Abstract
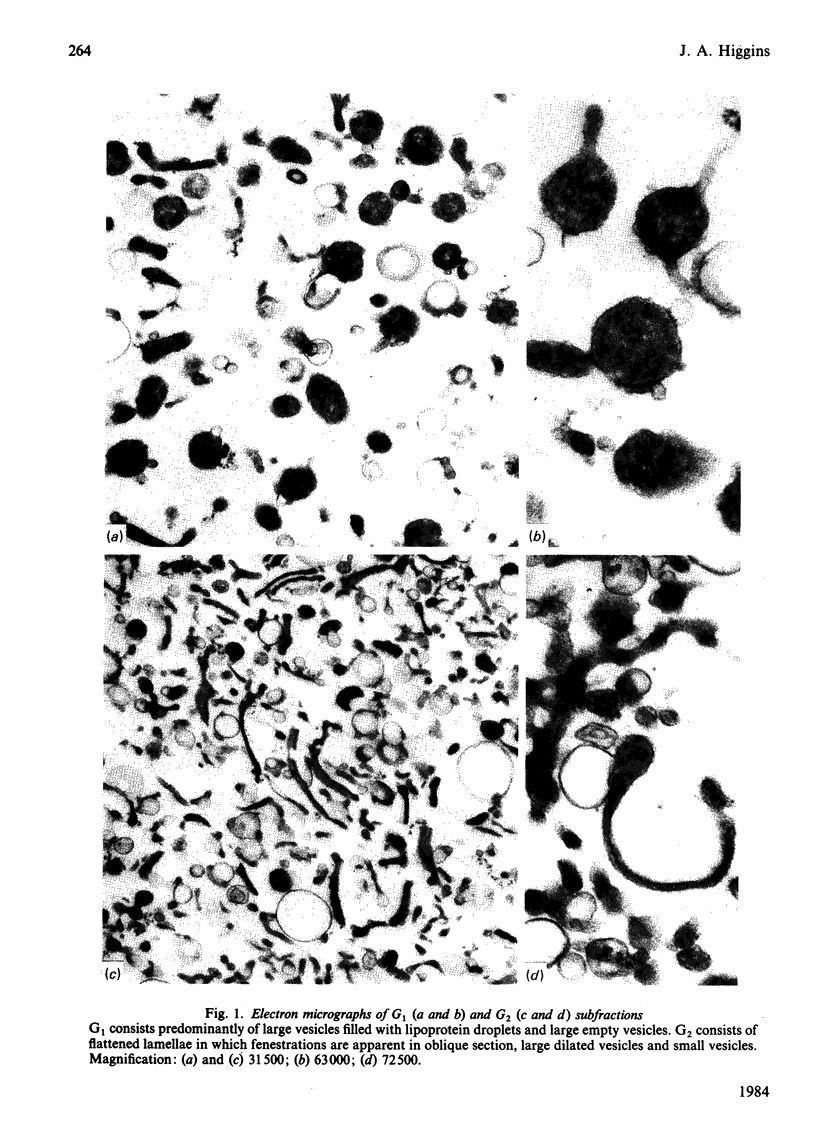
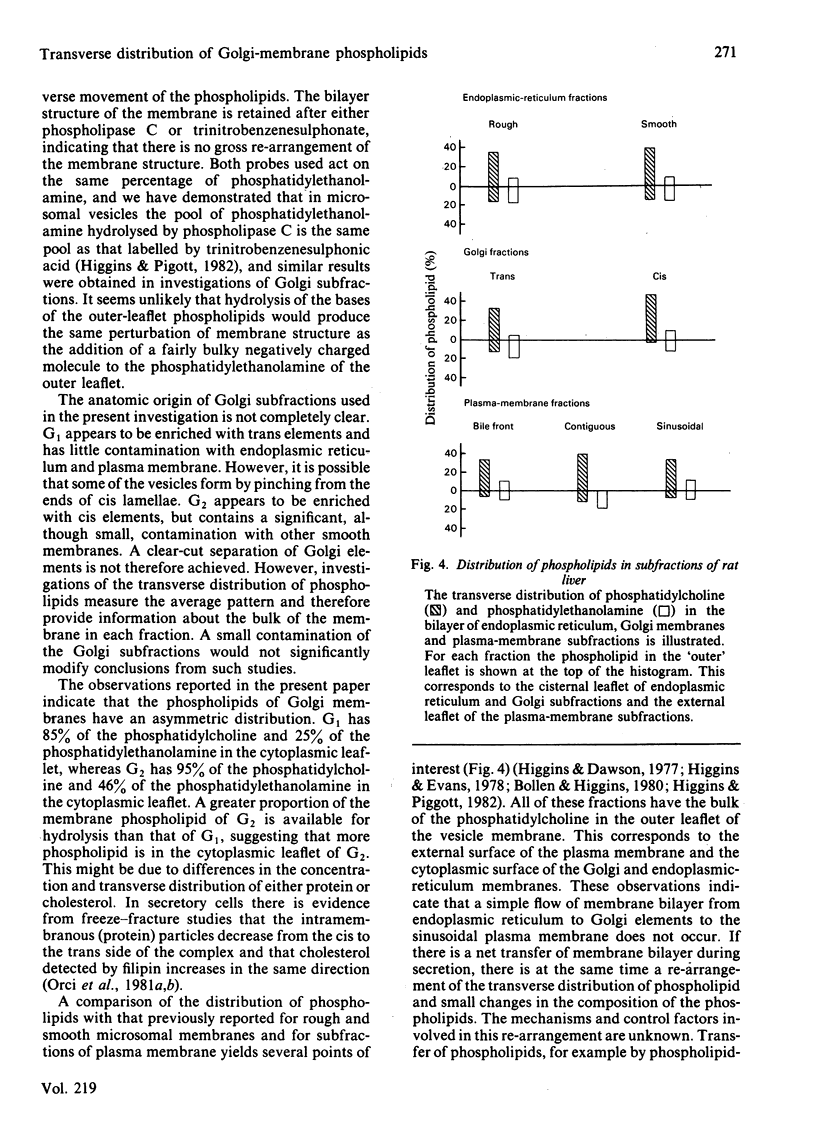
The transverse distribution of phospholipids in the membranes of subfractions of the Golgi complex was investigated by using phospholipase C and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid as probes. In trans-enriched Golgi membranes, 26% of the phosphatidylethanolamine is available for reaction with trinitrobenzenesulphonate or for hydrolysis by phospholipase C, and 72% of the phosphatidylcholine is hydrolysed by phospholipase C. In cis-enriched Golgi membranes, 45% of the phosphatidylethanolamine is available for reaction with trinitrobenzenesulphonate and for hydrolysis by phospholipase C, and 95% of the phosphatidylcholine is hydrolysed by phospholipase C. Under the conditions used with either probe the contents of the Golgi vesicles labelled with either [3H]palmitic acid or [14C]leucine were retained. Galactosyltransferase activity of the membrane vesicles was partially inhibited by the experimental procedures used to investigate the transverse distribution of phospholipids. However, the residual activity was latent, suggesting that the vesicles remained closed. Trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid caused no detectable morphological change in either Golgi fraction. Phospholipase C treatment caused morphological changes, including fusion of vesicles and the appearance of 'signet-ring' profiles in some vesicles; however, the vesicles remained closed and the bilayer was retained. It appears, therefore, that neither probe causes major disruption of the Golgi vesicles nor gains access to the inner surface of the membrane bilayer. These observations suggest that phospholipids have a transverse asymmetry in Golgi membranes, that this distribution differs in trans and cis membranes, and that the phospholipid structure of Golgi membranes is inconsistent with a simple flow of membrane bilayer from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi membranes to plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Low M. G., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Changes in lipid metabolism and cell morphology following attack by phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens) on red cells or lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 1;413(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J. Golgi fractions from livers of control and ethanol-intoxicated rats. Enzymic and morphologic properties following rapid isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 23;555(3):493–503. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90402-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Rachubinski R. A., Sikstrom R. A., Posner B. I., Paiement J. Galactose transfer to endogenous acceptors within Golgi fractions of rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):139–146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen I. C., Higgins J. A. Phospholipid asymmetry in rough- and smooth-endoplasmic-reticulum membranes of untreated and phenobarbital-treated rat liver. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):475–480. doi: 10.1042/bj1890475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude A. Growth and differentiation of cytoplasmic membranes in the course of lipoprotein granule synthesis in the hepatic cell. I. Elaboration of elements of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):745–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich J. H., Bergeron J. J., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Golgi fractions prepared from rat liver homogenates. I. Isolation procedure and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):45–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Bergeron J. J., Palade G. E. Cytochemistry of Golgi fractions prepared from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):8–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. The Golgi apparatus (complex)-(1954-1981)-from artifact to center stage. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):77s–103s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.77s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Dawson R. M. Asymmetry of the phospholipid bilayer of rat liver endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 1;470(3):342–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Evans W. H. Transverse organization of phospholipids across the bilayer of plasma-membrane subfractions of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):563–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1740563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A. Fine-structural changes in rat liver microsomes treated with phospholipase C. J Cell Sci. 1982 Feb;53:211–225. doi: 10.1242/jcs.53.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A. Heterogeneity of phospholipid synthesis in rat liver endoplasmic reticulum during proliferation of smooth membranes. J Cell Sci. 1976 Oct;22(1):173–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Pigott C. A. Asymmetric distribution of phosphatidylethanolamine in the endoplasmic reticulum demonstrated using trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid as a probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Ito A., Palade G. E. Endoplasmic reticulum marker enzymes in Golgi fractions--what does this mean? J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):581–589. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Hepatic Golgi fractions resolved into membrane and content subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):822–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Heterogeneity of lipoprotein particles in hepatic Golgi fractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):833–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Palade G. E. Presence of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase in rat liver Golgi membranes. Evidence obtained by immunoadsorption method. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):590–597. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Ruderman N. B., Herrera M. G. Electron microscopic and biochemical study of lipoprotein synthesis in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1967 Sep;8(5):429–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Debey P., Sabatini D. D. Selective release of content from microsomal vesicles without membrane disassembly. I. Permeability changes induced by low detergent concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):436–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. S., Widnell C. C. Evidence for the translocation of 5'-nucleotidase across hepatic membranes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4013–4017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Montesano R., Meda P., Malaisse-Lagae F., Brown D., Perrelet A., Vassalli P. Heterogeneous distribution of filipin--cholesterol complexes across the cisternae of the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):293–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Cherian M. G. The secretory pathways of rat serum glycoproteins and albumin. Localization of newly formed proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):231–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., STEPHENS N. A simplified spectrophotometric determination of ester groups in lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:244–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y. Lipid synthesis, intracellular transport, storage, and secretion. I. Electron microscopic radioautographic study of liver after injection of tritiated palmitate or glycerol in fasted and ethanol-treated rats. J Cell Biol. 1967 May;33(2):319–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Fahimi H. D. Immunocytochemical localization of albumin in the secretory apparatus of rat liver parenchymal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4970–4974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Golde L. M., Raben J., Batenburg J. J., Fleischer B., Zambrano F., Fleischer S. Biosynthesis of lipids in Golgi complex and other subcellular fractions from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 22;360(2):179–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Phosphoglyceride metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):243–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]