Abstract
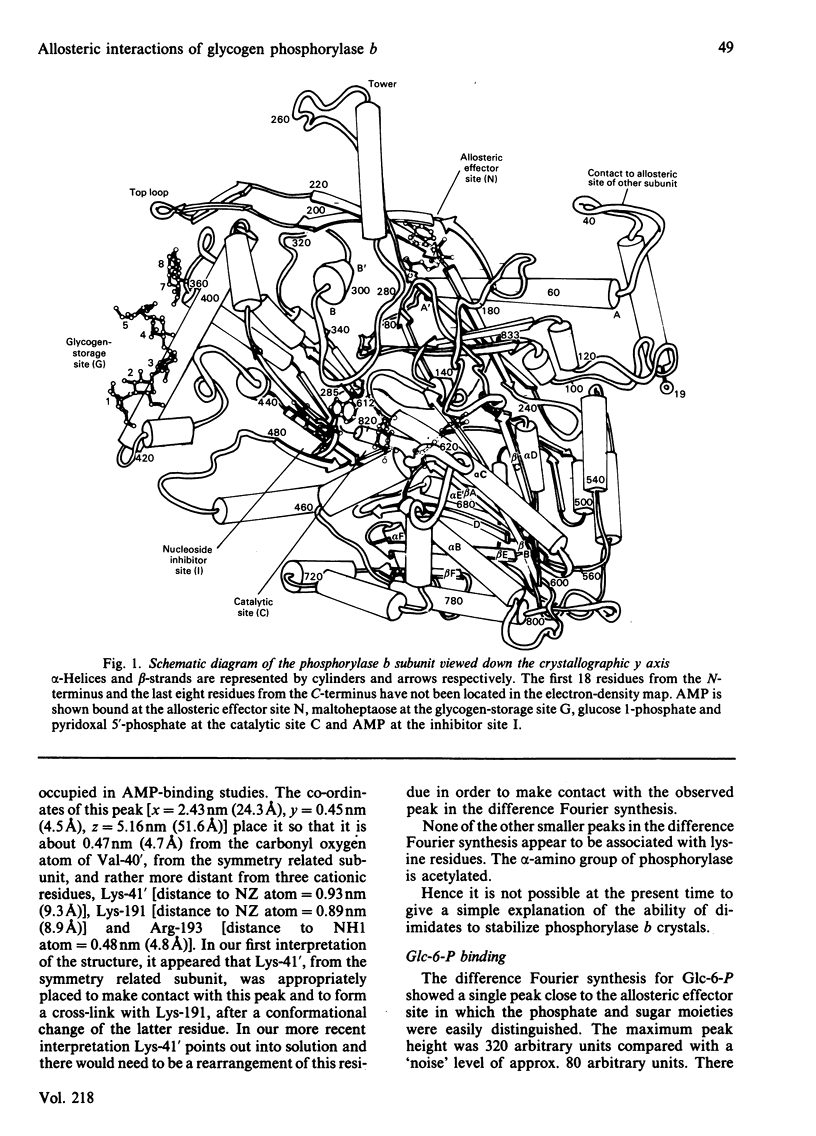
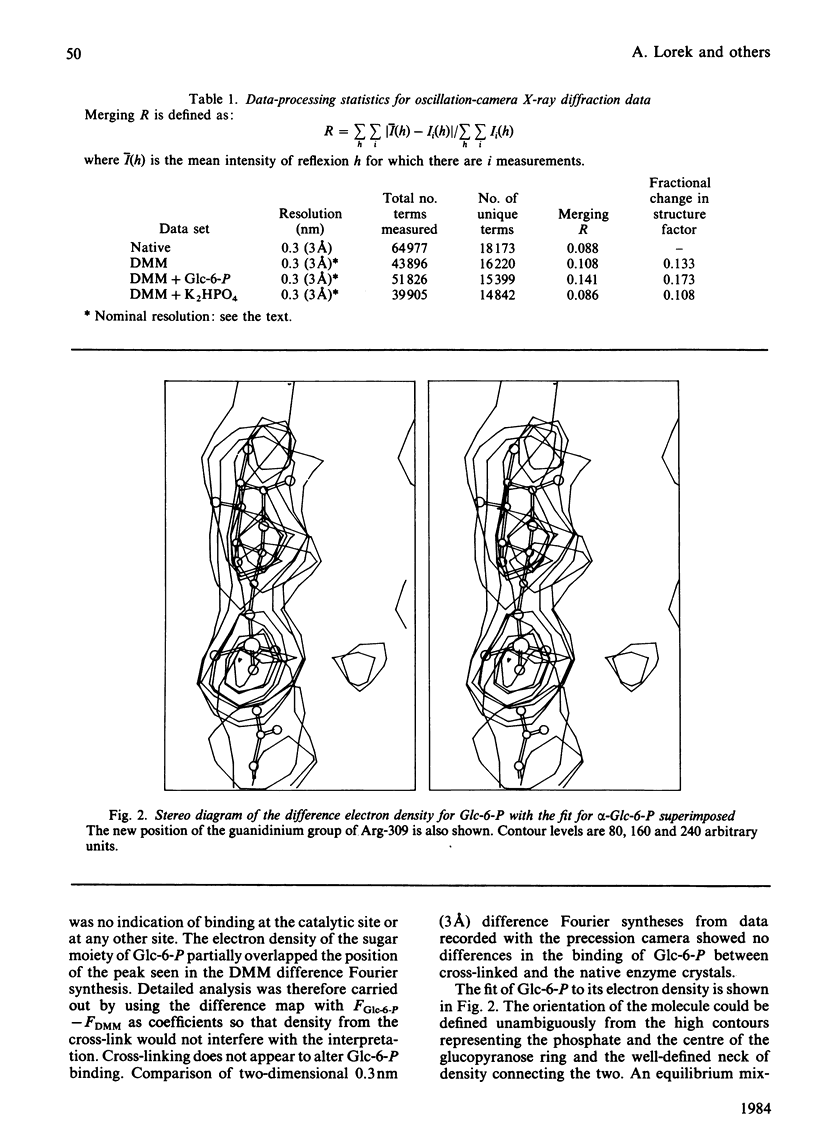
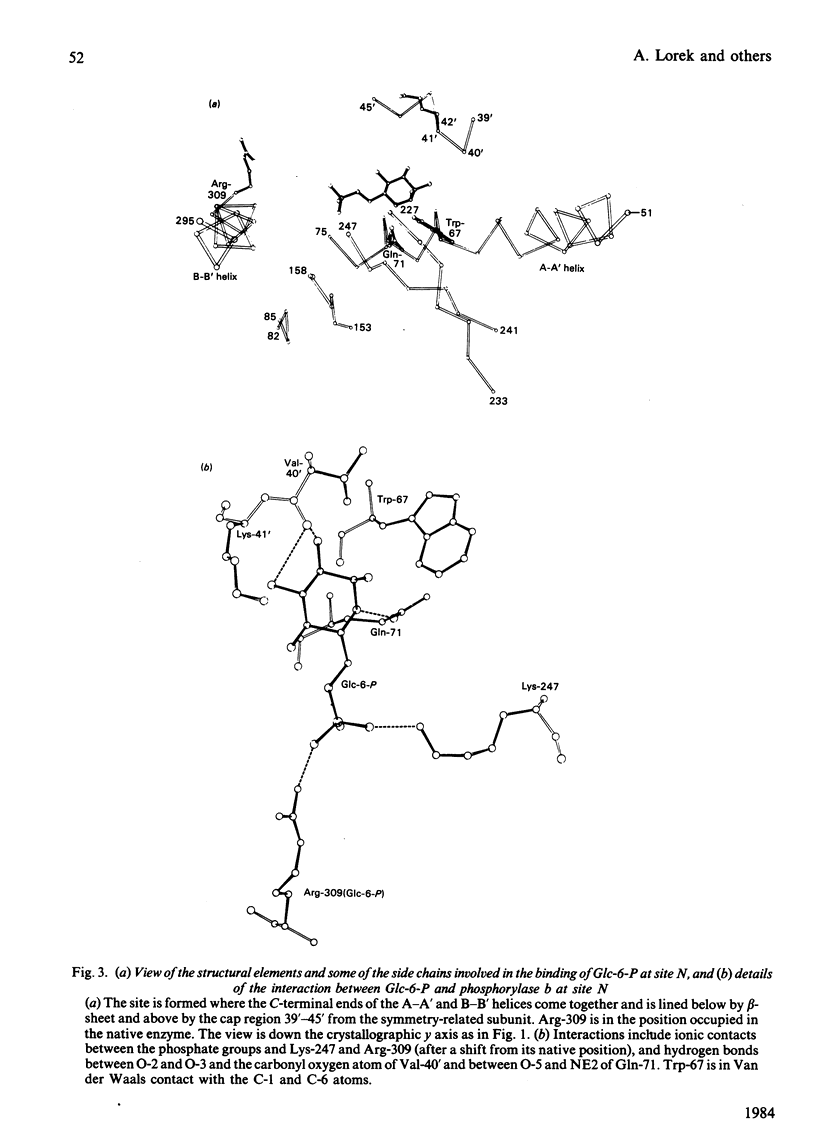
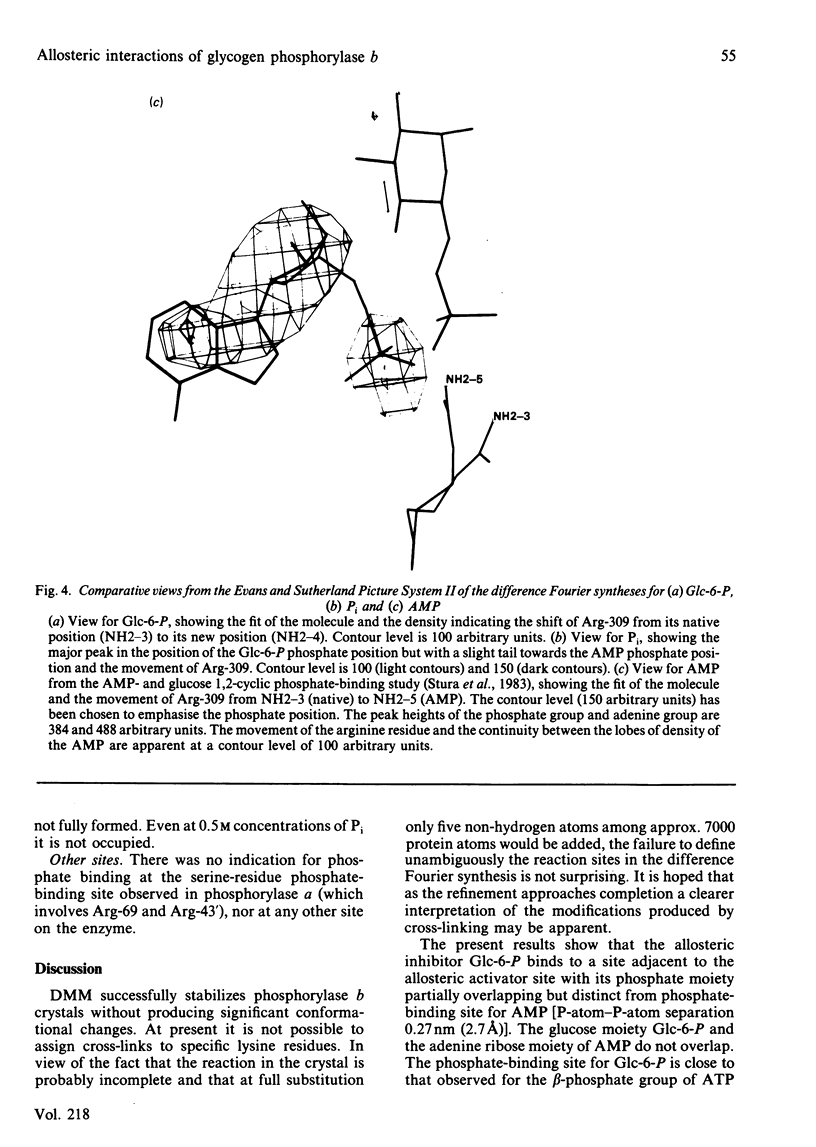
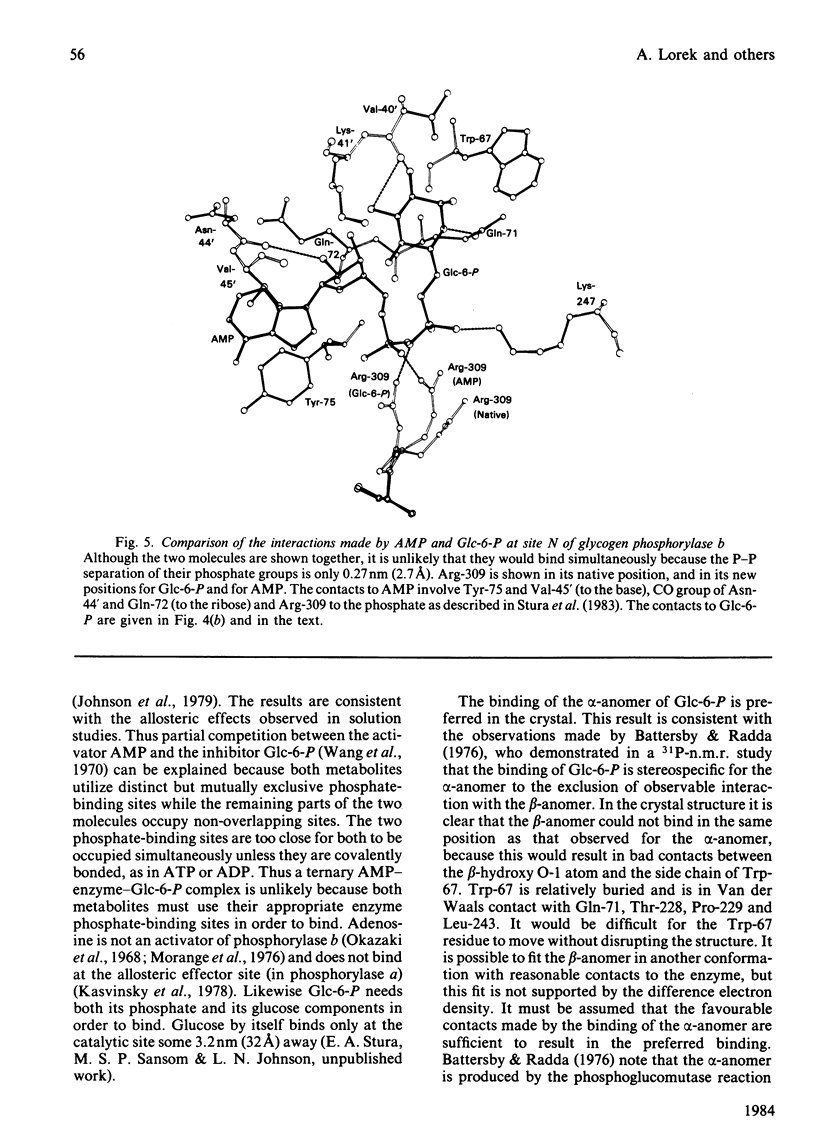
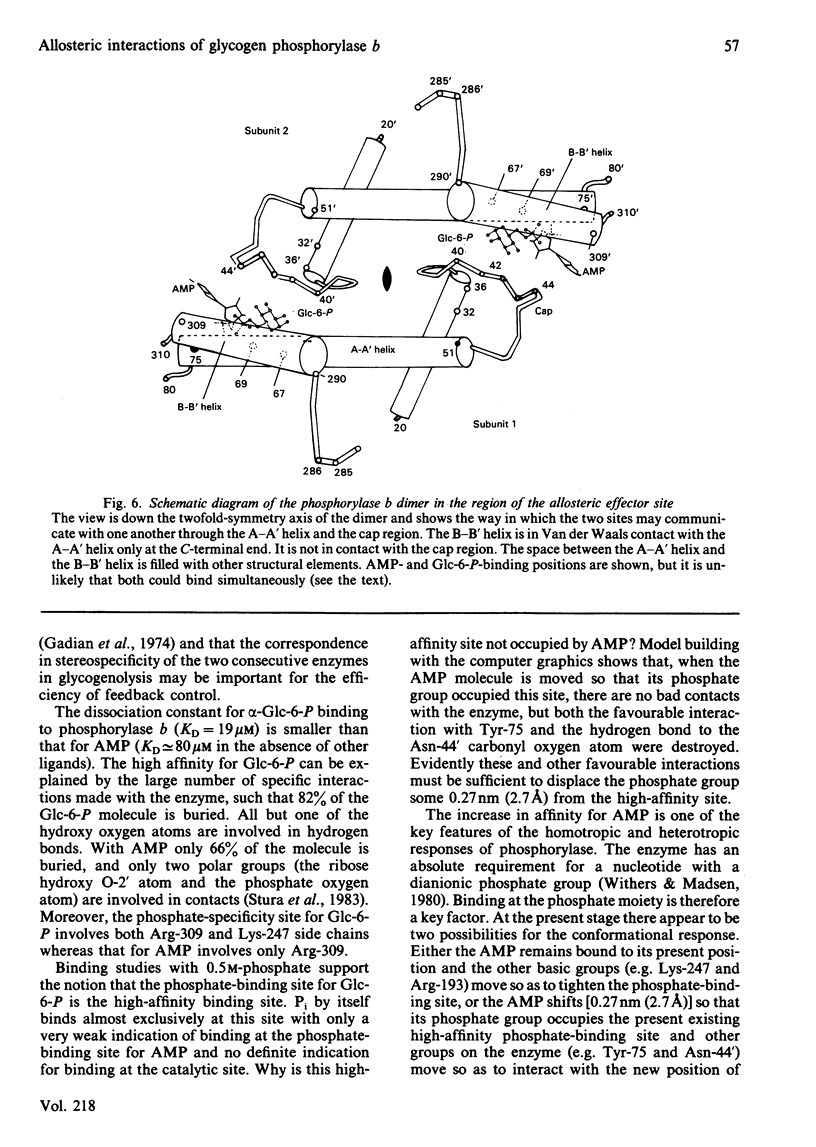
The binding to glycogen phosphorylase b of glucose 6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate (respectively allosteric inhibitor and substrate/activator of the enzyme) were studied in the crystal at 0.3 nm (3A) resolution. Glucose 6-phosphate binds in the alpha-configuration at a site that is close to the AMP allosteric effector site at the subunit-subunit interface and promotes several conformational changes. The phosphate-binding site of the enzyme for glucose 6-phosphate involves contacts to two cationic residues, Arg-309 and Lys-247. This site is also occupied in the inorganic-phosphate-binding studies and is therefore identified as a high-affinity phosphate-binding site. It is distinct from the weaker phosphate-binding site of the enzyme for AMP, which is 0.27 nm (2.7A) away. The glucose moiety of glucose 6-phosphate and the adenosine moiety of AMP do not overlap. The results provide a structural explanation for the kinetic observations that glucose 6-phosphate inhibition of AMP activation of phosphorylase b is partially competitive and highly co-operative. The results suggest that the transmission of allosteric conformational changes involves an increase in affinity at phosphate-binding sites and relative movements of alpha-helices. In order to study glucose 6-phosphate and phosphate binding it was necessary to cross-link the crystals. The use of dimethyl malondi-imidate as a new cross-linking reagent in protein crystallography is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey I. A., Williams S. R., Radda G. K., Gadian D. G. Activity of phosphorylase in total global ischaemia in the rat heart. A phosphorus-31 nuclear-magnetic-resonance study. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 15;196(1):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1960171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Fishman P. H., Pentchev P. G. Studies on mutarotases. II. Investigations of possible rate-limiting anomerizations in glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4827–4831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J., Chothia C. Haemoglobin: the structural changes related to ligand binding and its allosteric mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):175–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battersby M. K., Radda G. K. Intersubunit transmission of ligand effects in the glycogen phosphorylase b dimer. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3774–3780. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battersby M. K., Radda G. K. The stereospecificity of the glucose-6-phosphate binding site of glycogen phosphorylase b. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80995-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. J., Hsueh-Ching Wang J. Studies on the allosteric activation of glycogen phosphorylase b by nucleotides. II. Nucleotide structure in relation to mechanism of activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 15;212(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Johnson L. N., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Crystallographic studies of the activity of hen egg-white lysozyme. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Apr 18;167(1009):378–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. T., Kent S. B. Formation of non-amidine products in the reaction of primary amines with imido esters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):126–132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc-Carbon M. H., Buc H. C. Quaternary changes of rabbit-muscle glycogen phosphorylase b at low temperature: relaxation studies and titration of sulfhydryl groups. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Apr 1;52(3):575–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc H. On the allosteric interaction between 5'AMP and orthophosphate on phosphorylase b. Quantitative kinetic predictions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 10;28(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90406-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Hydrophobic bonding and accessible surface area in proteins. Nature. 1974 Mar 22;248(446):338–339. doi: 10.1038/248338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. C. Transmission of conformational change in insulin. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):500–505. doi: 10.1038/302500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. J., Gadian D. G., Wilkie D. R. Mechanical relaxation rate and metabolism studied in fatiguing muscle by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:465–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engers H. D., Madsen N. B. The effect of anions on the activity of phosphorylase b. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Richards R. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies on substrate binding to phosphoglucomutase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. J., Mann S. A., Philip G., Oliveira R. J. A probe into the catalytic activity and subunit assembly of glycogen phosphorylase. Desensitization of allosteric control by limited tryptic digestion. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6090–6098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths J. R., Dwek R. A., Radda G. K. Heterotropic interactions of ligands with phosphorylase b. