Abstract
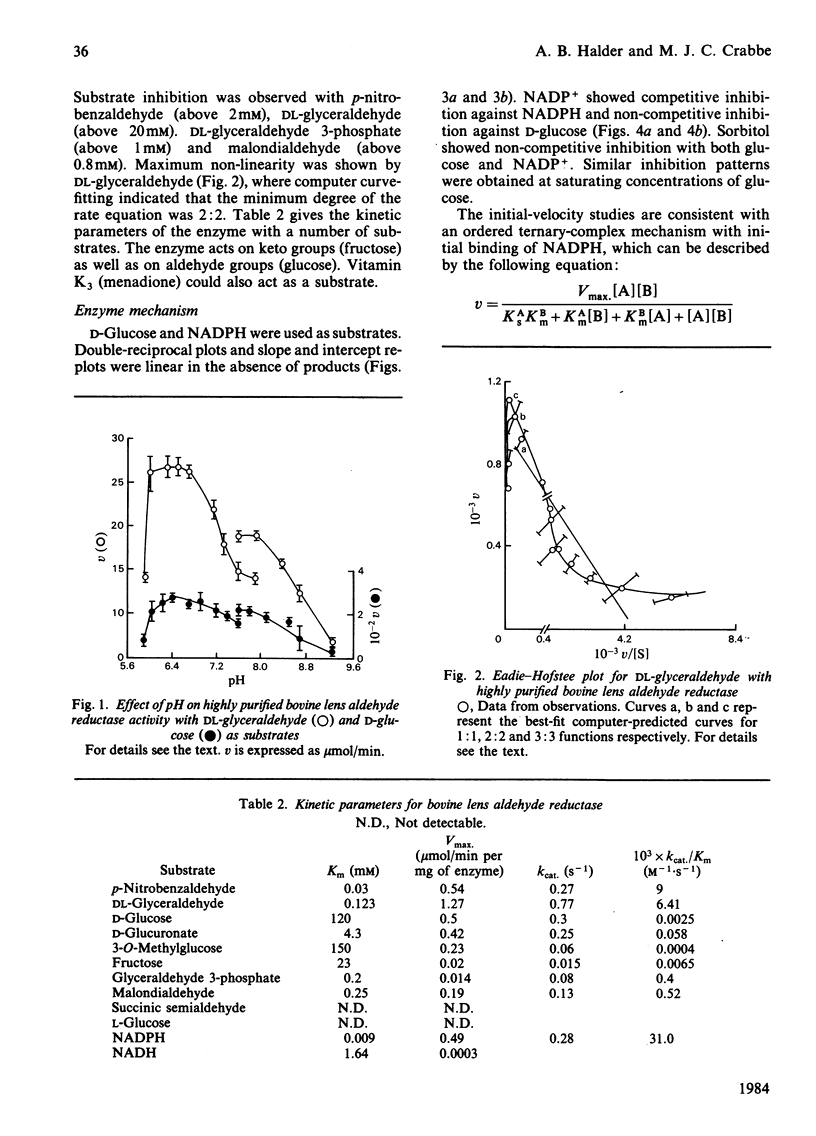
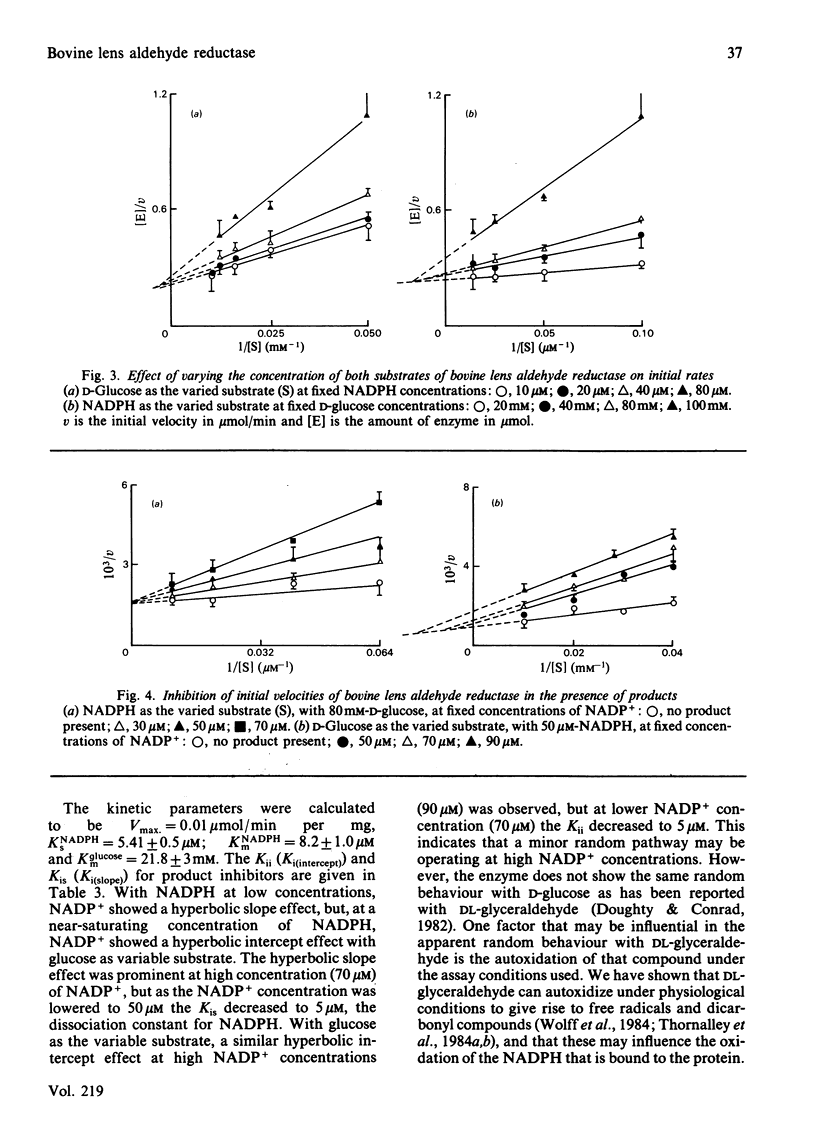
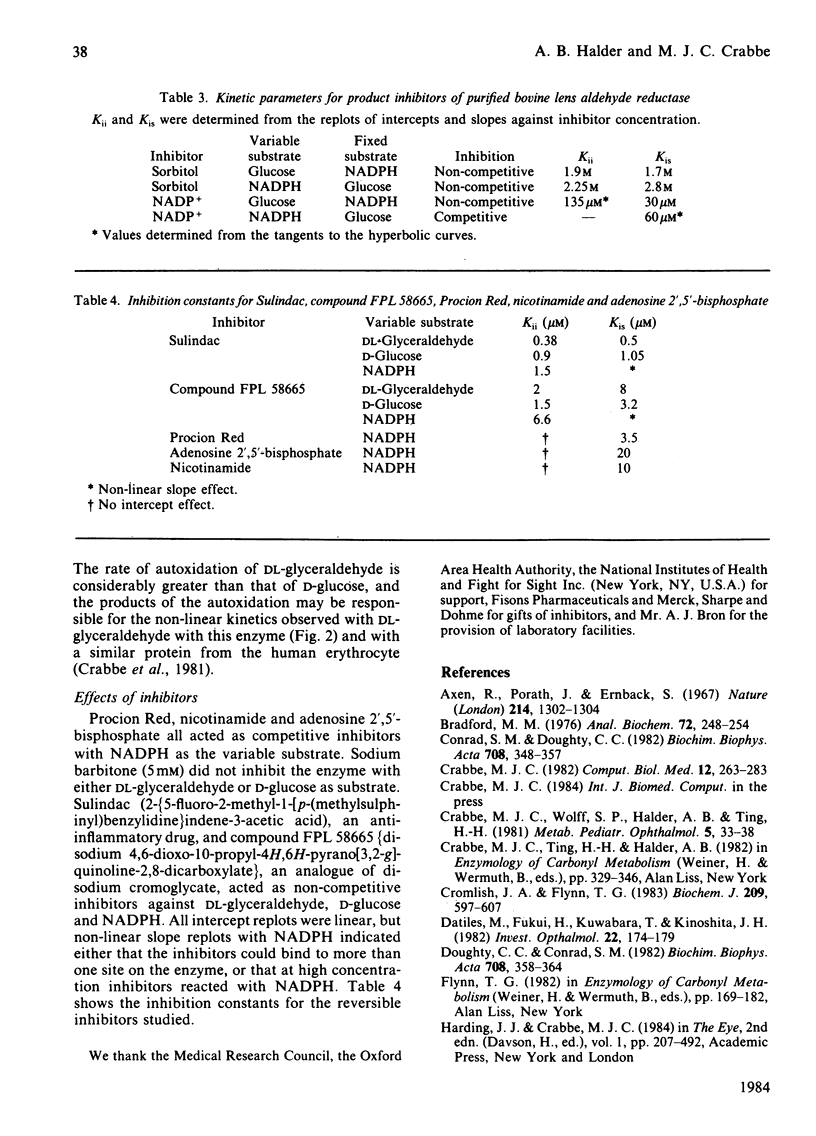
Aldehyde reductase (aldose reductase) was purified to homogeneity (as judged by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis) from bovine lens by affinity chromatography on NADP+-Sepharose. The enzyme, a monomer of Mr about 40000, was active with a variety of alpha- hydroxyketones , including fructose. The minimum degree of the rate equation was 2:2 in the case of DL-glyceraldehyde, but linear kinetics were observed for glucose and NADPH over the concentration range studied. The enzyme largely followed a ternary-complex mechanism, with initial binding of NADPH before glucose and final release of NADP+.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad S. M., Doughty C. C. Comparative studies on aldose reductase from bovine, rat and human lens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 19;708(3):348–357. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe M. J. An enzyme kinetics program for desk-top computers. Comput Biol Med. 1982;12(4):263–283. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(82)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe M. J., Wolff S., Halder A. B., Ting H. H. Diabetic cataracts- is aldose reductase important? Metab Pediatr Ophthalmol. 