Abstract
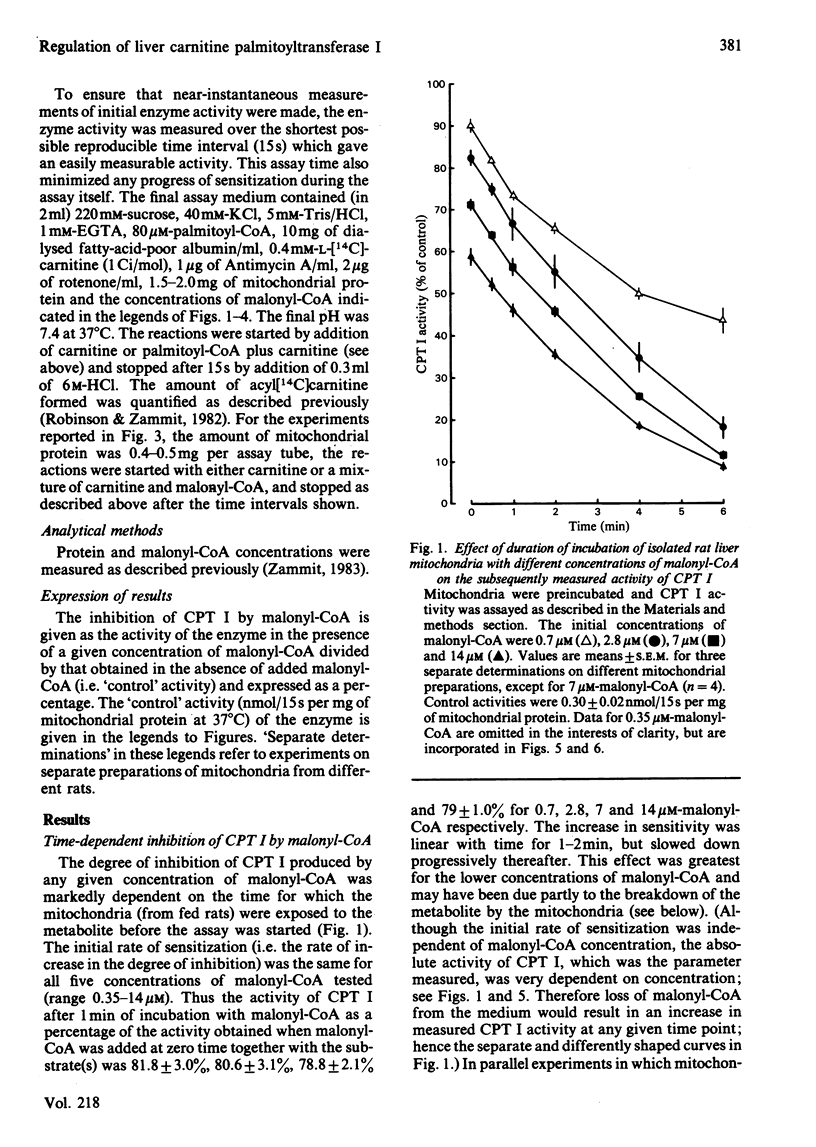
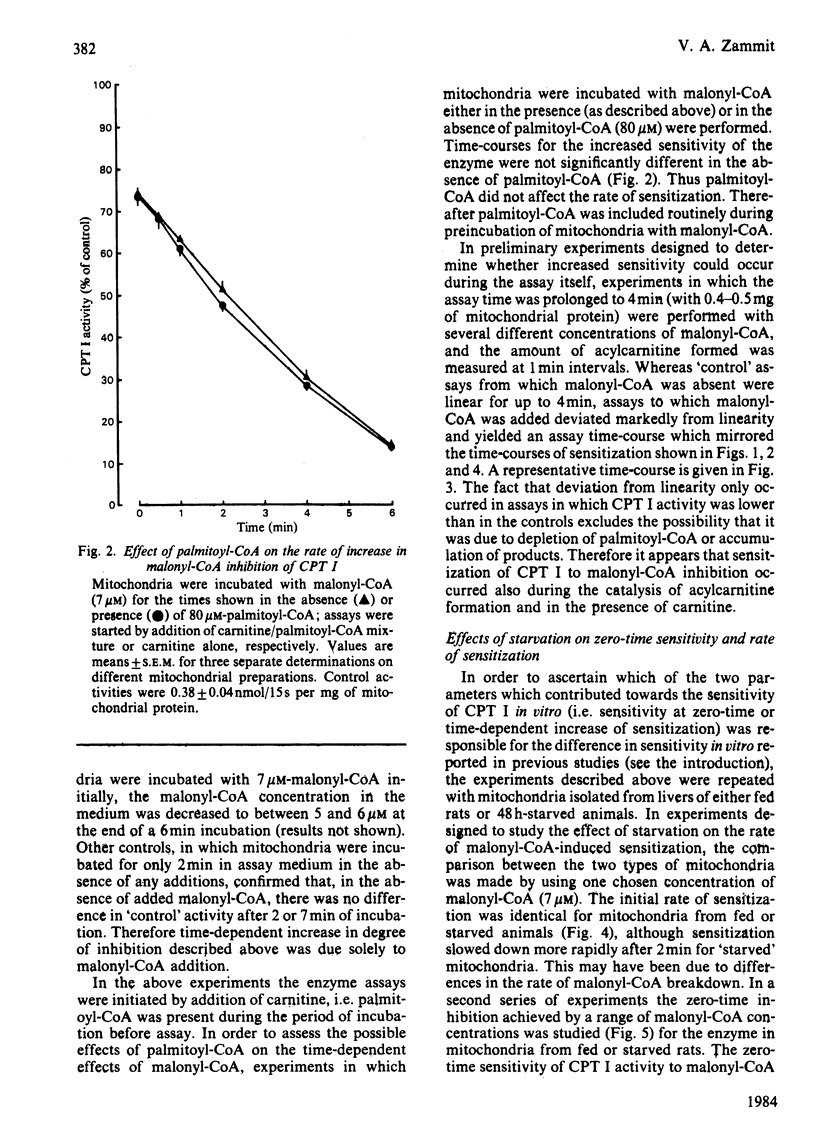
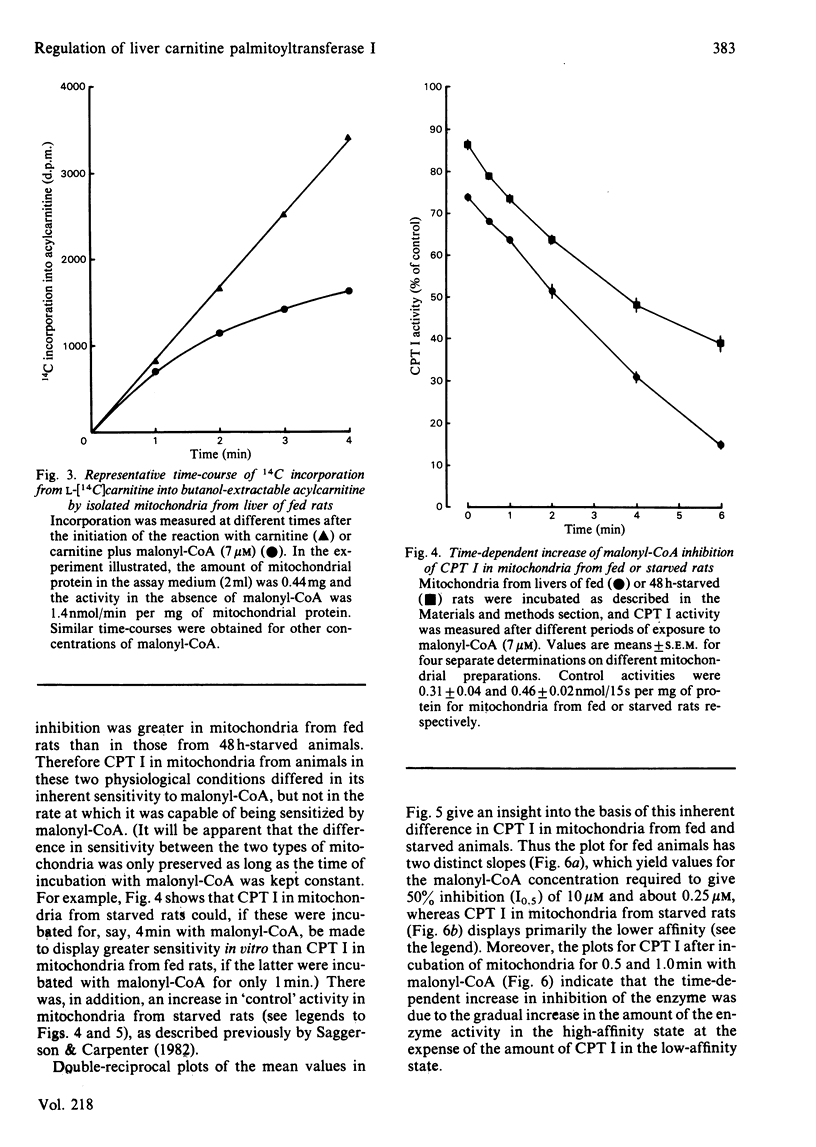
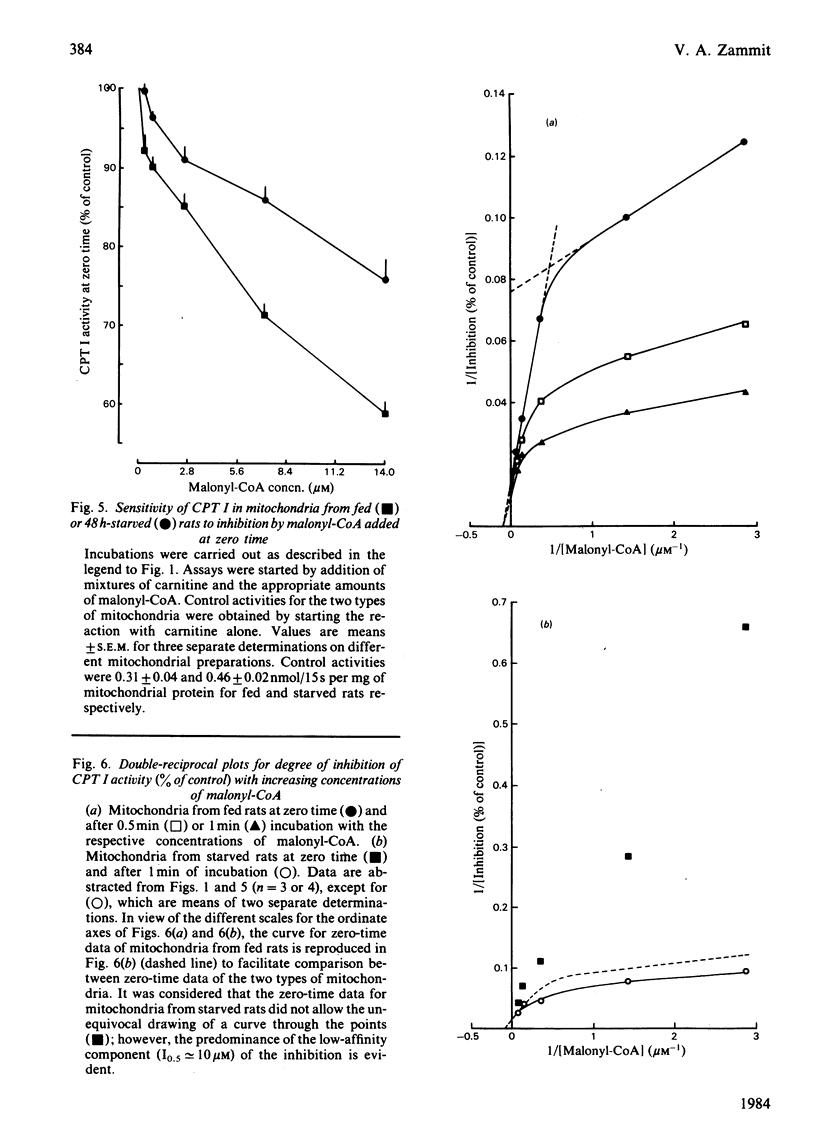
The degree of inhibition of CPT I (carnitine palmitoyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.21) in isolated rat liver mitochondria by malonyl-CoA was studied by measuring the activity of the enzyme over a short period (15s) after exposure of the mitochondria to malonyl-CoA for different lengths of time. Inhibition of CPT I by malonyl-CoA was markedly time-dependent, and the increase occurred at the same rate in the presence or absence of palmitoyl-CoA (80 microM), and in the presence of carnitine, such that the time-course of acylcarnitine formation deviated markedly from linearity when CPT I activity was measured in the presence of malonyl-CoA over several minutes. The initial rate of increase in degree of inhibition with time was independent of malonyl-CoA concentration. CPT I in mitochondria from 48 h-starved rats had a lower degree of inhibition by malonyl-CoA at zero time, but was equally capable of being sensitized to malonyl-CoA, as judged by an initial rate of increase of inhibition identical with that of the enzyme in mitochondria from fed rats. Double-reciprocal plots for the degree of inhibition produced by different malonyl-CoA concentrations at zero time for the enzyme in mitochondria from fed or starved animals indicated that the enzyme in the latter mitochondria was predominantly in a state with low affinity