Abstract
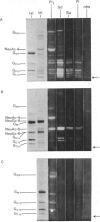
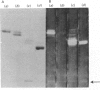
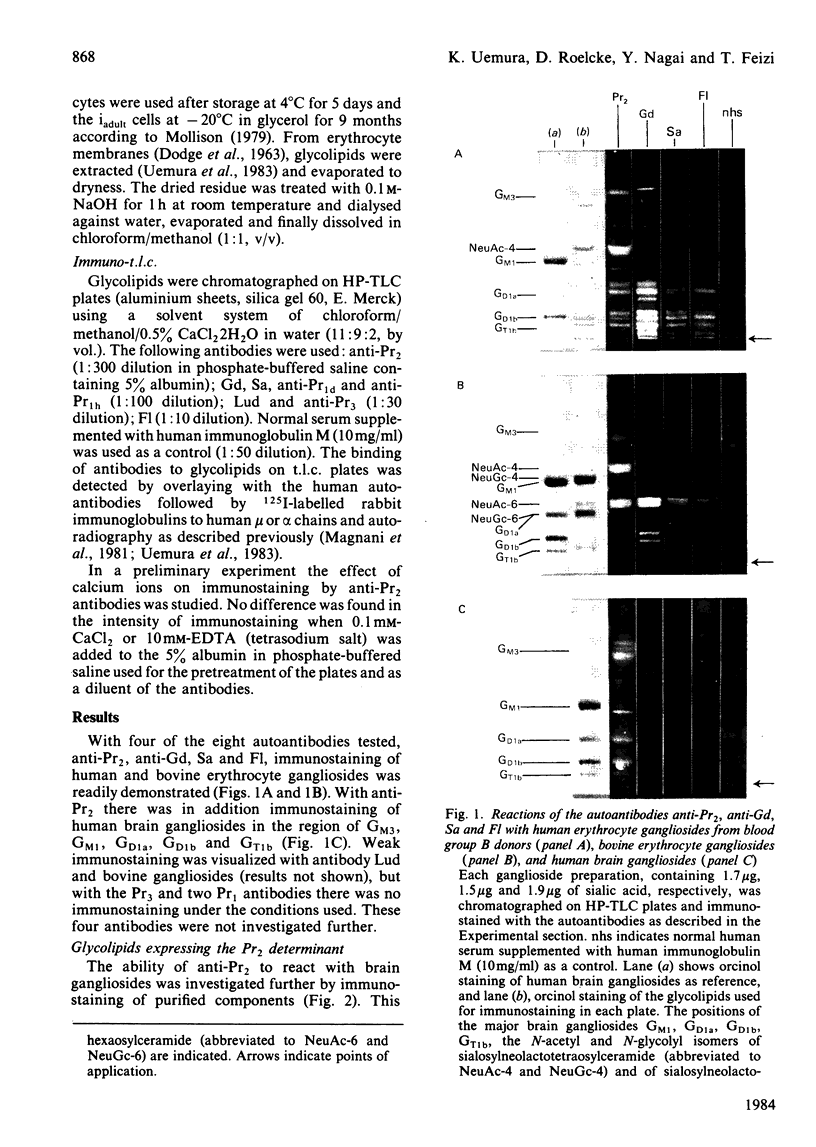
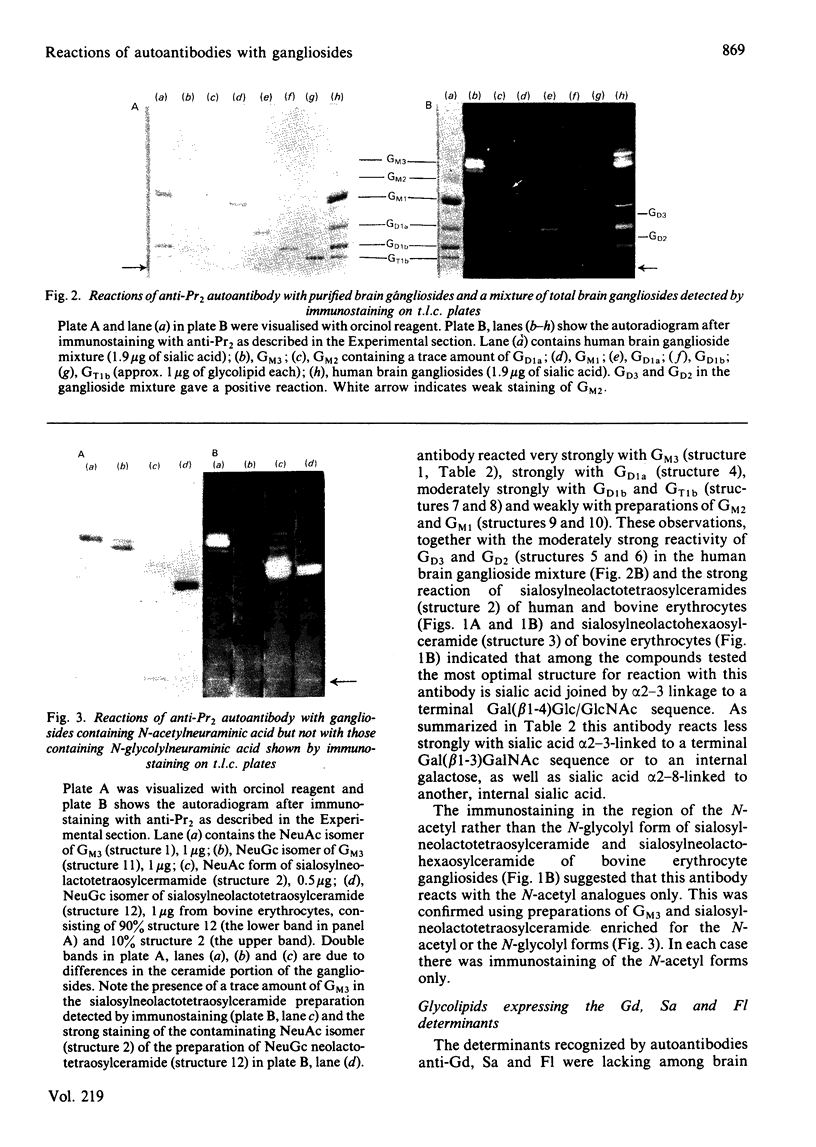
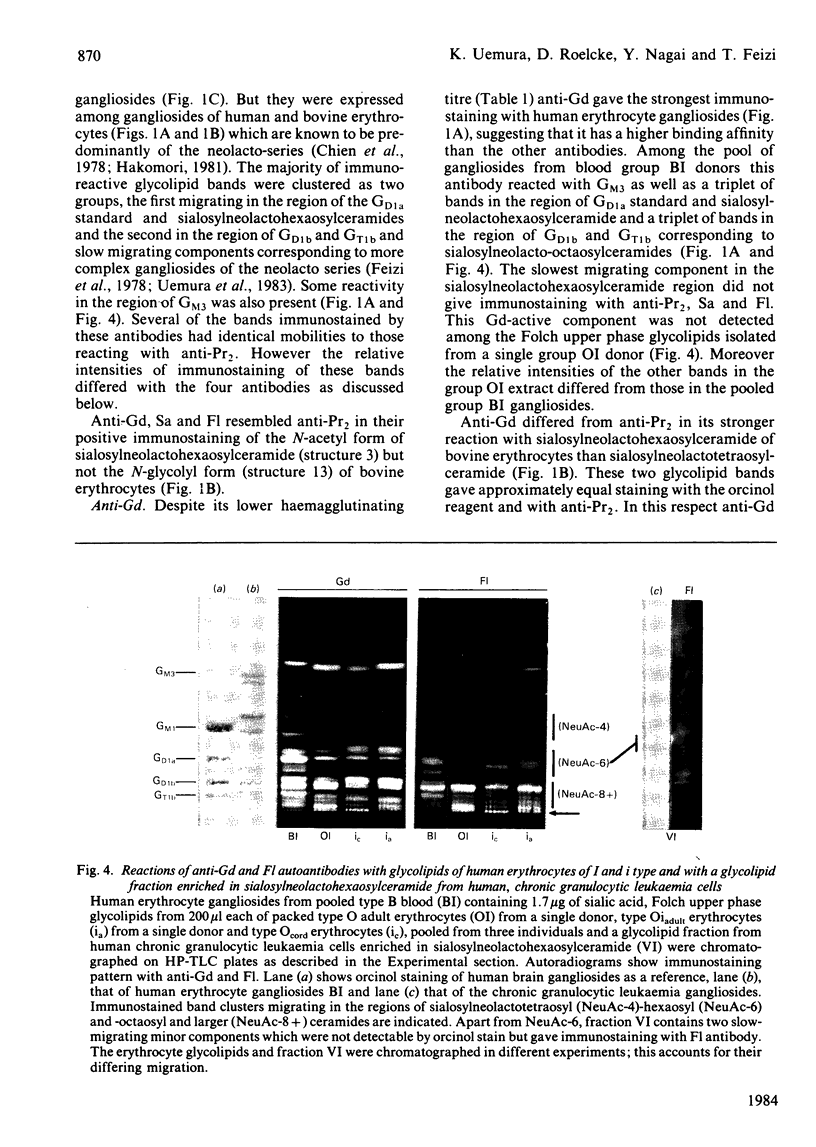
The thin layer chromatogram binding assay was used to study the reaction of several natural-monoclonal autoantibodies which recognize sialic acid-dependent antigens of human erythrocytes. Immunostaining of gangliosides derived from human and bovine erythrocytes was achieved with four autoantibodies designated anti-Pr2, anti-Gd, Sa and Fl, each of which has a different haemagglutination pattern with untreated and proteinase-treated erythrocytes and with cells of I and i antigen types. From the chromatogram binding patterns of anti-Pr2 with gangliosides of the neolacto and the ganglio series, it is deduced that this antibody reacts best with N-acetylneuraminic acid when it is alpha 2-3- or alpha 2-6-linked to a terminal Gal(beta 1-4)Glc/GlcNAc GlcNAc sequence and to a lesser extent when it is alpha 2-3-linked to a terminal Gal(beta 1-3)GalNAc sequence or to an internal galactose and when it is alpha 2-8-linked to another, internal N-acetylneuraminic acid residue. The other three antibodies differ from anti-Pr2 in their lack of reaction with glycolipids of the ganglio series. They react with the NeuAc(alpha 2-3)Gal(beta 1-4)Glc/GlcNAc sequence as found in GM3 and in glycolipids of the neolacto series, but show a preference for the latter, longer sequences. Thus all four antibodies react with sialylated oligosaccharides containing i type (linear) and I type (branched) neolacto backbones. Fl antibody differs from the other three in its stronger reaction with branched neolacto sequences in accordance with its stronger agglutination of erythrocytes of I rather than i type. The four antibodies show a specificity for N-acetyl- rather than N-glycolyl-neuraminic acid.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chien J. L., Li S. C., Laine R. A., Li Y. T. Characterization of gangliosides from bovine erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4031–4035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert W., Fey J., Gärtner C., Geisen H. P., Rautenberg U., Roelcke D., Weicker H. Isolation and partial characterization of the Pr autoantigen determinants. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jun;16(6):413–419. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Childs R. A., Hakomori S. I., Powell M. E. Blood-group-Ii-active gangliosides of human erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):245–254. doi: 10.1042/bj1730245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Childs R. A., Watanabe K., Hakomori S. I. Three types of blood group I specificity among monoclonal anti-I autoantibodies revealed by analogues of a branched erythrocyte glycolipid. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):975–980. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. The antigens Ii, SSEA-1 and ABH are in interrelated system of carbohydrate differentiation antigens expressed on glycosphingolipids and glycoproteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;152:167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. The blood group Ii system: a carbohydrate antigen system defined by naturally monoclonal or oligoclonal autoantibodies of man. Immunol Commun. 1981;10(2):127–156. doi: 10.3109/08820138109050693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Glycosphingolipids in cellular interaction, differentiation, and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:733–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Roelcke D., Peterson K. A., Okada Y., Levery S. B., Hakomori S. Characterization of an epitope (determinant) structure in a developmentally regulated glycolipid antigen defined by a cold agglutinin Fl, recognition of alpha-sialosyl and alpha-L-fucosyl groups in a branched structure. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Aug 16;120:143–157. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura N., Taketomi T. A new procedure for the isolation of brain gangliosides, and determination of their long chain base compositions. J Biochem. 1977 May;81(5):1217–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundu S. K., Marcus D. M., Roelcke D. Glycosphingolipid receptors for anti-Gd and anti-p cold agglutinins. Immunol Lett. 1982 May;4(5):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunishita T., Uemura K., Okano A., Taketomi T. Isolation of basic protein-acidic lipid complex from myelin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1979 Dec;49(6):391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledeen R. W., Yu R. K., Eng L. F. Gangliosides of human myelin: sialosylgalactosylceramide (G7) as a major component. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):829–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher B. A., Lee W. M., Westrick M. A. Glycosphingolipids of normal and leukemic human leukocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Sep 3;47(2):81–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00234409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Brockhaus M., Smith D. F., Ginsburg V., Blaszczyk M., Mitchell K. F., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. A monosialoganglioside is a monoclonal antibody-defined antigen of colon carcinoma. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):55–56. doi: 10.1126/science.7209516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi T., Ando S., Magai Y. High resolution preparative column chromatographic system for gangliosides using DEAE-Sephadex and a new porus silica, Iatrobeads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;441(3):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Watanabe K., Hakomori S. Blood group i and I activities of "lacto-N-norhexaosylceramide" and its analogues: the structural requirements for i-specificities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1286–1293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. A further cold agglutinin, F1, recognizing a N-acetylneuraminic acid-determined antigen. Vox Sang. 1981;41(2):98–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1981.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Brossmer R., Riesen W. Inhibition of human anti-Gd cold agglutinins by sialyllactose. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(3):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. Cold agglutination. Antibodies and antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Jan;2(2):266–280. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Ebert W., Geisen H. P. Anti-Pr3: serological and immunochemical identification of a new anti-Pr subspecificity. Vox Sang. 1976;30(2):122–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1976.tb02802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Pruzanski W., Ebert W., Römer W., Fischer E., Lenhard V., Rauterberg E. A new human monoclonal cold agglutinin Sa recognizing terminal N-acetylneuraminyl groups on the cell surface. Blood. 