1981;5(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromlish J. A., Flynn T. G. Purification and characterization of an enzymically active cleavage product of pig kidney aldehyde reductase. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):597–607. doi: 10.1042/bj2090597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datiles M., Fukui H., Kuwabara T., Kinoshita J. H. Galactose cataract prevention with sorbinil, an aldose reductase inhibitor: a light microscopic study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982 Feb;22(2):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty C. C., Conrad S. M. A reaction mechanism for aldose reductase from lens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 19;708(3):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90449-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedziniak J. A., Chylack L. T., Jr, Cheng H. M., Gillis M. K., Kalustian A. A., Tung W. H. The sorbitol pathway in the human lens: aldose reductase and polyol dehydrogenase. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Mar;20(3):314–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., PASSONNEAU J. V., ROCK M. K. The stability of pyridine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2756–2759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbach K., Guilford H., Ohlsson R., Scott M. General ligands in affinity chromatography. Cofactor-substrate elution of enzymes bound to the immobilized nucleotides adenosine 5'-monophosphate and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(4):625–631. doi: 10.1042/bj1270625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheaff C. M., Doughty C. C. Physical and kinetic properties of homogenous bovine lens aldose reductase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2696–2702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J., Wolff S. P., Crabbe M. J., Stern A. The oxidation of oxyhaemoglobin by glyceraldehyde and other simple monosaccharides. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 1;217(3):615–622. doi: 10.1042/bj2170615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting H. H., Crabbe M. J. Bovine lens aldehyde dehydrogenase. Purification and preliminary characterization. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):351–359. doi: 10.1042/bj2150351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma S. D., Kinoshita J. H. The absence of cataracts in mice with congenital hyperglycemia. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Dec;19(6):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