for malonyl-CoA (concentration required to give 50% inhibition, I0.5 congruent to 10 microM), whereas that in mitochondria from fed rats displayed two distinct sets of affinities: low (congruent to 10 microM) and high (less than 0.3 microM). Plots for mitochondria after incubation for 0.5 or 1 min with malonyl-CoA indicated that the increased sensitivity observed with time was due to a gradual increase in the high-affinity state in both types of mitochondria. These results suggest that the sensitivity of CPT I in rat liver mitochondria in vitro had two components: (i) an instantaneous sensitivity inherent to the enzyme which depends on the nutritional state of the animal from which the mitochondria are isolated, and (ii) a slow, malonyl-CoA-induced, time-dependent increase in sensitivity. It is suggested that the rate of malonyl-CoA-induced sensitization of the enzyme to malonyl-CoA inhibition is limited by a slow first-order process, which occurs after the primary event of interaction of malonyl-CoA with the mitochondria.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook G. A., Nielsen R. C., Hawkins R. A., Mehlman M. A., Lakshmanan M. R., Veech R. L. Effect of glucagon on hepatic malonyl coenzyme A concentration and on lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4421–4424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. A., Otto D. A., Cornell N. W. Malonyl-CoA inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase: interpretation of I50 and K1 values. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):525–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2120525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner D. B., Corin R. E. Formation of a receptor state from which insulin dissociates slowly in hepatic cells and plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9005–9008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guynn R. W., Veloso D., Veech R. L. The concentration of malonyl-coenzyme A and the control of fatty acid synthesis in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7325–7331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. R., Tubbs P. K. The effects of temperature and some inhibitors on the carnitine exchange system of heart mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson I. N., Zammit V. A. Sensitivity of carnitine acyltransferase I to malonly-CoA inhibition in isolated rat liver mitochondria is quantitatively related to hepatic malonyl-CoA concentration in vivo. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):177–179. doi: 10.1042/bj2060177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Carpenter C. A. Effects of fasting and malonyl CoA on the kinetics of carnitine palmitoyltransferase and carnitine octanoyltransferase in intact rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):166–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Carpenter C. A. Response to starvation of hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity and its regulation by malonyl-CoA. Sex differences and effects of pregnancy. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2080673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stakkestad J. A., Bremer J. The outer carnitine palmitoyltransferase and regulation of fatty acid metabolism in rat liver in different thyroid states. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 7;750(2):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. Increased sensitivity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I activity to malonyl-CoA inhibition after preincubation of intact rat liver mitochondria with micromolar concentrations of malonyl-CoA in vitro. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):953–956. doi: 10.1042/bj2100953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. Regulation of hepatic fatty acid metabolism. The activities of mitochondrial and microsomal acyl-CoA:sn-glycerol 3-phosphate O-acyltransferase and the concentrations of malonyl-CoA, non-esterified and esterified carnitine, glycerol 3-phosphate, ketone bodies and long-chain acyl-CoA esters in livers of fed or starved pregnant, lactating and weaned rats. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):75–83. doi: 10.1042/bj1980075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. The effect of glucagon treatment and starvation of virgin and lactating rats on the rates of oxidation of octanoyl-L-carnitine and octanoate by isolated liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):293–300. doi: 10.1042/bj1900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


