Abstract
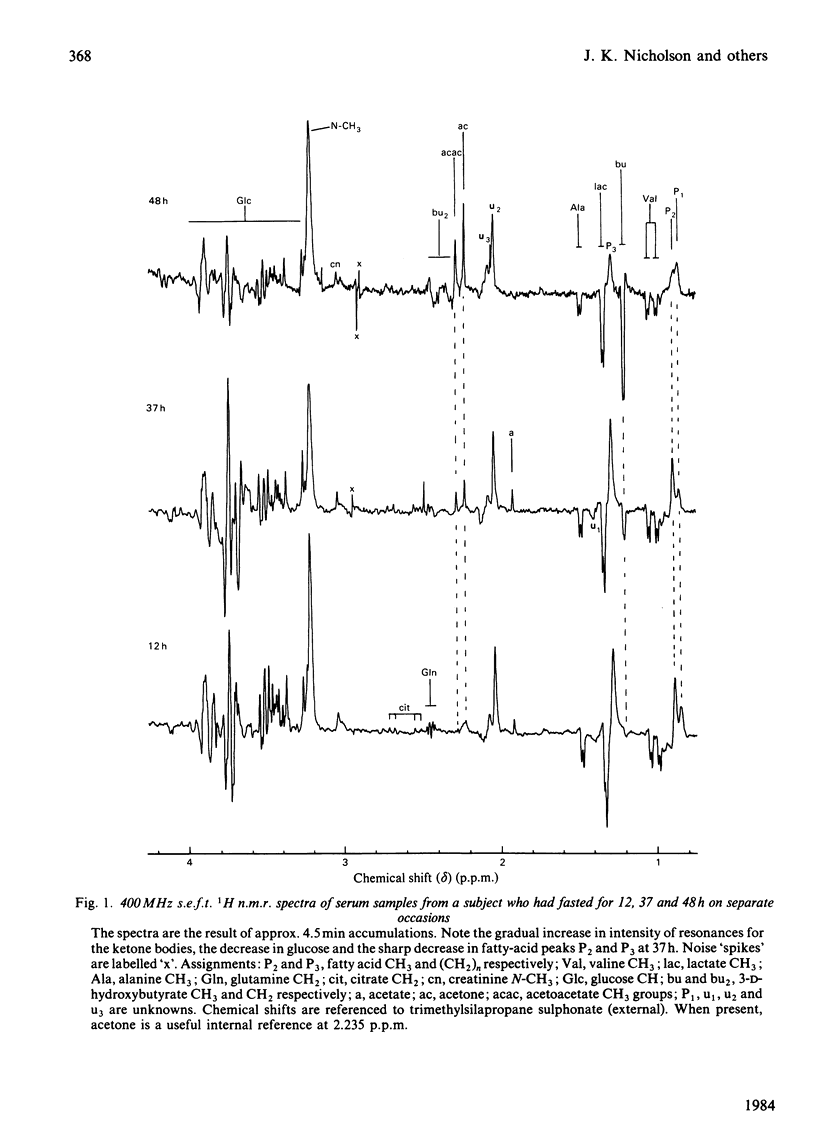
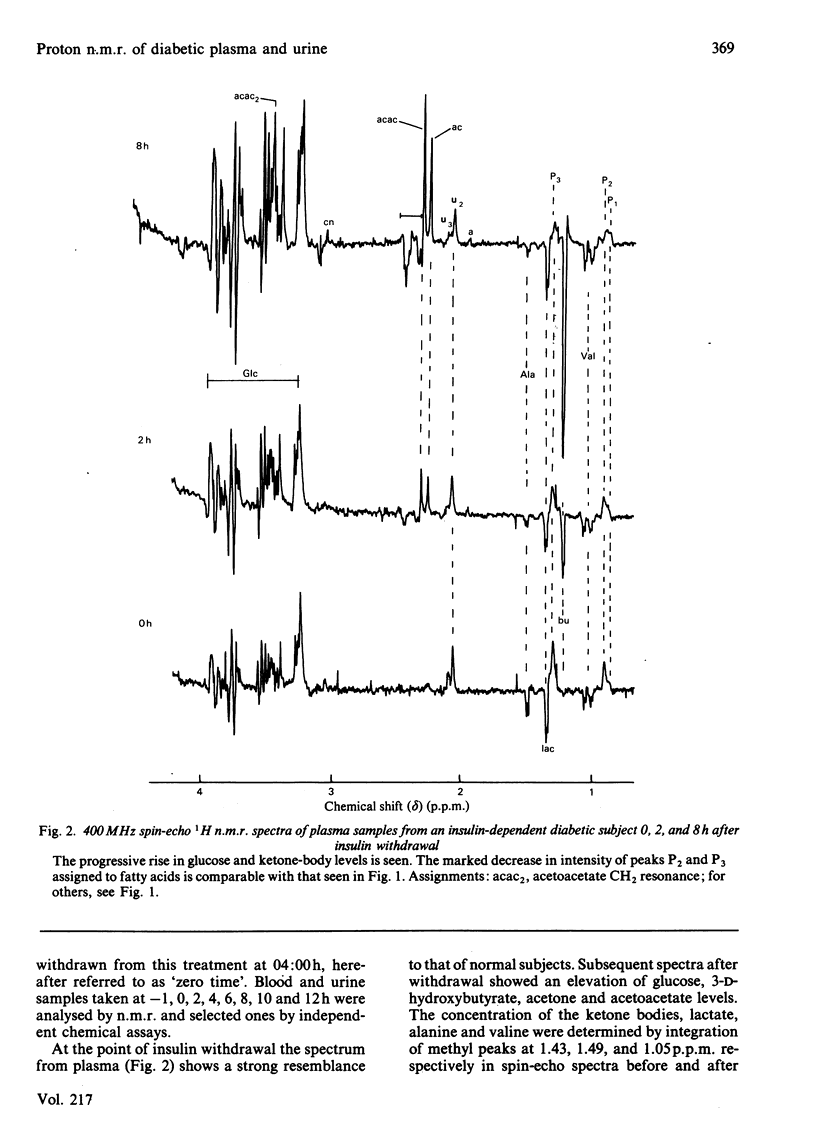
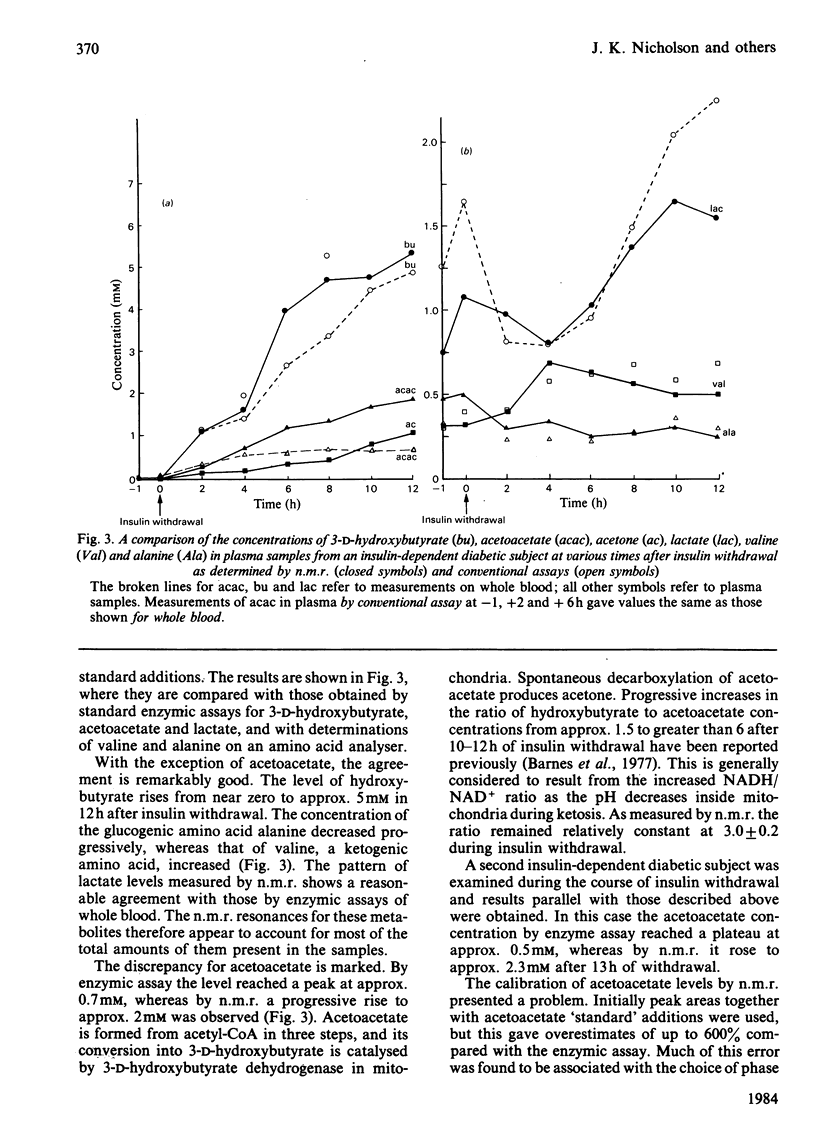
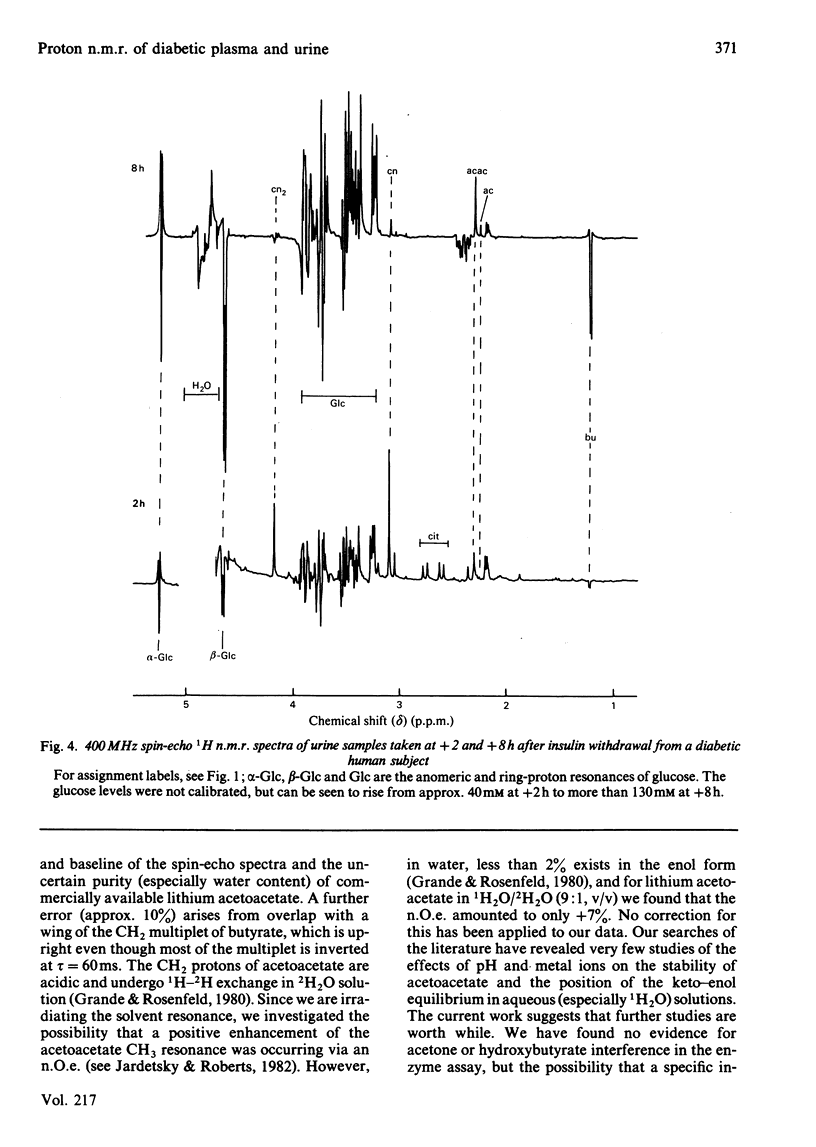
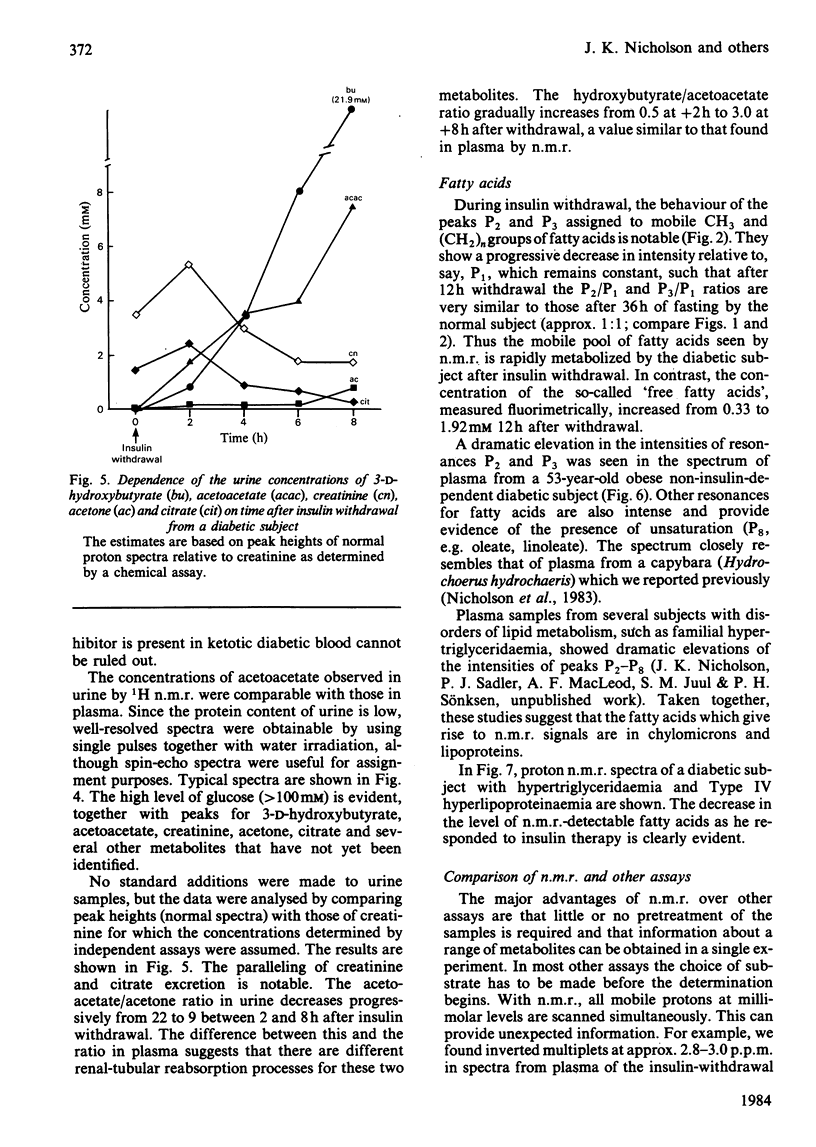
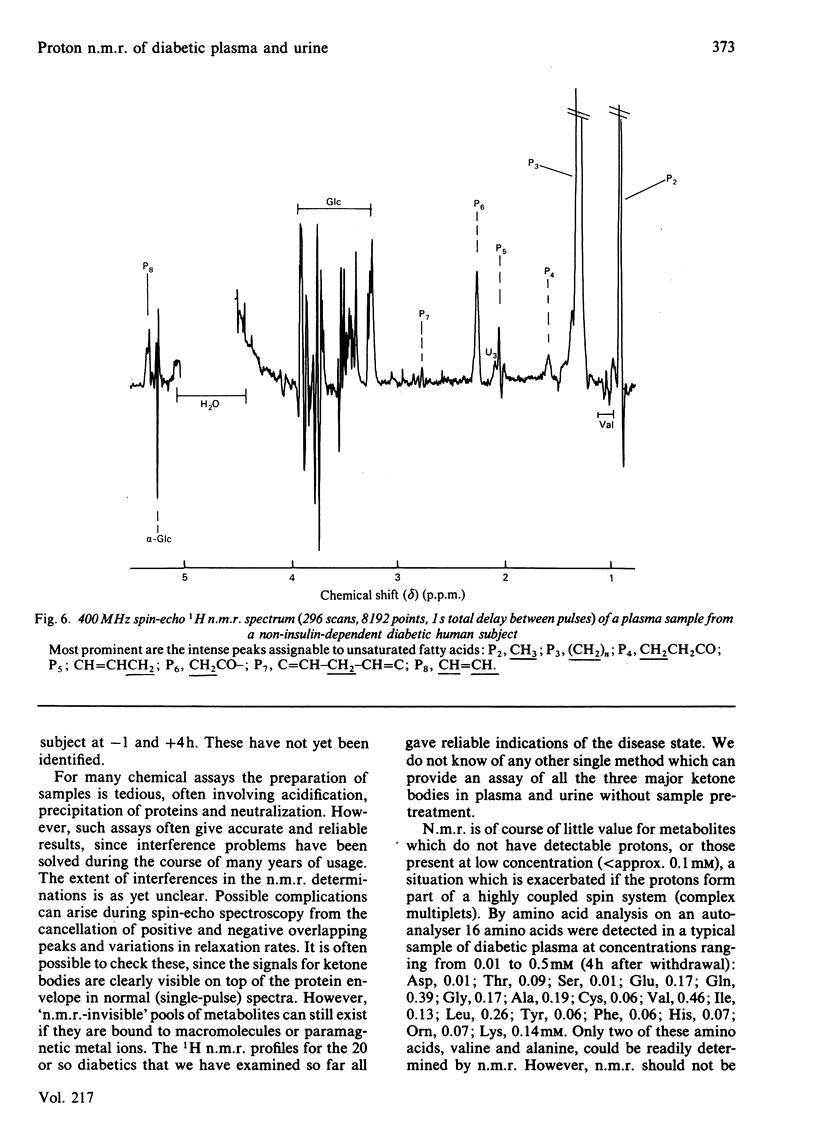
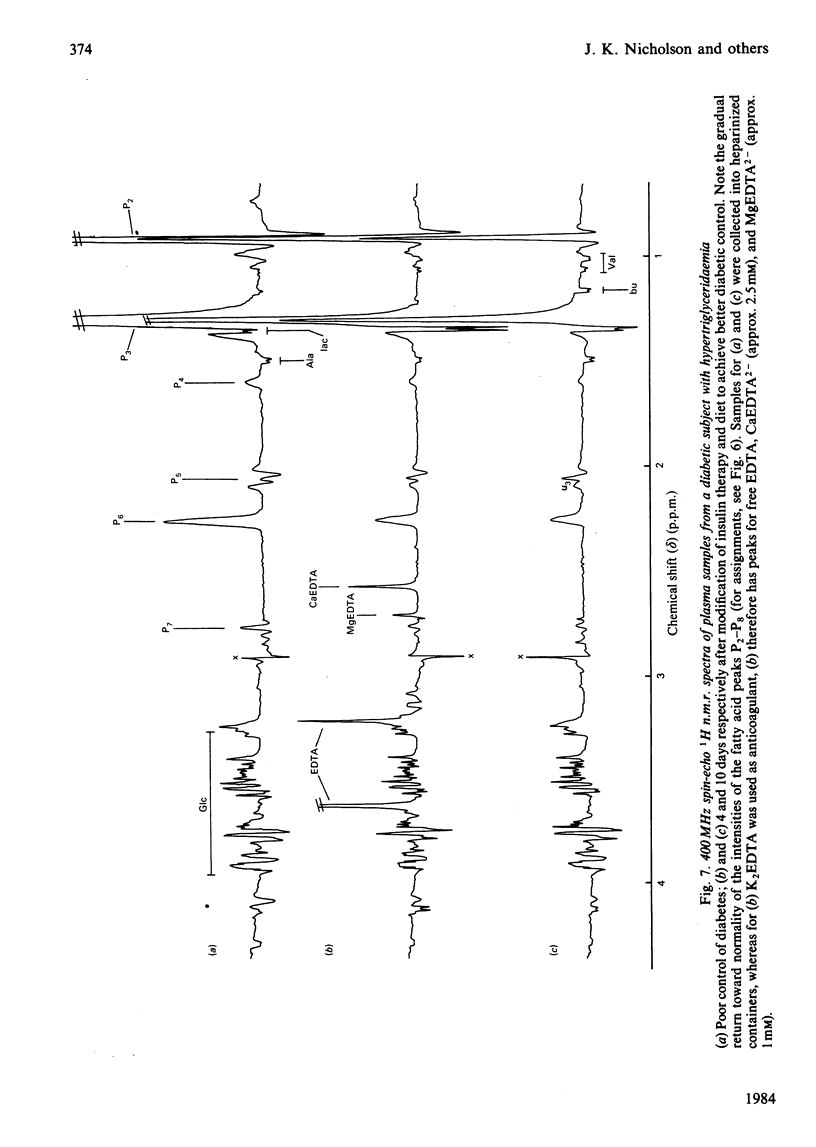
Resonances for the ketone bodies 3-D-hydroxybutyrate, acetone and acetoacetate are readily detected in serum, plasma and urine samples from fasting and diabetic subjects by 1H n.m.r. spectroscopy at 400 MHz. Besides the simultaneous observation of metabolites, the major advantage of n.m.r. is that little or no pretreatment of samples is