Abstract
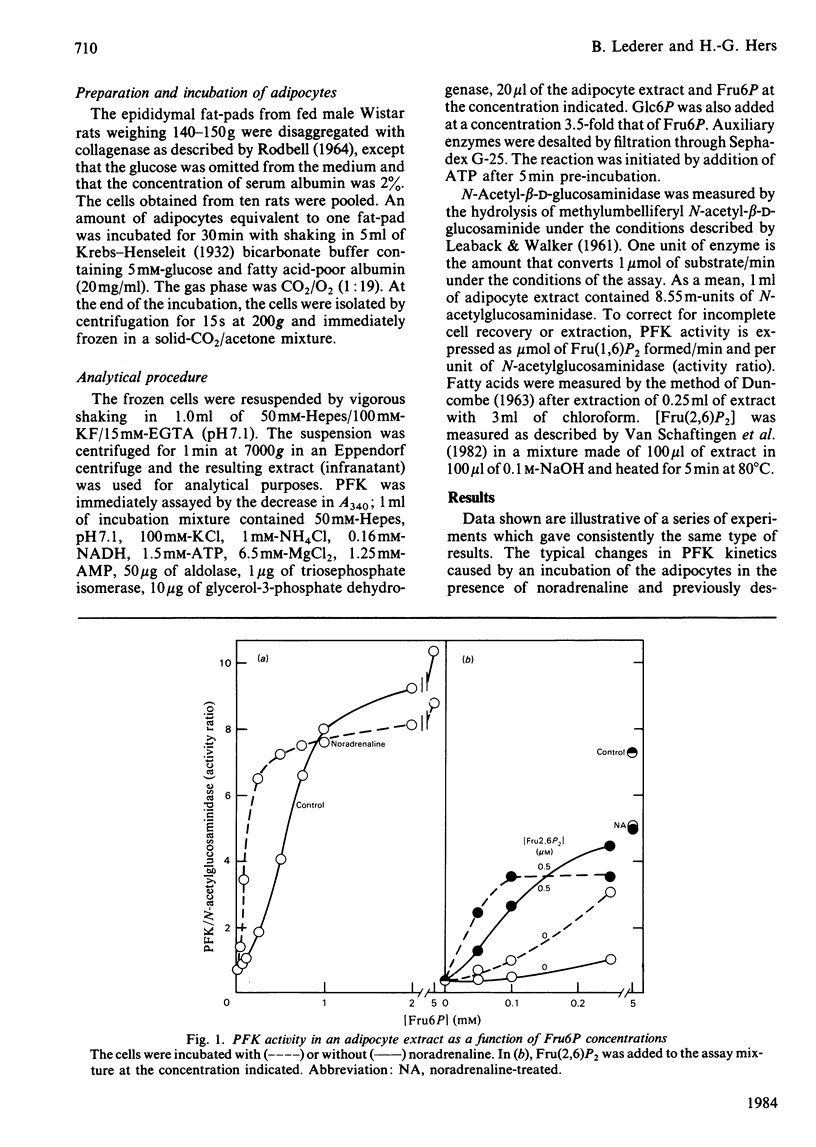
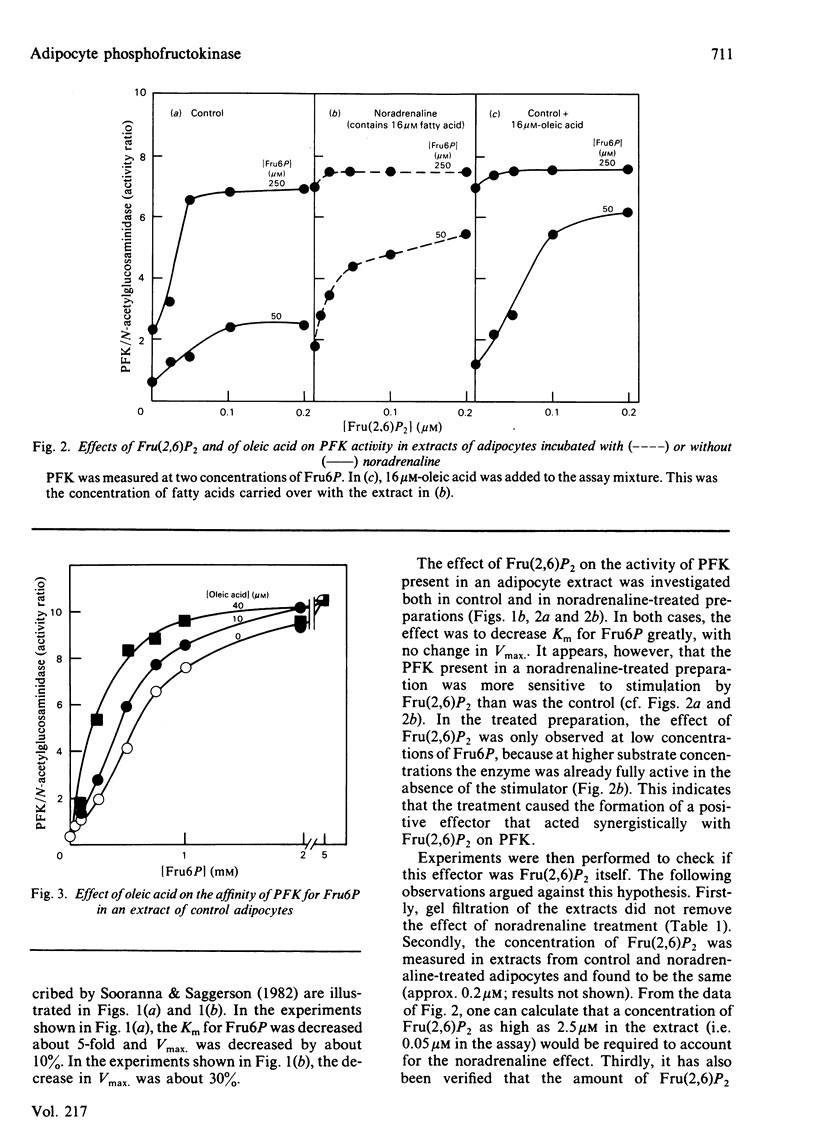
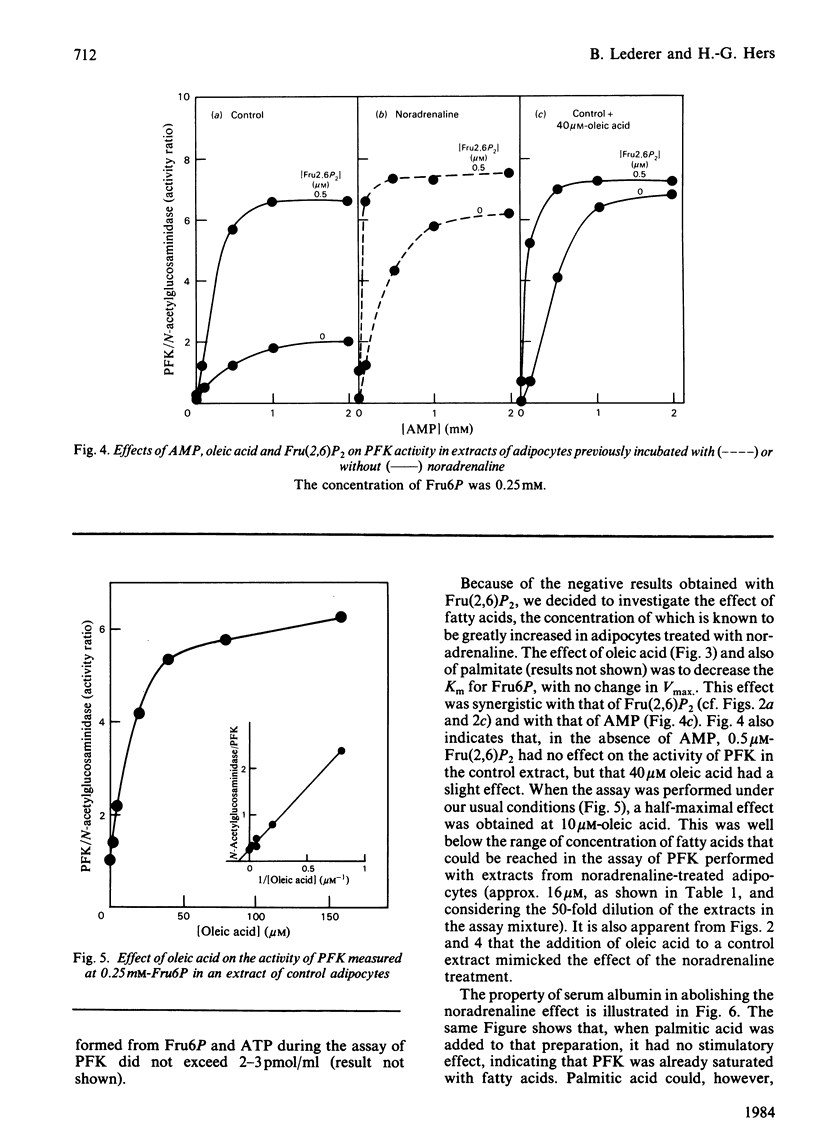
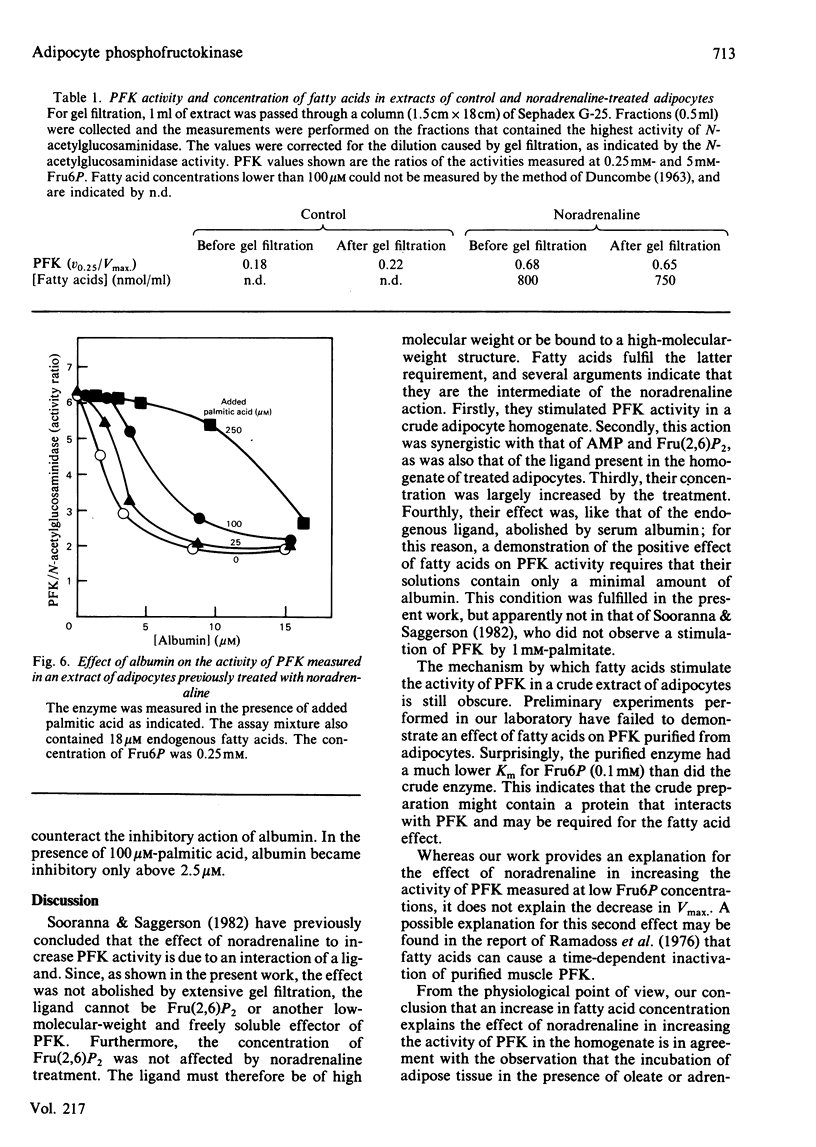
We confirmed that, as reported by Sooranna & Saggerson [(1982) Biochem. J. 202, 753-758], the affinity of 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase (PFK) for fructose 6-phosphate in an adipocyte extract was increased after incubation of the cells in the presence of noradrenaline. The participation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in this kinetic modification could be excluded, because the noradrenaline effect persisted after extensive gel filtration of the extracts and also because the treatment did not cause any change in the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the adipocytes. Oleic acid was found to be another potent positive effector of PFK in an adipocyte extract, with a Ka of 10 microM. Its effect was synergistic with that of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and AMP, and was counteracted by serum albumin. Palmitic acid had a similar effect. We conclude that the large increase in fatty acid concentration caused by noradrenaline treatment is an explanation for the activation of phosphofructokinase at low fructose 6-phosphate concentrations in an adipocyte extract.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncombe W. G. The colorimetric micro-determination of long-chain fatty acids. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88(1):7–10. doi: 10.1042/bj0880007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin M. L., Denton R. M. Regulation of glycolysis and L-glycerol 3-phosphate concentration in rat epididymal adipose tissue in vitro. Role of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):207–214. doi: 10.1042/bj1130207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate 2 years after its discovery. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2060001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEABACK D. H., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase. 4. The fluorimetric assay of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:151–156. doi: 10.1042/bj0780151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadoss C. S., Uyeda K., Johnston J. M. Studies on the fatty acid inactivation of phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):98–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Greenbaum A. L. The regulation of triglyceride synthesis and fatty acid synthesis in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):193–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1190193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sooranna S. R., Saggerson E. D. Rapid modulation of adipocyte phosphofructokinase activity by noradrenaline and insulin. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 15;202(3):753–758. doi: 10.1042/bj2020753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Formation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate from fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by intramolecular cyclisation followed by alkaline hydrolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):319–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Control of the fructose-6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bisphosphate cycle in isolated hepatocytes by glucose and glucagon. Role of a low-molecular-weight stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):887–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1920887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, the probably structure of the glucose- and glucagon-sensitive stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):897–901. doi: 10.1042/bj1920897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


