Abstract
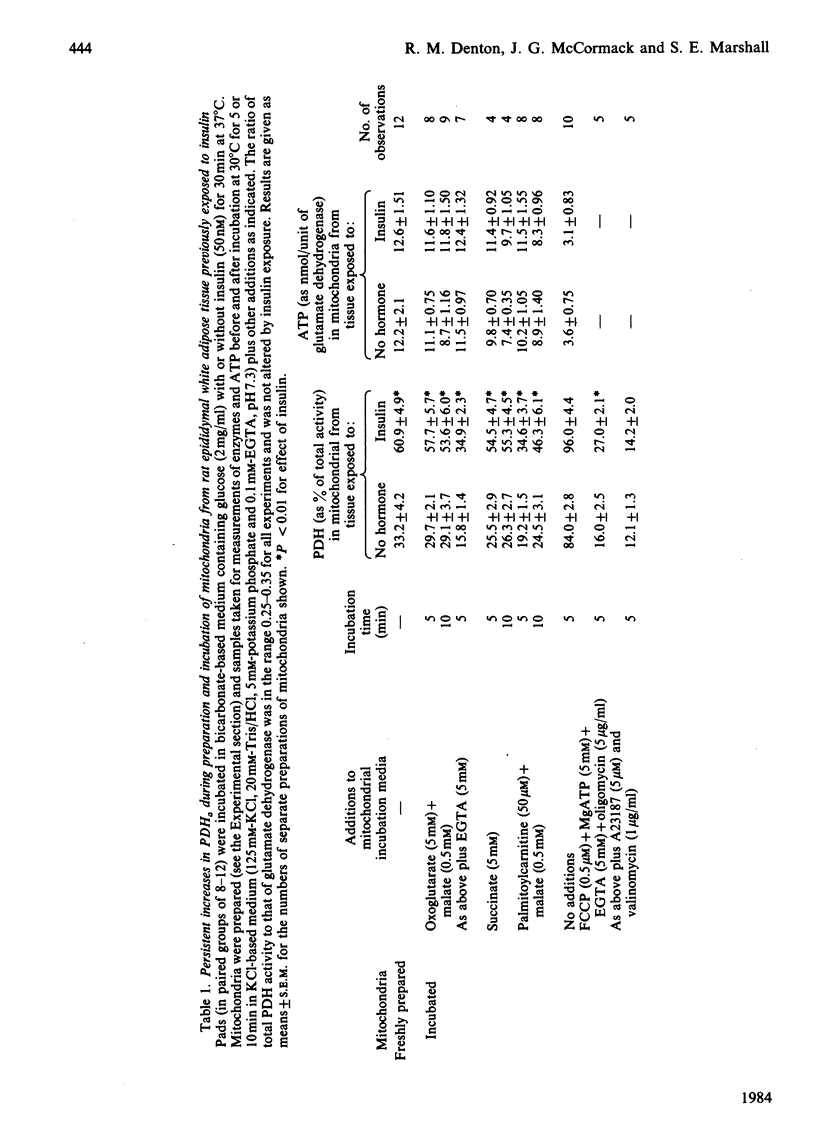
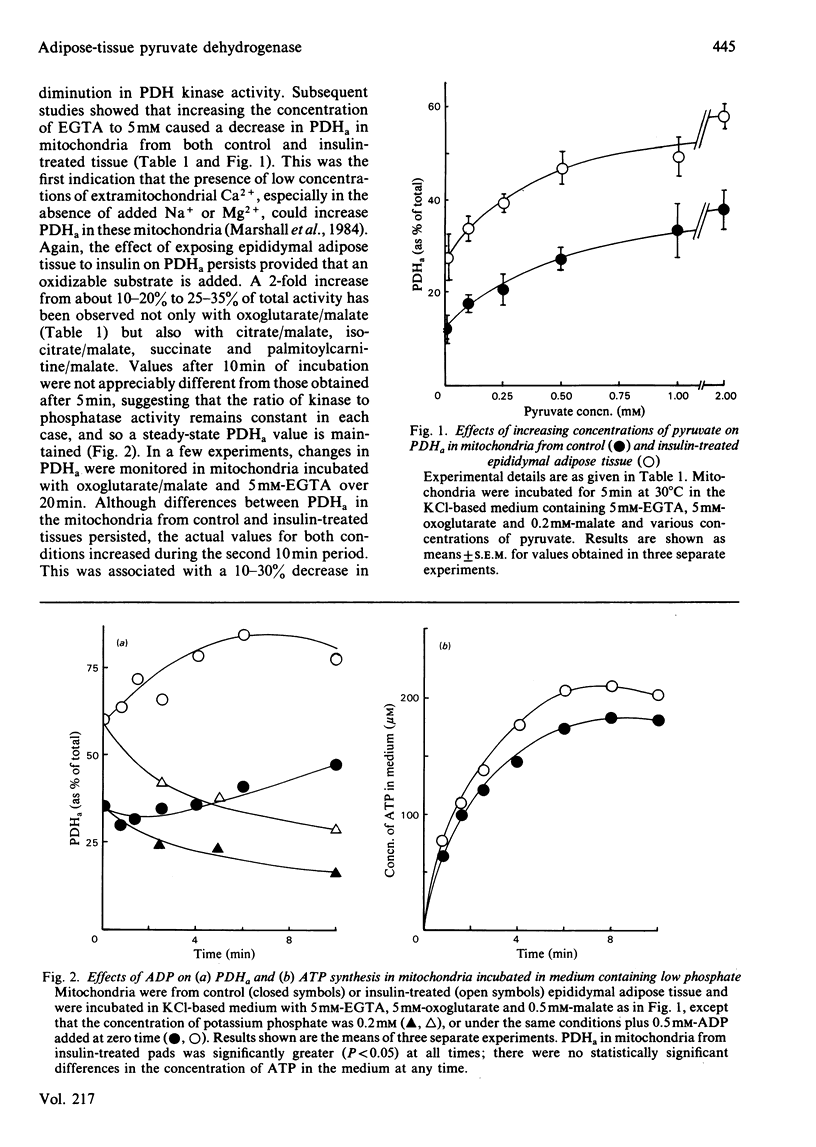
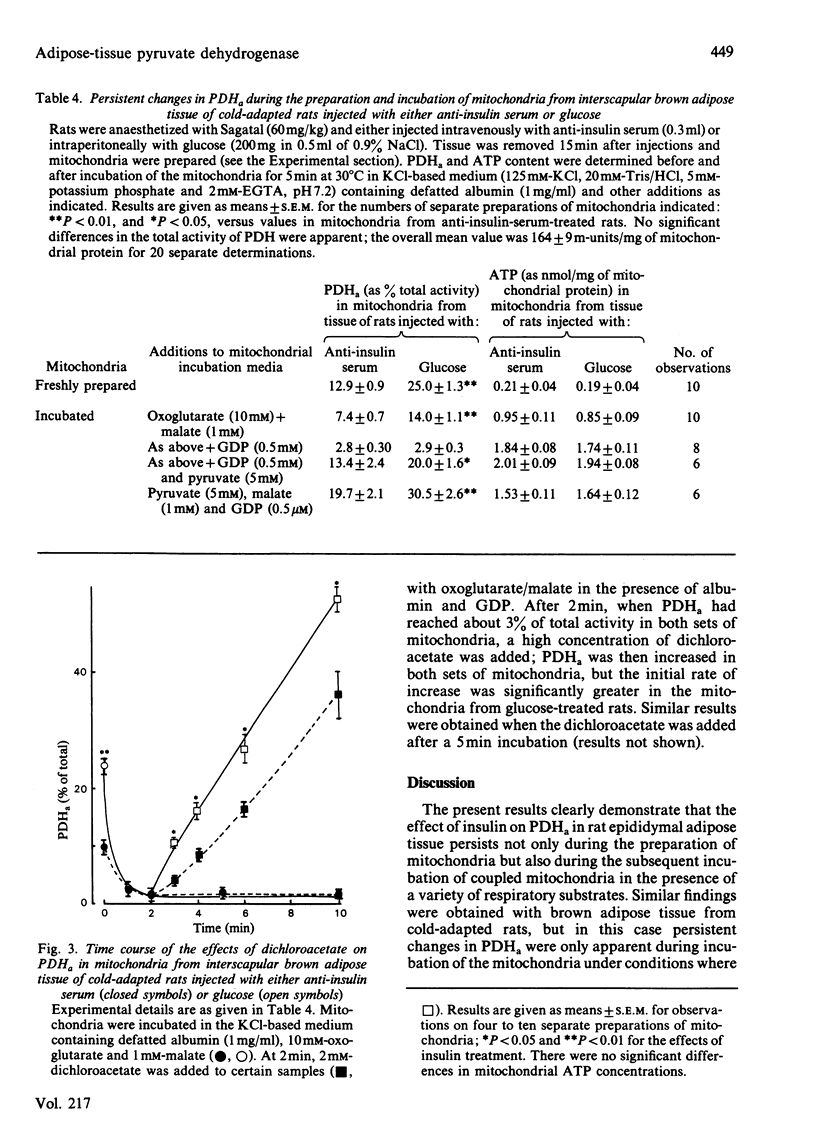
Increases in the amount of the active non-phosphorylated form of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat epididymal adipose tissue, as a result of incubation with insulin, persist not only during the preparation of mitochondria but also during subsequent incubation of coupled mitochondria in the presence of respiratory substrates. No effect on insulin was found if the hormone was added directly to mitochondria in the presence or absence of added plasma membranes. Concentrations of several possible regulators of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (ATP, ADP, NADH, NAD+, acetyl-CoA, CoA and potassium) were measured in rat epididymal-adipose-tissue mitochondria incubated under conditions where differences in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity persist as a result of insulin action. No alterations were found, and it is suggested that inhibition of the kinase is not the principal means by which insulin activates pyruvate dehydrogenase. The intramitochondrial concentration of magnesium was also unaffected. Differences in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in interscapular brown adipose tissue associated with manipulation of plasma insulin concentrations of cold-adapted rats were also shown to persist during the preparation and subsequent incubation of mitochondria in the presence or absence of GDP. It is pointed out that the persistence of the effect of insulin on pyruvate dehydrogenase in incubated mitochondria will facilitate the recognition of the mechanism of this action of the hormone. Evidence that the short-term action of insulin involves an increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase activity rather than inhibition of that of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., McCormack J. G., Prentki M., Jeanrenaud B., Denton R. M. Parallel increases in rates of fatty acid synthesis and in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in isolated rat hepatocytes incubated with insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 16;717(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera C. R., Namihira G., Hamilton L., Munk P., Eley M. H., Linn T. C., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XVI. Studies on the subunit structure of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from bovine kidney and heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter M. A., Goheer M. A., Coore H. G. Absent pyruvate inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in lactating rat mammary gland following various treatments. Removal of circulating insulin and prolactin and exposure to protein synthesis inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begum N., Tepperman H. M., Tepperman J. Effect of high fat and high carbohydrate diets on adipose tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase and its activation by a plasma membrane-enriched fraction and insulin. Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):1914–1921. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-1914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Denton R. M., Tanner M. J. Use of a novel rapid preparation of fat-cell plasma membranes employing Percoll to investigate the effects of insulin and adrenaline on membrane protein phosphorylation within intact fat-cells. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):457–467. doi: 10.1042/bj1920457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:65–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon B., Lindberg O. Mitochondria from brown adipose tissue: isolation and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:65–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Randle P. J., Denton R. M. Regulation of heart muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):625–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1430625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Randle P. J., Denton R. M. Stimulation of phosphorylation and inactivation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by physiological inhibitors of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):808–809. doi: 10.1038/257808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Coore H. G., Martin B. R., Randle P. J. Insulin activates pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):115–116. doi: 10.1038/newbio231115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M. Hormonal regulation of fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue through changes in the activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.4.1) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.2). Proc Nutr Soc. 1975 Dec;34(3):217–224. doi: 10.1079/pns19750042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Hughes W. A. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and the hormonal regulation of fat synthesis in mammalian tissues. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(8):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Bridges B. J., Cooper R. H., Kerbey A. L., Pask H. T., Severson D. L., Stansbie D., Whitehouse S. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Oct 31;9(1):27–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01731731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Martin B. R. Stimulation by calcium ions of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):161–163. doi: 10.1042/bj1280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Randall D. D., Roche T. E., Burgett M. W., Pelley J. W., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XVII. Kinetic and regulatory properties of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase from bovine kidney and heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Brownsey R. W., Denton R. M. Studies on the incorporation of [32P]phosphate into pyruvate dehydrogenase in intact rat fat-cells. Effects of insulin. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):469–481. doi: 10.1042/bj1920469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Incorporation of 32Pi into pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate in mitochondria from control and insulin-treated adipose tissue. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):471–473. doi: 10.1038/264471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Seals J. R. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activation in adipocyte mitochondria by an insulin-generated mediator from muscle. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1407–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.505013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungas R. L. Effect of insulin on fatty acid ynthesis from pyruvate, lactage, or endogenous sources in adipose tissue: evidence for the hormonal regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Endocrinology. 1970 Jun;86(6):1368–1375. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-6-1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Radcliffe P. M., Randle P. J. Diabetes and the control of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat heart mitochondria by concentration ratios of adenosine triphosphate/adenosine diphosphate, of reduced/oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide and of acetyl-coenzyme A/coenzyme A. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):509–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1640509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Cooper R. H., Whitehouse S., Pask H. T., Denton R. M. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat heart. Mechanism of regulation of proportions of dephosphorylated and phosphorylated enzyme by oxidation of fatty acids and ketone bodies and of effects of diabetes: role of coenzyme A, acetyl-coenzyme A and reduced and oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):327–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1540327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase/activator in rat heart mitochondria, Assay, effect of starvation, and effect of protein-synthesis inhibitors of starvation. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):103–111. doi: 10.1042/bj2060103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Thermolabile factor accelerates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase reaction in heart mitochondria of starved or alloxan-diabetic rats. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 18;127(2):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiechle F. L., Jarett L., Kotagal N., Popp D. A. Partial purification from rat adipocyte plasma membranes of a chemical mediator which simulates the action of insulin on pyruvate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2945–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Denton R. M., Pask H. T., Randle P. J. Mechanisms regulating adipose-tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):763–773. doi: 10.1042/bj1290763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. Evidence that fatty acid synthesis in the interscapular brown adipose tissue of cold-adapted rats is increased in vivo by insulin by mechanisms involving parallel activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):627–630. doi: 10.1042/bj1660627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. Role of calcium ions in the regulation of intramitochondrial metabolism. Properties of the Ca2+-sensitive dehydrogenases within intact uncoupled mitochondria from the white and brown adipose tissue of the rat. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):95–105. doi: 10.1042/bj1900095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Studies on the interactions of Ca2+ and pyruvate in the regulation of rat heart pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Effects of starvation and diabetes. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2020419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S. P., Lynn W. S. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in adipocyte plasma membrane and its activation by insulin. Possible role in the hormone's effects on adenylate cyclase and the hexose monophosphate shunt. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Nov;184(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. Brown adipose tissue mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 3;549(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetzke-Brunner I., Schön H., Wieland O. H. Insulin activates pyruvate dehydrogenase by lowering the mitochondrial acetyl-CoA/CoA ratio as evidenced by digitonin fractionation of isolated fat cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetzke-Brunner I., Wieland O. H. Activation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in isolated fat cell mitochondria by hydrogen peroxide and t-butyl hydroperoxide. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 15;122(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Pelley J. W., Reed L. J. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase and phosphatase by acetyl-CoA/CoA and NADH/NAD ratios. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):575–582. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycles and the regulation of fuel selection in mammals. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:107–129. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:95–106. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche T. E., Reed L. J. Monovalent cation requirement for ADP inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1341–1348. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90461-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Randle P. J. Occupancy of phosphorylation sites in pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate complex in rat heart in vivo. Relation to proportion of inactive complex and rate of re-activation by phosphatase. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 15;206(2):221–229. doi: 10.1042/bj2060221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Randle P. J. Occupancy of sites of phosphorylation in inactive rat heart pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate in vivo. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):935–946. doi: 10.1042/bj1930935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Siegel M. I., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Putative mediators of insulin action: regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and adenylate cyclase activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3513–3517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A., Jacobs S., Siegel M., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the release from liver plasma membranes of a chemical modulator of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 15;102(3):1041–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91643-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Czech M. P. Characterization of a pyruvate dehydrogenase activator released by adipocyte plasma membranes in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Czech M. P. Evidence that insulin activates an intrinsic plasma membrane protease in generating a secondary chemical mediator. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6529–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Denton R. M., Bridges B. J., Randle P. J. Exchangeable and total calcium pools in mitochondria of rat epididymal fat-pads and isolated fat-cells. Role in the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):209–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1540209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Denton R. M., Pask H. T., Randle P. J. Calcium and magnesium ions as effectors of adipose-tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):225–237. doi: 10.1042/bj1400225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess E. A., Wieland O. H. Purification and characterization of pyruvate-dehydrogenase phosphatase from pig-heart muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):96–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansbie D., Denton R. M., Bridges B. J., Pask H. T., Randle P. J. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase activity in rat epididymal fat-pads. Effects of starvation, alloxan-diabetes and high-fat diet. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):225–236. doi: 10.1042/bj1540225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Waller C. A., Reid K. B. Amino acid sequences around the sites of phosphorylation in the pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):419–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1810419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping D. L., Goheer M. A., Coore H. G., Mayes P. A. Regulation by insulin and free fatty acids of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in perfused rat liver [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(4):1000–1001. doi: 10.1042/bst0051000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Löffler G., Schirmann A., Wieland O. Control of pyruvate dehydrogenase interconversion in adipose tissue by insulin. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Cooper R. H., Randle P. J. Mechanism of activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate and other halogenated carboxylic acids. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):761–774. doi: 10.1042/bj1410761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland O. H. The mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: structure and regulation. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;96:123–170. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J., Hutcheson E. T., Roche T. E., Pettit F. H., Brown J. R., Reed L. J., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. Sites of phosphorylation on pyruvate dehydrogenase from bovine kidney and heart. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2364–2370. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


