Abstract
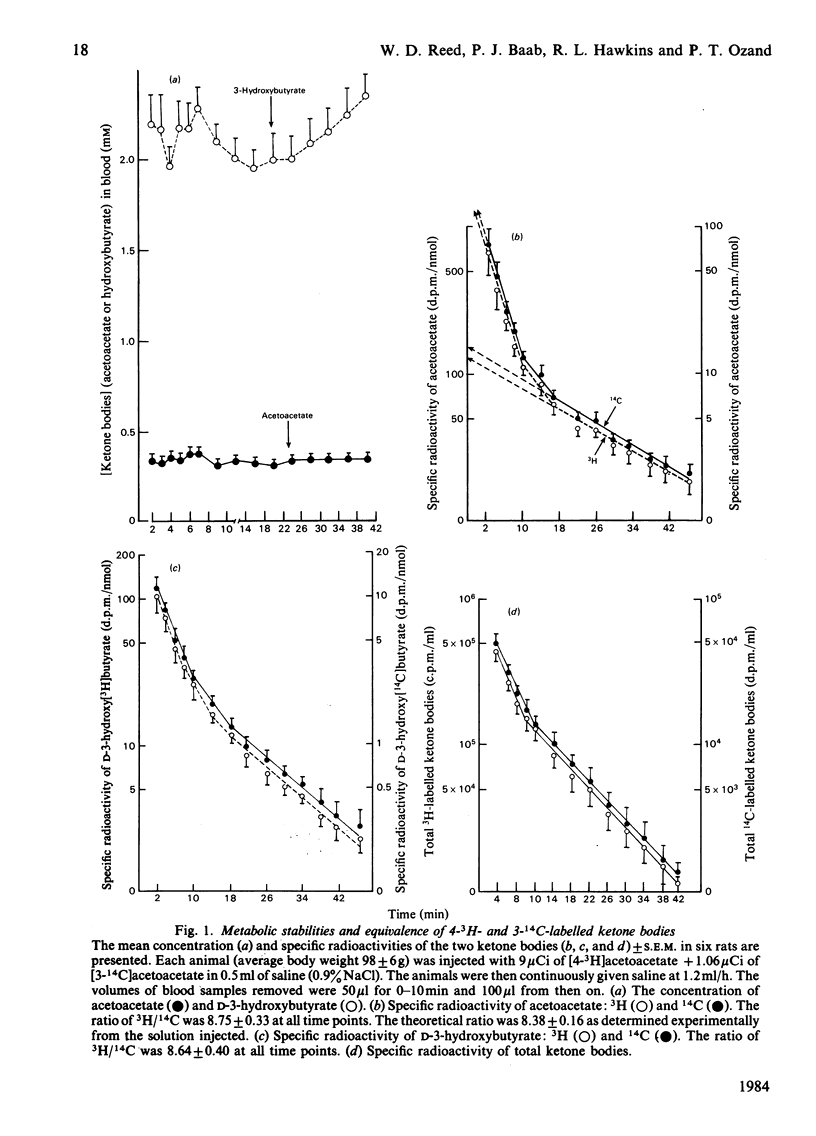
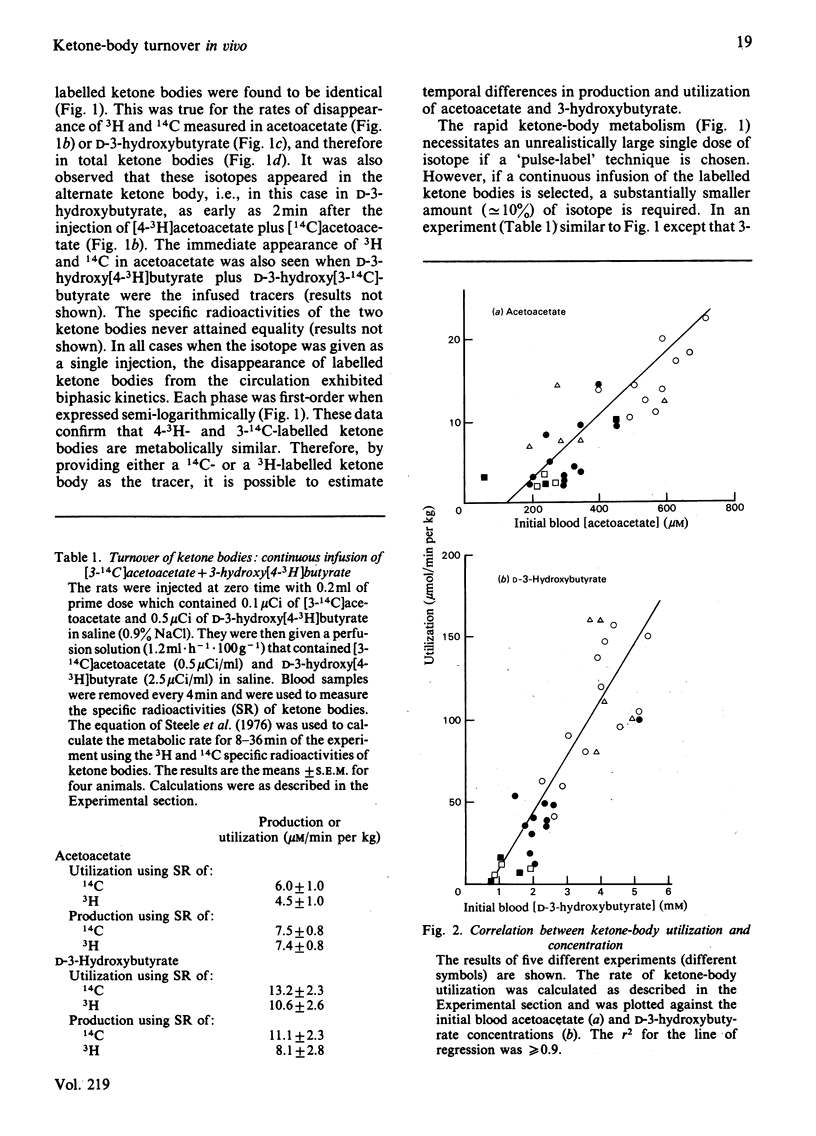
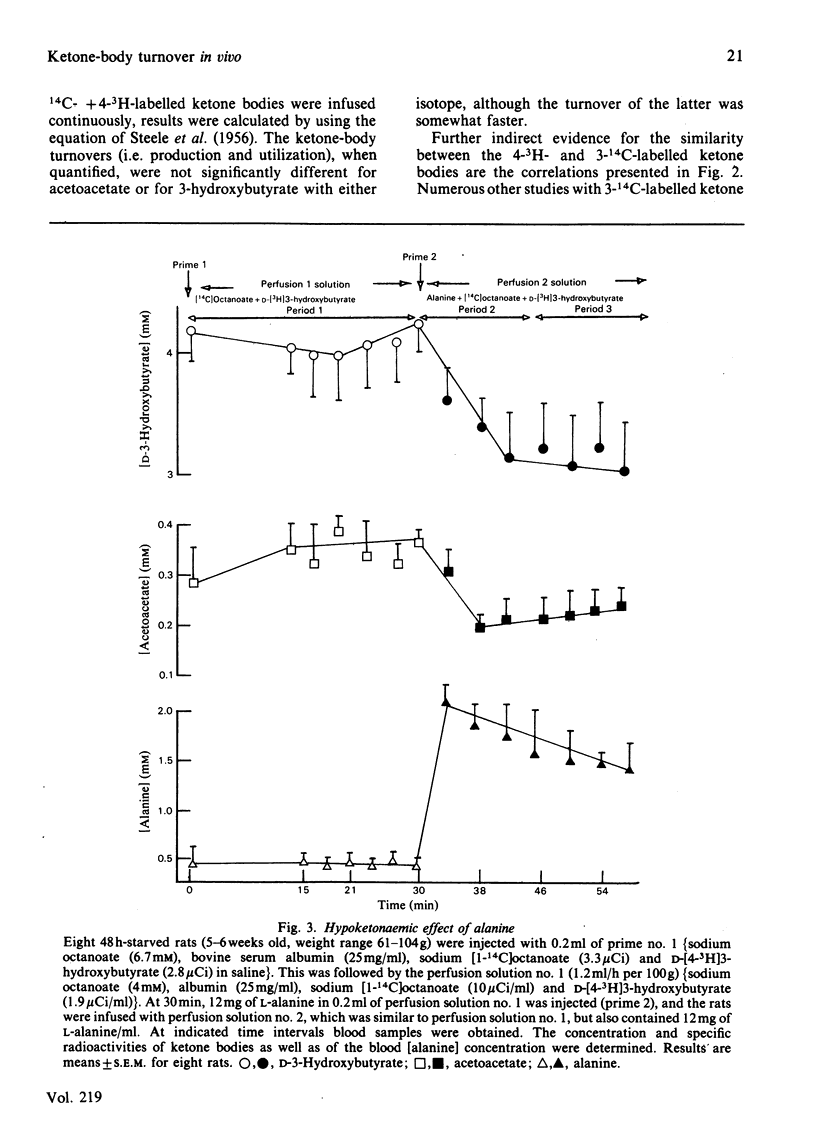
The synthesis of 4-3H-labelled ketone bodies, and their use along with 14C-labelled ketone-body precursors, is employed using an 'in vivo' rat infusion model to measure ketone-body turnover. The use of two isotopes is necessary to measure ketone-body turnover when ketogenesis may occur from more than one precursor such as glucose and fatty or amino acids. Requirements of isotopic equivalence in terms of metabolic similarity, valid stoichiometry and the lack of differences in the kinetics of relevant enzymes is demonstrated for the 4-3H- and 14C-labelled ketone bodies. The hypoketonaemic effect of L-alanine is shown by two distinct phases after the administration of L-alanine. During the first 12 min after alanine administration ther was a 50% decrease in acetoacetate and a 30% decrease in 3-hydroxybutyrate production, with no significant change in the utilization of either compound. The hypoketonaemic action of alanine during the following 16 min was primarily associated with an uptake of 3-hydroxybutyrate that was somewhat greater than the increase in its production. There were essentially equivalent decreases in production and utilization of acetoacetate, resulting in no significant net change in the level of this ketone body in the blood.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allred J. B., Guy D. G. Determination of coenzyme A and acetyl CoA in tissue extracts. Anal Biochem. 1969 May;29(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E. O., Fery F., Neef M. A. Changes induced by exercise in rates of turnover and oxidation of ketone bodies in fasting man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Jan;44(1):5–11. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.44.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E. O. Kinetics of ketone body metabolism in fasting humans. Metabolism. 1979 Jan;28(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton R. N. Isotopic study of ketone body kinetics: invalidity of calculations based upon specific radioactivity of total ketone bodies. Metabolism. 