Abstract
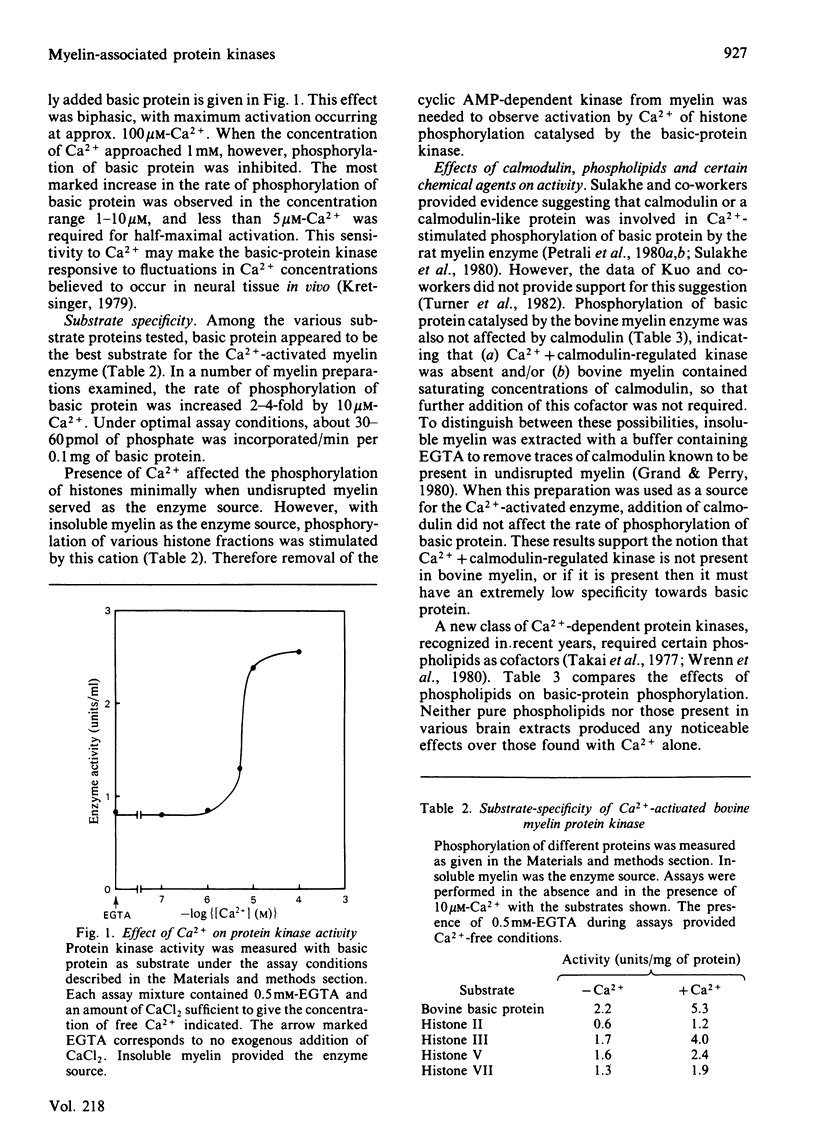
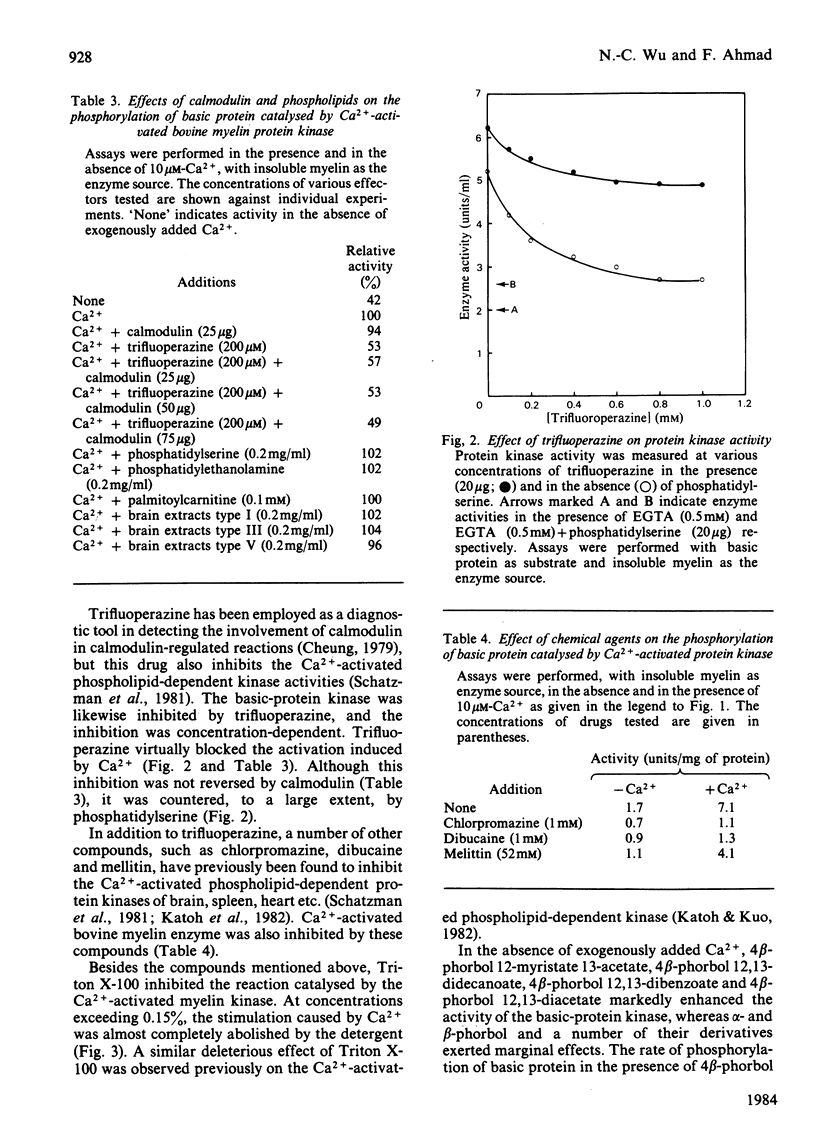
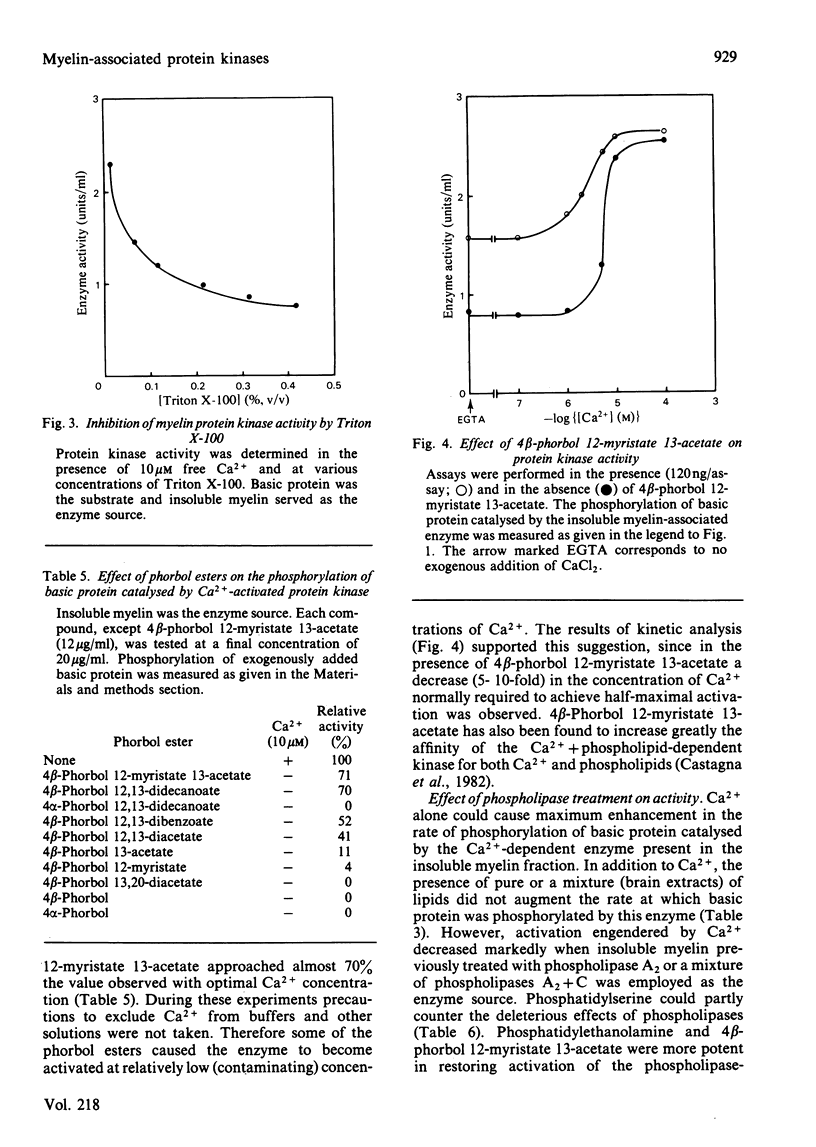
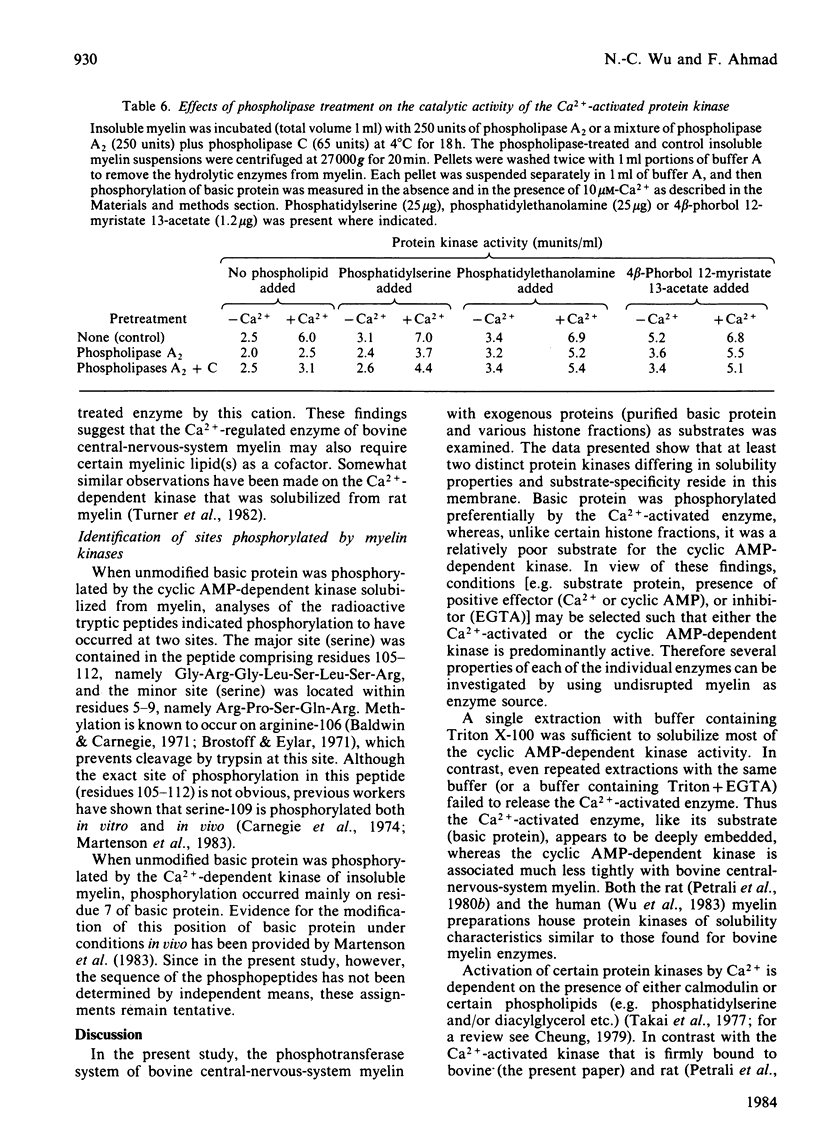
Bovine central-nervous-system myelin was found to contain both Ca2+-activated and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Each enzyme possesses unique solubility and substrate-specificity characteristics. The Ca2+-activated enzyme, like its substrate (basic protein), is probably deeply embedded in the neural membrane, whereas the cyclic AMP-dependent kinase appears to be much less tightly associated with myelin. Treatment of insoluble myelin fraction housing the Ca2+-activated kinase with phospholipase A2 and phospholipases A2 + C causes a decrease in its ability to become activated by Ca2+. This can be countered by phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine. Whereas the activity of the Ca2+-activated membrane-associated kinase is inhibited by chlorpromazine, dibucaine, melittin and Triton X-100, it is activated by certain phorbol diesters (4 beta-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, 4 beta-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate, 4 beta-phorbol 12,13-dibenzoate and 4 beta-phorbol 12,13-diacetate), which appear to exert this effect by lowering the concentration of Ca2+ normally required for the activation of this enzyme. Together these results suggest that the activation of the membrane-associated kinase by Ca2+ most probably requires certain lipids, perhaps those already present in the membrane.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal H. C., O'Connell K., Randle C. L., Agrawal D. Phosphorylation in vivo of four basic proteins of rat brain myelin. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):39–47. doi: 10.1042/bj2010039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal H. C., Randle C. L., Agrawal D. In vivo phosphorylation of two myelin basic proteins of developing rabbit brain. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12243–12246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Carnegie P. R. Isolation and partial characterization of methylated arginines from the encephalitogenic basic protein of myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):69–74. doi: 10.1042/bj1230069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbarese E., Carson J. H., Braun P. E. Accumulation of the four myelin basic proteins in mouse brain during development. