferase YcYc at all values of pH. The observed differences in bile acids appeared to be due, in part, to differences in their state of ionization. In contrast with the above results, transferase YaYa was inhibited by at least 80% by the non-substrate ligands at all values of pH. These effects of pH on the three transferases could not be accounted for by pH-induced changes in the enzyme's affinity for the inhibitor. Thus those glutathione S-transferases that contain the Yc subunit are able to act simultaneously as both enzymes and binding proteins. In addition to enzyme structure, the state of ionization of the non-substrate ligands may also influence whether the transferases can perform both functions simultaneously.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arieff A. I., Park R., Leach W. J., Lazarowitz V. C. Pathophysiology of experimental lactic acidosis in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1980 Aug;239(2):F135–F142. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.2.F135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. M., Kirsch R. E., Tuff S. A., Marks I., Saunders S. J. Ligandin heterogeneity : evidence that the two non-identical subunits are the monomers of two distinct proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava M. M., Listowsky I., Arias I. M. Ligandin. Bilirubin binding and glutathione-S-transferase activity are independent processes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4112–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer T. D., Kenney W. C., Zakim D. Structural, functional and hybridization studies of the glutathione S-transferases of rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 15;32(12):1843–1850. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Strange R. C., Percy-Robb I. W. A study of the structures of the YaYa and YaYc glutathione S-transferases from rat liver cytosol. Evidence that the Ya monomer is responsible for lithocholate-binding activity. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):491–502. doi: 10.1042/bj1970491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Strange R. C., Percy-Robb I. W. Identification of two lithocholic acid-binding proteins. Separation of ligandin from glutathione S-transferase B. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):699–708. doi: 10.1042/bj1810699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagt D. L., Wilson S. P., Dean V. L., Simons P. C. Bilirubin binding to rat liver ligandins (glutathione S-transferases A and B). Relationship between bilirubin binding and transferase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1997–2001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby W. B. The glutathione S-transferases: a group of multifunctional detoxification proteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;46:383–414. doi: 10.1002/9780470122914.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N. Physiological significance of glutathione S-transferases. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):G439–G444. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.6.G439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketley J. N., Habig W. H., Jakoby W. B. Binding of nonsubstrate ligands to the glutathione S-transferases. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8670–8673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara A., Sato K. Immunological relationships among subunits of glutathione S-transferases A, AA, B and ligandin and hybrid formation between AA and ligandin by guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90901-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluwe W. M., Hook J. B. Potentiation of acute chloroform nephrotoxicity by the glutathione depletor diethyl maleate and protection by the microsomal enzyme inhibitor piperonyl butoxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;59(3):457–466. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsman M. L., Kwant G., Mook G. A., Zijlstra W. G. Light-absorbing properties, stability, and spectral stabilization of indocyanine green. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Apr;40(4):575–583. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Two hepatic cytoplasmic protein fractions, Y and Z, and their possible role in the hepatic uptake of bilirubin, sulfobromophthalein, and other anions. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2156–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI106182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack G., Ketterer B., Arias I. M. Ligandin: a hepatic protein which binds steroids, bilirubin, carcinogens and a number of exogenous organic anions. Nature. 1971 Dec 24;234(5330):466–467. doi: 10.1038/234466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. O., Edelman G. M. Fluorescent probes for conformational states of proteins. II. The binding of 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate to alpha-chymotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):559–566. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Palma L. A. Preparation and properties of crystalline biliverdin IX alpha. Simple methods for preparing isomerically homogeneous biliverdin and [14C[biliverdin by using 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyanobenzoquinone. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):193–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1890193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessayre D., Dolder A., Artigou J. Y., Wandscheer J. C., Descatoire V., Degott C., Benhamou J. P. Effect of fasting on metabolite-mediated hepatotoxicity in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):264–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange R. C., Cramb R., Hayes J. D., Percy-Robb I. W. Partial purification of two lithocholic acid-binding proteins from rat liver 100 000g supernatants. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):425–429. doi: 10.1042/bj1650425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessey D. A., Zakim D. Inhibition of glutathione S-transferase by bile acids. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):321–325. doi: 10.1042/bj1970321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W., Weisiger R. A., Jakoby W. B. The multiple roles of the glutathione transferases (ligandins). Prog Liver Dis. 1979;6:213–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


