Abstract
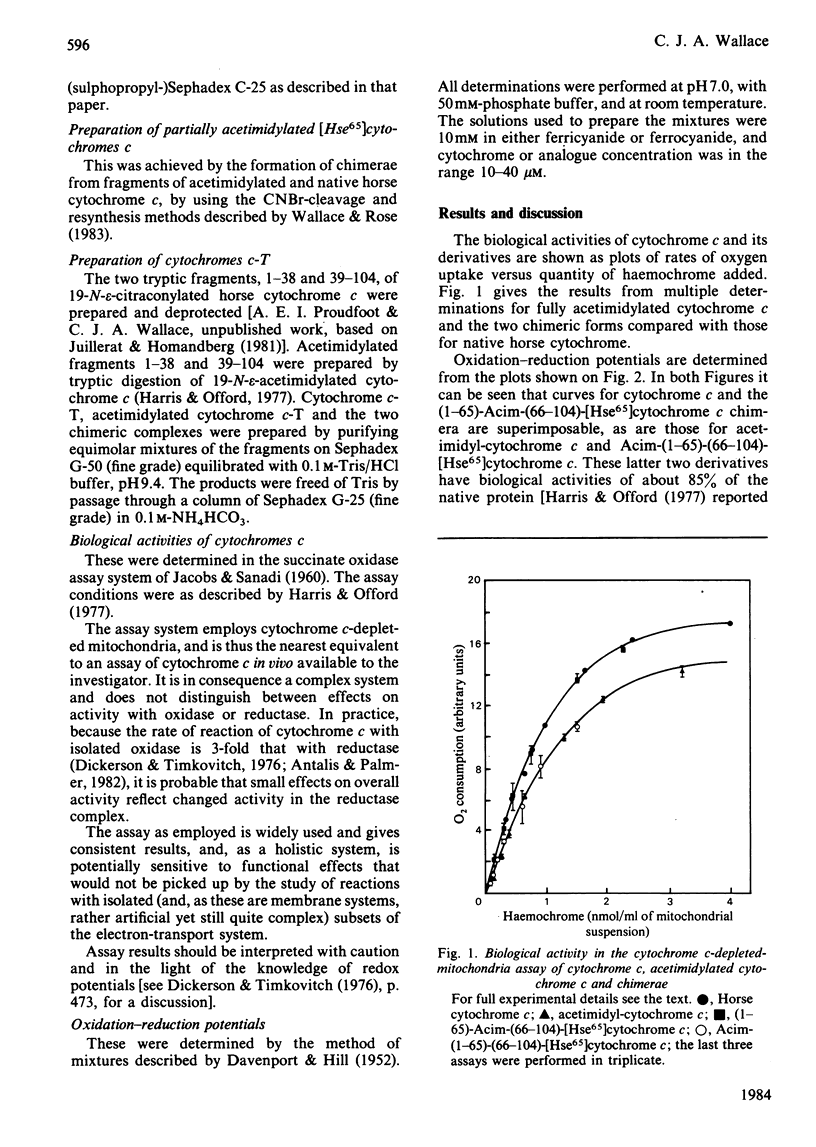
The biological consequences of acetimidylation of all 19 epsilon-amino groups of horse cytochrome c are a slight decrease in both the redox potential of the protein and its ability to stimulate oxygen uptake in the cytochrome c-depleted-mitochondria assay. Examination of a number of specific partially acetimidylated analogues and acetimidylated cytochromes c of other species has shown that the changes in biological properties, which are associated with a slight structural change as monitored by n.m.r. spectroscopy [Boswell, Moore, Williams, Harris, Wallace, Bocieck & Welti (1983) Biochem. J. 213, 679-686], appear to stem from modification of residues in a restricted region of the sequence. The failure of the redox potential of Saccharomyces cerevisae cytochrome c to be affected by acetimidylation suggests that it is lysine-53, absent from that species, that is the sensitive residue.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antalis T. M., Palmer G. Kinetic characterization of the interaction between cytochrome oxidase and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6194–6206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosshard H. R., Zürrer M. The conformation of cytochrome c in solution. Localization of a conformational difference between ferri- and ferrocytochrome c on the surface of the molecule. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6694–6699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell A. P., Moore G. R., Williams R. J., Harris D. E., Wallace C. J., Bocieck S., Welti D. Ionization of tyrosine and lysine residues in native and modified horse cytochrome c. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):679–686. doi: 10.1042/bj2130679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell A. P., Moore G. R., Williams R. J., Wallace C. J., Boon P. J., Nivard R. J., Tesser G. I. Structural studies of eukaryotic cytochrome c modified at methionine-65. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):493–502. doi: 10.1042/bj1930493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Darley-Usmar V., Fuller S., Millett F. Structural and functional features of the interaction of cytochrome c with complex III and cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 8;138(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Harbury H. A. Reconstitution of horse heart cytochrome c: interaction of the components obtained upon cleavage of the peptide bond following methionine residue 65. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3036–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Harbury H. A. Reconstitution of horse heart cytochrome c: reformation of the peptide bond linking residues 65 and 66. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1400–1406. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVENPORT H. E., HILL R. The preparation and some properties of cytochrome f. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Apr 24;139(896):327–345. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. E., Offord R. E. A functioning complex between tryptic fragments of cytochrome c. A route to the production of semisynthetic analogues. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 1;161(1):21–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1610021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS E. E., SANADI D. R. The reversible removal of cytochrome c from mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:531–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juillerat M., Homandberg G. A. Clostripain-catalyzed re-formation of a peptide bond in a cytochrome C fragment complex. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Oct;18(4):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1981.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. N., Boswell A. P., Huang Z. X., Eley C. G., Moore G. R. The conformation of eukaryotic cytochrome c around residues 39, 57, 59 and 74. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):687–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2130687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlauder G. G., Kassner R. J. Comparative solvent perturbation of horse heart cytochrome c and Rhodospirillum rubrum cytochrome c2. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4110–4113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Dickerson R. E. Conformation change of cytochrome c. I. Ferrocytochrome c structure refined at 1.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 25;153(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace C. J., Harris D. E. The preparation of fully N-epsilon-acetimidylated cytochrome c. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 1;217(3):589–594. doi: 10.1042/bj2170589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace C. J., Rose K. The semisynthesis of analogues of cytochrome c. Modifications of arginine residues 38 and 91. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):651–658. doi: 10.1042/bj2150651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilgus H., Ranweiler J. S., Wilson G. S., Stellwagen E. Spectral and electrochemical studies of cytochrome c peptide complexes. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3265–3272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