required. N.m.r. determinations of 3-D-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, lactate, valine and alanine were compared with determinations made with conventional assays at six 2-hourly intervals after insulin withdrawal from a diabetic subject. The n.m.r. results closely paralleled those of other assays although, by n.m.r., acetoacetate levels continued to rise rather than reaching a plateau 4h after insulin withdrawal. The 3-D-hydroxybutyrate/acetoacetate ratio in urine during withdrawal gradually increased to the value observed in plasma (3.0 +/- 0.2) as determined by n.m.r. The acetoacetate/acetone ratio in urine (17 +/- 6) was much higher than in plasma (2.5 +/- 0.7). Depletion of a mobile pool of fatty acids in plasma during fasting, as seen by n.m.r., paralleled that seen during insulin withdrawal. These fatty acids were thought to be largely in chylomicrons, acylglycerols and lipoproteins, and were grossly elevated in plasma samples from a non-insulin-dependent diabetic and in cases of known hyperlipidaemia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes A. J., Bloom S. R., Goerge K., Alberti G. M., Smythe P., Alford F. P., Chisholm D. J. Ketoacidosis in pancreatectomized man. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 2;296(22):1250–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706022962202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock J. L. Analysis of serum by high-field proton nuclear magnetic resonance. Clin Chem. 1982 Sep;28(9):1873–1877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F. F., Campbell I. D. N.m.r. studies of red cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Jun 25;289(1037):395–406. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M., Young D. A. Free fatty acid estimation by a semi-automated fluorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Dec 27;49(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Leslie R. B., Hirz R., Scanu A. M. High-resolution NMR spectra of high-density serum lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 29;176(3):524–536. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels A., Williams R. J., Wright P. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the adrenal gland and some other organs. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):321–323. doi: 10.1038/261321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. K., Buckingham M. J., Sadler P. J. High resolution 1H n.m.r. studies of vertebrate blood and plasma. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):605–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2110605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steim J. M., Edner O. J., Bargoot F. G. Structure of human serum lipoproteins: nuclear magnetic resonance supports a micellar model. Science. 1968 Nov 22;162(3856):909–911. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3856.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., MELLANBY J., KREBS H. A. Enzymic determination of D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:90–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0820090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


