Abstract
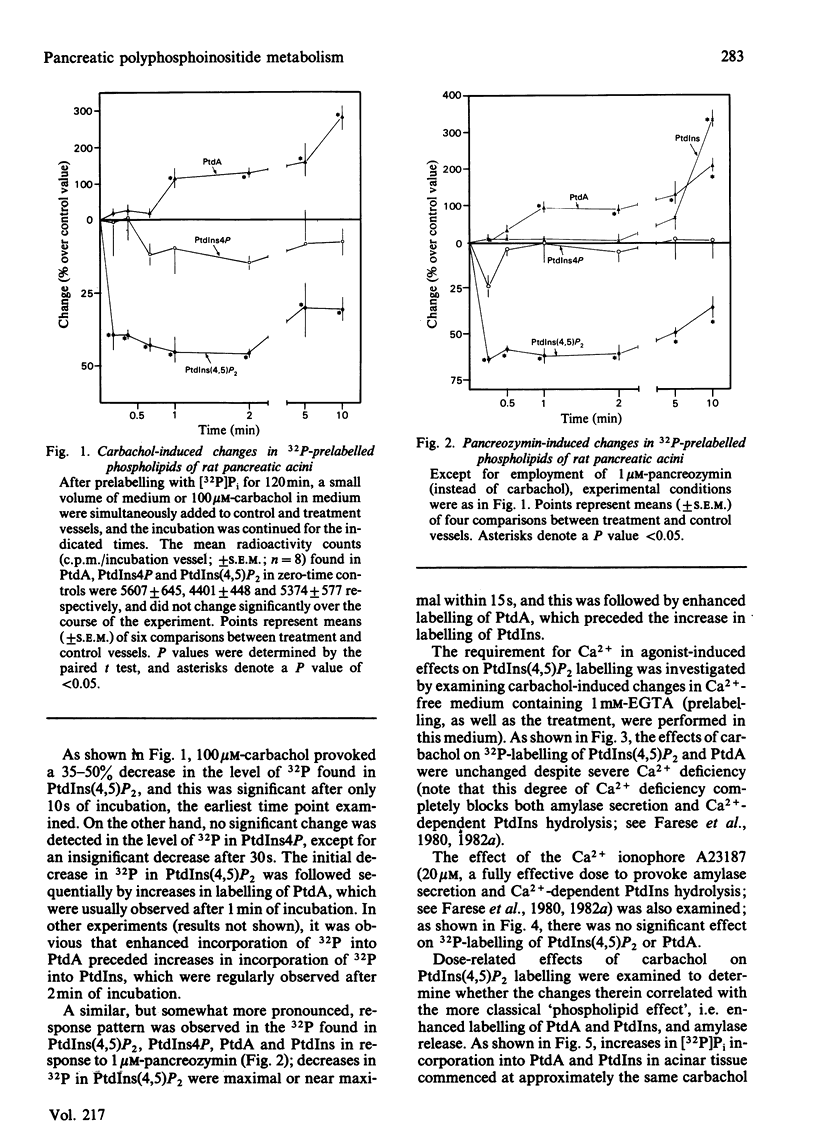
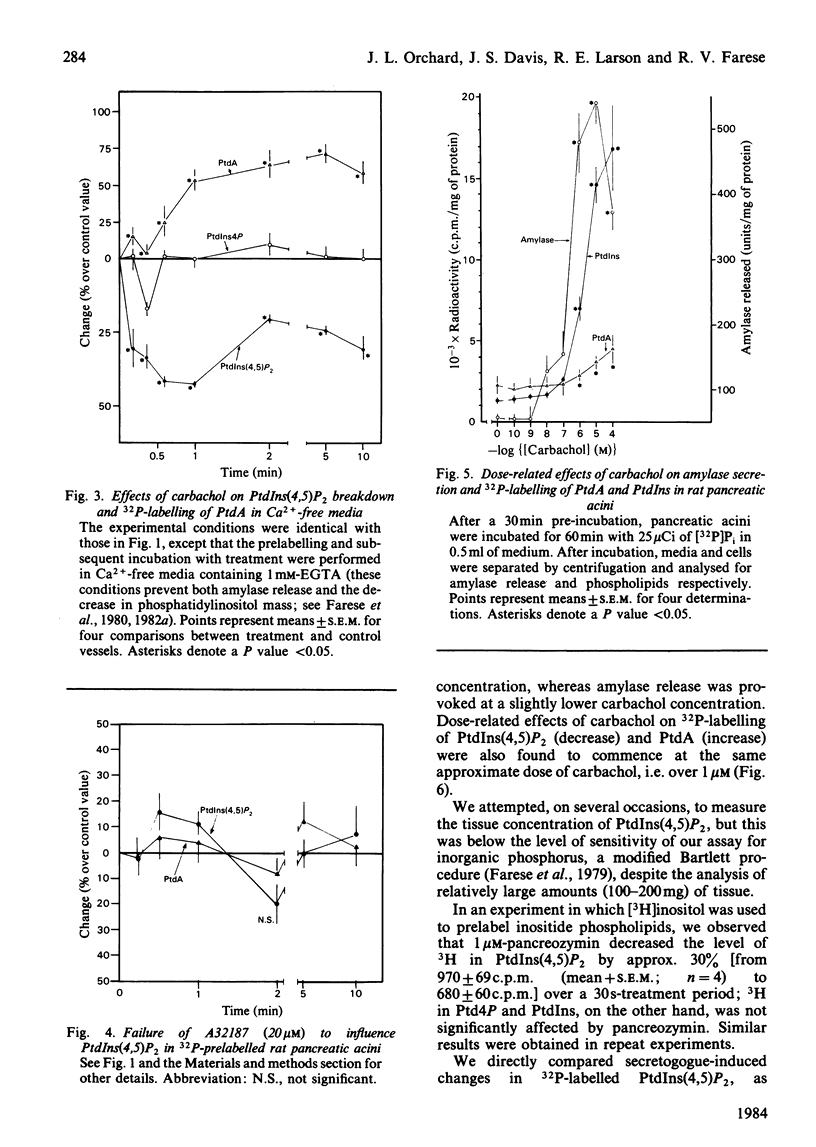
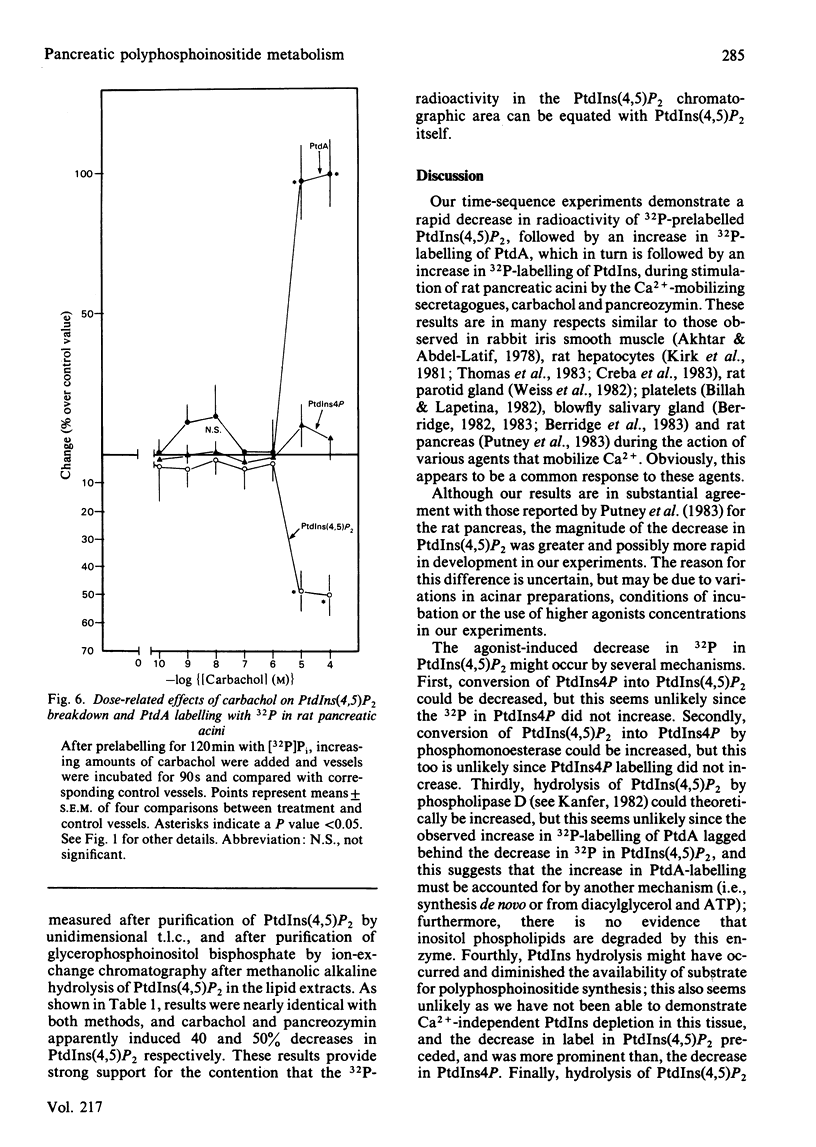
We studied the possibility that hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] may be the initiating event for the increase in [32P]Pi incorporation into phosphatidic acid (PtdA) and phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) during carbachol and pancreozymin (cholecystokinin-octapeptide) action in the rat pancreas. After prelabelling acini for 2h, [32P]Pi incorporation into PtdA, PtdIns(4,5)P2 and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) had reached equilibrium. Subsequent addition of carbachol or pancreozymin caused 32P in PtdIns(4,5)P2 to decrease by 30-50% within 10-15 s, and this was followed by sequential increases in [32P]Pi incorporation into PtdA and PtdIns. Similar changes in 32P-labelling of PtdIns4P were not consistently observed. Confirmation that the decrease in 32P in chromatographically-purified PtdIns(4,5)P2 reflected an actual decrease in this substance was provided by the fact that similar results were obtained (a) when PtdIns(4,5)P2 was prelabelled with [2-3H]inositol, and (b) when PtdIns(4,5)P2 was measured as its specific product (glycerophosphoinositol bisphosphate) after methanolic alkaline hydrolysis and ion-exchange chromatography. The secretogogue-induced breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 was not inhibited by Ca2+ deficiency (severe enough to inhibit amylase secretion and Ca2+-dependent