1980 Apr;55(4):677–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D., Riesen W., Geisen H. P., Ebert W. Serological identification of the new cold agglutinin specificity anti-Gd. Vox Sang. 1977;33(5):304–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1977.tb04480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. Serological studies on the Pr 1 -Pr 2 antigens using dog erythrocytes. Differentiation of Pr 2 from Pr 1 and detection of a Pr 1 heterogeneity: Pr 1h -Pr 1d . Vox Sang. 1973 Apr;24(4):354–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1973.tb02653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. Specificity of IgA cold agglutinins: anti-Pr 1 . Eur J Immunol. 1973 Apr;3(4):206–212. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. The Lud cold agglutinin: a further antibody recognizing N-acetylneuraminic acid-determined antigens not fully expressed at birth. Vox Sang. 1981 Nov-Dec;41(5-6):316–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1981.tb01056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer W., Seelig H. P., Lenhard V., Roelcke D. The distribution of I/i, Pr and Gd antigens in mammalian tissues. Invest Cell Pathol. 1979 Jul-Sep;2(3):157–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui B., Hakomori S. A ceramide tetrasaccharide of human erythrocyte membrane reacting with anti-type XIV pneumococcal polysaccharide antiserum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 13;330(2):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura K., Childs R. A., Hanfland P., Feizi T. A multiplicity of erythrocyte glycolipids of the neolacto series revealed by immuno-thin-layer chromatography with monoclonal anti-I and anti-i antibodies. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF01120703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura K., Yuzawa M., Taketomi T. Characterization of major glycolipids in bovine erythrocyte membrane. J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):463–471. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Hakomori S. I., Childs R. A., Feizi T. Characterization of a blood group I-active ganglioside. Structural requirements for I and i specificities. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3221–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Powell M. E., Hakomori S. I. Isolation and characterization of gangliosides with a new sialosyl linkage and core structures. II. Gangliosides of human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8223–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]