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 2;61(1):243–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMREICH E., CORI C. F. THE ROLE OF ADENYLIC ACID IN THE ACTIVATION OF PHOSPHORYLASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:131–138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajdu J., Dombrádi V., Bot G., Friedrich P. Structural changes in glycogen phosphorlase as revealed by cross-linking with bifunctional diimidates: phosphorylase b. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):4037–4041. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. A., Johnson L. N., Stuart D. I., Stura E. A., Wilson K. S., Zanotti G. Phosphorylase: control and activity. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):23–41. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Jenkins J. A., Wilson K. S., Stura E. A., Zanotti G. Proposals for the catalytic mechanism of glycogen phosphorylase beta prompted by crystallographic studies on glucose 1-phosphate binding. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 15;140(4):565–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Madsen N. B., Mosley J., Wilson K. S. The crystal structure of phosphorylase beta at 6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 25;90(4):703–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Stura E. A., Wilson K. S., Sansom M. S., Weber I. T. Nucleotide binding to glycogen phosphorylase b in the crystal. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 5;134(3):639–653. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasvinsky P. J., Madsen N. B., Sygusch J., Fletterick R. J. The regulation of glycogen phosphorylase alpha by nucleotide derivatives. Kinetic and x-ray crystallographic studies. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3343–3351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. A., Dalgarno D. C., Esnouf M. P., Klevit R. E., Scott G. M., Williams R. J. The mobility of calcium-trigger proteins and its function. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;93:72–97. doi: 10.1002/9780470720752.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., PARMEGGIANI A. REGULATION OF GLYCOGENOLYSIS IN MUSCLE. 3. CONTROL OF MUSCLE GLYCOGEN PHOSPHORYLASE ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2440–2445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen N. B., KasvinskyPJ, Fletterick R. J. Allosteric transitions of phosphorylase a and the regulation of glycogen metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9097–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen N. B., Shechosky S. Allosteric properties of phosphorylase b. II. Comparison with a kinetic model. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3301–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melpidou A. E., Oikonomakos N. G. Effect of glucose-6-P on the catalytic and structural properties of glycogen phosphorylase a. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80884-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morange M., Blanco F. G., Vandenbunder B., Buc H. AMP analogs: their function in the activation of glycogen phosphorylase b. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):553–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Nakazawa A., Hayaishi O. Studies on the interaction between regulatory enzymes and effectors. II. Effect of adenosine 5'-monophosphate analogues on glycogen phosphorylase B. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5266–5271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim Z. H., Perrett D., Griffiths J. R. Skeletal muscle purine nucleotide levels in normal and phosphorylase kinase deficient mice. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80687-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim Z. H., Perrett D., Lutaya G., Griffiths J. R. Metabolic adaptation in phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Changes in metabolite concentrations during tetanic stimulation of mouse leg muscles. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):331–341. doi: 10.1042/bj1860331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprang S., Fletterick R. J. Subunit interactions and the allosteric response in phosphorylase. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):175–192. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84932-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stura E. A., Zanotti G., Babu Y. S., Sansom M. S., Stuart D. I., Wilson K. S., Johnson L. N., Van de Werve G. Comparison of AMP and NADH binding to glycogen phosphorylase b. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):529–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Koide A., Hermann J., Ericsson L. H., Kumar S., Wade R. D., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Fischer E. H. Complete amino acid sequence of rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4762–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu J. I., Graves D. J. Inhibition of the phosphorylase kinase catalyzed reaction by glucose-6-P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Tu J. I., Lo F. M. Effect of glucose 6-phosphate on the nucleotide site of glycogen phosphorylase b. A general approach for negative heterotropic interactions. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3115–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Johnson L. N., Wilson K. S., Yeates D. G., Wild D. L., Jenkins J. A. Crystallographic studies on the activity of glycogen phosphorylase b. Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):433–437. doi: 10.1038/274433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers S. G., Madsen N. B. Nucleotide activation of glycogen phosphorylase b occurs only when the nucleotide phosphate is in a dianionic form. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