hydrolysis of PtdIns), and ionophore A23187 treatment did not provoke PtdIns(4,5)P2 hydrolysis. The increase in the hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and the increase in [32P]Pi incorporation into PtdA commenced at the same concentration of carbachol in dose-response studies. Our findings suggest that the hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 is an early event in the action of pancreatic secretogogues that mobilize Ca2+, and it is possible that this hydrolysis may initiate the Ca2+-independent labelling of PtdA and PtdIns. Ca2+ mobilization may follow these responses, and subsequently cause Ca2+-dependent hydrolysis of PtdIns and exocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar R. A., Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium ion requirement for acetylcholine-stimulated breakdown of triphosphoinositide in rabbit iris smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Mar;204(3):655–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and calcium signalling in the blowfly salivary gland. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):385–397. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes P., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate: lipids in search of a function. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):467–502. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Sabir M. A. Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent effects of pancreatic secretagogues on phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 12;710(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Sabir M. A. Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent mechanisms for phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and 32P-labeling during cholinergic stimulation of the rat submaxillary gland in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Nov;219(1):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Sabir M. A. Effects of Ca2+ ionophore A23187 and Ca2+ deficiency on pancreatic phospholipids and amylase release in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 15;633(3):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Sabir A. M., Vandor S. L. Adrenocorticotropin acutely increases adrenal polyphosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6842–6844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. Enzyme secretion and the incorporation of P32 into phospholipides of pancreas slices. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):967–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Burgess G. M., Halenda S. P., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P. Effects of secretagogues on [32P]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism in the exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2120483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Receptor-mediated net breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):555–560. doi: 10.1042/bj2060555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