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):779–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S., Eylar E. H. Localization of methylated arginine in the A1 protein from myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Dunkley P. R., Kemp B. E., Murray A. W. Phosphorylation of selected serine and threonine residues in myelin basic protein by endogenous and exogenous protein kinases. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):147–150. doi: 10.1038/249147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Kemp B. E., Dunkley P. R., Murray A. W. Phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by an adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):569–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1350569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou F. C., Chou C. H., Shapira R., Kibler R. F. Basis of microheterogeneity of myelin basic protein. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2671–2679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E. Chromatographic fractionation of myelin basic protein. Partial characterization and methylarginine contents of the multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2392–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Brostoff S., Hashim G., Caccam J., Burnett P. Basic A1 protein of the myelin membrane. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5770–5784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The binding of calmodulin to myelin basic protein and histone H2B. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):227–240. doi: 10.1042/bj1890227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Intracellular signals in the brain. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:277–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Kuo J. F. Subcellular distribution of phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase in guinea pig heart, spleen and cerebral cortex, and inhibition of the enzyme by Triton X-100. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):590–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Raynor R. L., Wise B. C., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Helfman D. M., Fain J. N., Kuo J. F. Inhibition by melittin of phospholipid-sensitive and calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):217–224. doi: 10.1042/bj2020217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. The informational role of calcium in the cytosol. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Law M. J., Deibler G. E. Identification of multiple in vivo phosphorylation sites in rabbit myelin basic protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O., Appel S. H. Myelin basic protein phosphatase activity in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1977 Jul;29(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb03920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kakiuchi S. In vitro and in vivo phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by exogenous and endogenous adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in brain. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2769–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kakiuchi S. Phosphoprotein phosphatases for myelin basic protein in myelin and cytosol fractions of brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):458–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T. Isolation of myelin from nerve tissue. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:435–444. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrali E. H., Thiessen B. J., Sulakhe P. V. Characteristics of magnesium-dependent, Ca2+ -stimulated endogenous protein kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of basic proteins in myelin isolated from rat brain stem white matter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):520–535. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrali E. H., Thiessen B. J., Sulakhe P. V. Magnesium ion-dependent, calcium ion stimulated, endogenous protein kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of basic proteins in myelin fraction of rat brain white matter. Int J Biochem. 1980;11(1):21–36. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase: inhibition by antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. Self-association of myelin basic protein: enhancement by detergents and lipids. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2697–2701. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck A. J., Appel S. H. Phosphorylation of myelin basic protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5416–5420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulakhe P. V., Petrali E. H., Davis E. R., Thiessen B. J. Calcium ion stimulated endogenous protein kinase catalyzed phosphorylation of basic proteins in myelin subfractions and myelin-like membrane fraction from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5363–5371. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Inoue M., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. I. Purification and characterization of an active enzyme from bovine cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7603–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Ashby C. D., Walsh D. A. Criteria for the classification of protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:290–299. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. S., Chou C. H., Kibler R. F., Kuo J. F. Basic protein in brain myelin is phosphorylated by endogenous phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1397–1404. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Rudolph S. A., Greengard P. Solubilization of a phosphoprotein and its associated cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase from synaptic membrane fractions, and some kinetic evidence for their existence as a complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):492–503. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyemura K., Tobari C., Hirano S., Tsukada Y. Comparative studies on the myelin proteins of bovine peripheral nerve and spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2607–2614. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn R. W., Katoh N., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Stimulation by phosphatidylserine and calmodulin of calcium-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous proteins from cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12042–12046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu N. C., Martinez J. J., Ahmad F. Phosphoprotein phosphatase of human central nervous system myelin: purification to apparent homogeneity of a low Mr phosphatase and characterization of the high Mr phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu N. C., Yourist J. E., Rector W. D., Ahmad F. Partial characterization of the phosphotransferase system of human central-nervous-system myelin. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):789–795. doi: 10.1042/bj2090789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourist J. E., Ahmad F., Brady A. H. Solubilization and partial characterization of a phosphoprotein phosphatase from human myelin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 10;522(2):452–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