1980 Apr;29(4):392–396. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton R. N. The interconversion and disposal of ketone bodies in untreated and injured post-absorptive rats. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):531–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1360531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates M. W. Kinetics of ketone body metabolism in fasted and diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):984–991. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley B. M., Williamson D. H. Acetoacetate and brain lipogenesis: developmental pattern of acetoacetyl-coenzyme A synthetase in the soluble fraction of rat brain. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):653–656. doi: 10.1042/bj1320653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITZ I. B. Action of carnitine on long chain fatty acid oxidation by liver. Am J Physiol. 1959 Aug;197:297–304. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M., Castro J. Effect of oral alanine on blood beta-hydroxybutyrate and plasma glucose, insulin, free fatty acids, and growth hormone in normal and diabetic subjects. Metabolism. 1974 Apr;23(4):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huth W., Dierich C., von Oeynhausen V., Seubert W. On the mechanism of ketogenesis and its control. I. On a possible role of acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase in the control of ketone body production. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Jun;354(6):635–649. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T. CoA cycling: an enzymatic amplification method for determination of CoASH and acetyl CoA. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jun;66(2):372–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller U., Cherrington A. D., Liljenquist J. E. Ketone body turnover and net hepatic ketone production in fasted and diabetic dogs. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E238–E247. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Foster D. W. Ketogenesis and cholesterol synthesis in normal and neoplastic tissues of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4251–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Leatherman G. F., Foster D. W. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. The site of inhibition of hepatic fatty acid oxidation by malonyl-CoA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4128–4136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosadini R., Datta H., Hodson A., Alberti K. G. A possible mechanism for the anti-ketogenic action of alanine in the rat. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):323–332. doi: 10.1042/bj1900323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozand P. T., Reed W. D., Girard J., Hawkins R. L., Collins R. M., Jr, Tildon J. T., Cornblath M. Hypoketonaemic effect of L-alamine. Specific decrease in blood concentrations of 3-hydroxybutyrate in the rat. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):557–564. doi: 10.1042/bj1640557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozand P. T., Reed W. D., Hawkins R. L., Stevenson J. H., Tildon J. T., Cornblath M. Effect of L-alanine infusion on gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis in the rat in vivo. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):583–591. doi: 10.1042/bj1700583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. D., Ozand P. T. Enzymes of L-(+)-3-hydroxybutyrate metabolism in the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Nov;205(1):94–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. D., Ozand P. T., Tildon J. T., Cornblath M. Effects of starvation and development on mitochondrial acetoacetyl-coenzyme A thiolase of rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):27–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1640027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Veloso D., Ellington E. V., Krebs H. A. Changes in the concentrations of hepatic metabolites on administration of dihydroxyacetone or glycerol to starved rats and their relationship to the control of ketogenesis. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):575–584. doi: 10.1042/bj1140575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


