Abstract
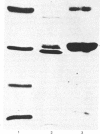
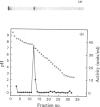
The purification of cathepsin D from pig uterus by two-step affinity chromatography on concanavalin A- and pepstatin-Sepharose was described previously [Afting & Becker (1981) Biochem. J. 197, 519-522]. In this paper, chemical and physical properties of the proteinase are presented. The purified enzyme showed three bands on SDS (sodium dodecyl sulphate)/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, one main band corresponding to an Mr of 31 000 and two minor bands with Mr values of 43 000 and 15 000 respectively. Gel filtration on Bio-gel P-150 and sedimentation-diffusion equilibrium studies give an Mr for the main band of about 35 000. The pI of the enzyme was determined to be 7.2. Haemoglobin was the best substrate, with a Km value of 6.4 X 10(-6)M. It was hydrolysed with a pH optimum between 3.0 and 3.3 for a substrate concentration of 100 microM. The proteinase was stable over the pH range of 3.5-6.5. At pH 6 the enzyme showed stability up to a temperature of 50 degrees C; at pH 3 the activity was already decreased below 40 degrees C. Carbohydrate studies resulted in the staining of all three bands on an SDS/polyacrylamide gel by thymol/H2SO4. After treatment with endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H, all three bands were shifted to a region of lower Mr. Of various inhibitors tested, only pepstatin was strongly inhibiting, with a Ki of 2.1 X 10(-9)M.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERMANN W. W., POTTER V. R. Enzyme inhibition in relation to chemotherapy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1949 Oct;72(1):1–9. doi: 10.3181/00379727-72-17313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afting E. G., Becker M. L., Elce J. S. Proteinase and proteinase-inhibitor activities of rat uterine myometrium during pregnancy and involution. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):99–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1770099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afting E. G., Recker M. L. Two-step affinity-chromatographic purification of cathepsin D from pig myometrium with high yield. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):519–522. doi: 10.1042/bj1970519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Cathepsin D. Purification of isoenzymes from human and chicken liver. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):601–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1170601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M., Tang J. Purification and properties of cathepsin D from porcine spleen. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4528–4536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Conner G. E., Blobel G. Biosynthesis of a lysosomal enzyme. Partial structure of two transient and functionally distinct NH2-terminal sequences in cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11224–11231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. Bovine spleen cathepsin B1 and collagenolytic cathepsin. A comparative study of the properties of the two enzymes in the degradation of native collagen. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):199–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1530199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J. B., Andrews J. R., Voynick I. M., Fruton J. S. The specificity of cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6701–6708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaumann H., Ericsson J. L., Marzella L. Mechanisms of intralysosomal degradation with special reference to autophagocytosis and heterophagocytosis of cell organelles. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;73:149–182. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Tang J. Cathepsin D isozymes from porcine spleens. Large scale purification and polypeptide chain arrangements. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11405–11417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakova O. V., Orekhovich V. N. Vydelenie katepsinov gruppy D s pomoshch'iu khromatografii po srodstvu. Biokhimiia. 1975 Sep-Oct;40(5):969–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress L. F., Peanasky R. J., Klitgaard H. M. Purification, properties, and specificity of hog thyroid proteinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):375–389. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):269–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okitani A., Matsumoto T., Kitamura Y., Kato H. Purification of cathepsin D from rabbit skeletal muscle and its action towards myofibrils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 15;662(2):202–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESS E. M., PORTER R. R., CEBRA J. The isolation and properties of a proteolytic enzyme, cathepsin D, from bovine spleen. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:501–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0740501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puizdar V., Turk V. Cathepsinogen D: characterization and activation to cathepsin D and inhibitory peptides. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen D. Glycoprotein detection in polyacrylamide gel with thymol and sulfuric acid. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):474–476. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt D., Jacobsohn E., Haschen R. J. Purification and properties of cathepsin D from human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Sun E. T. Mechanism of inhibition of pepsin by pepstatin. Effect of inhibitor structure on dissociation constant and time-dependent inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 15;29(16):2205–2212. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky A. I., Woessner J. F., Jr Multiple forms of cathepsin D from bovine uterus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2069–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Turk V. Cathepsin D: rapid isolation by affinity chromatography on haemoglobin-agarose resin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 1;48(1):245–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P., Broghammer U., Kirschke H., Langner J. Intrazellulärer Proteinabbau. VI. Isolierung, Eligenschaften und biologische Bedeutung von Kathepsin D aus der Rattenleber. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1976;35(3-4):269–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Morrison J. F. The kinetics of reversible tight-binding inhibition. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:437–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Katsuda N., Kato K. Affinity purification and properties of cathepsin-E-like acid proteinase from rat spleen. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):499–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]