Abstract
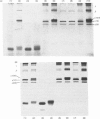
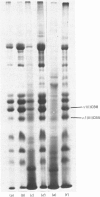
In the past it has been proven difficult to separate and characterize collagen from muscle because of its relative paucity in this tissue. The present report presents a comprehensive methodology, combining methods previously described by McCollester [(1962) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 57, 427-437] and Laurent, Cockerill, McAnulty & Hastings [(1981) Anal. Biochem. 113, 301-312], in which the three major tracts of muscle connective tissue, the epimysium, perimysium and endomysium, may be prepared and separated from the bulk of muscle protein. Connective tissue thus prepared may be washed with salt and treated with pepsin to liberate soluble native collagen, or can be washed with sodium dodecyl sulphate to produce a very clean insoluble collagenous product. This latter type of preparation may be used for quantification of the ratio of the major genetic forms of collagen or for measurement of reducible cross-link content to give reproducible results. It was shown that both the epimysium and perimysium contain type I collagen as the major component and type III collagen as a minor component; perimysium also contained traces of type V collagen. The endomysium, the sheaths of individual muscle fibres, was shown to contain both type I and type III collagen as major components. Type V collagen was also present in small amounts, and type IV collagen, the collagenous component of basement membranes, was purified from endomysial preparations. This is the first biochemical demonstration of the presence of type IV collagen in muscle endomysium. The preparation was shown to be very similar to other type IV collagens from other basement membranes on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and was indistinguishable from EHS sarcoma collagen and placenta type IV collagen in the electron microscope after rotary shadowing.
Full text
PDF




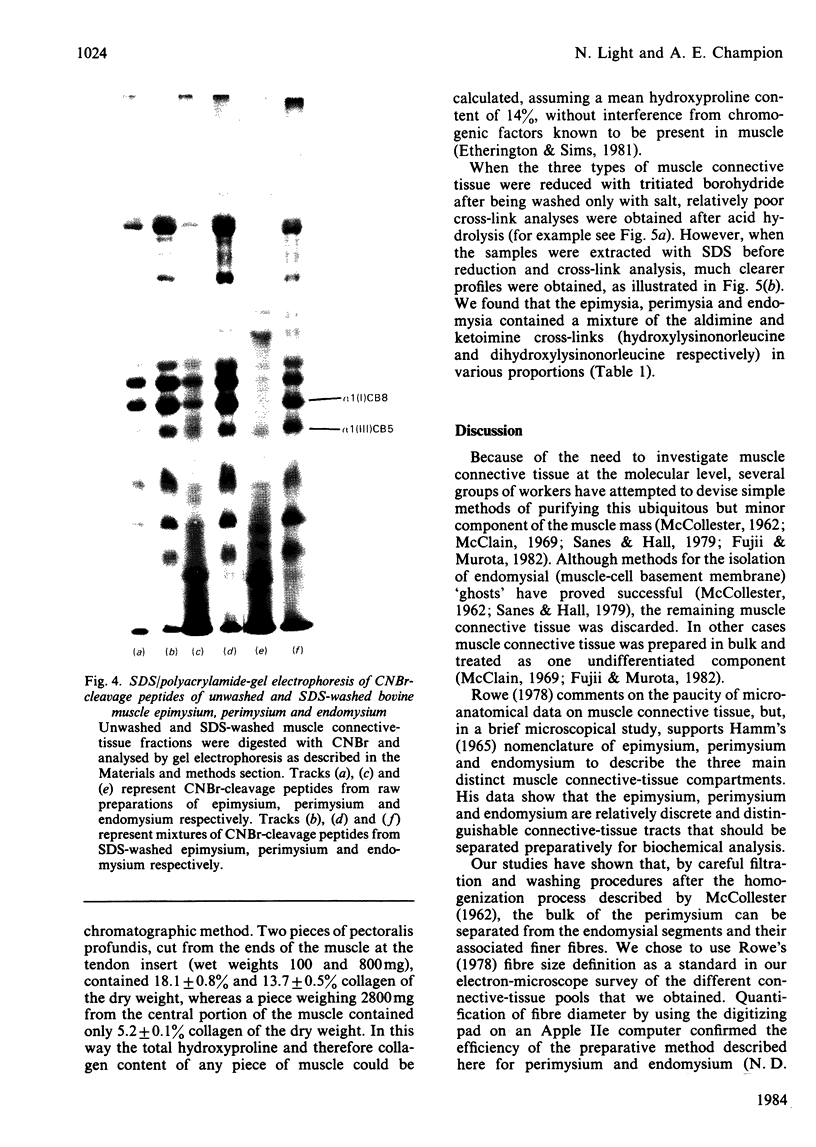
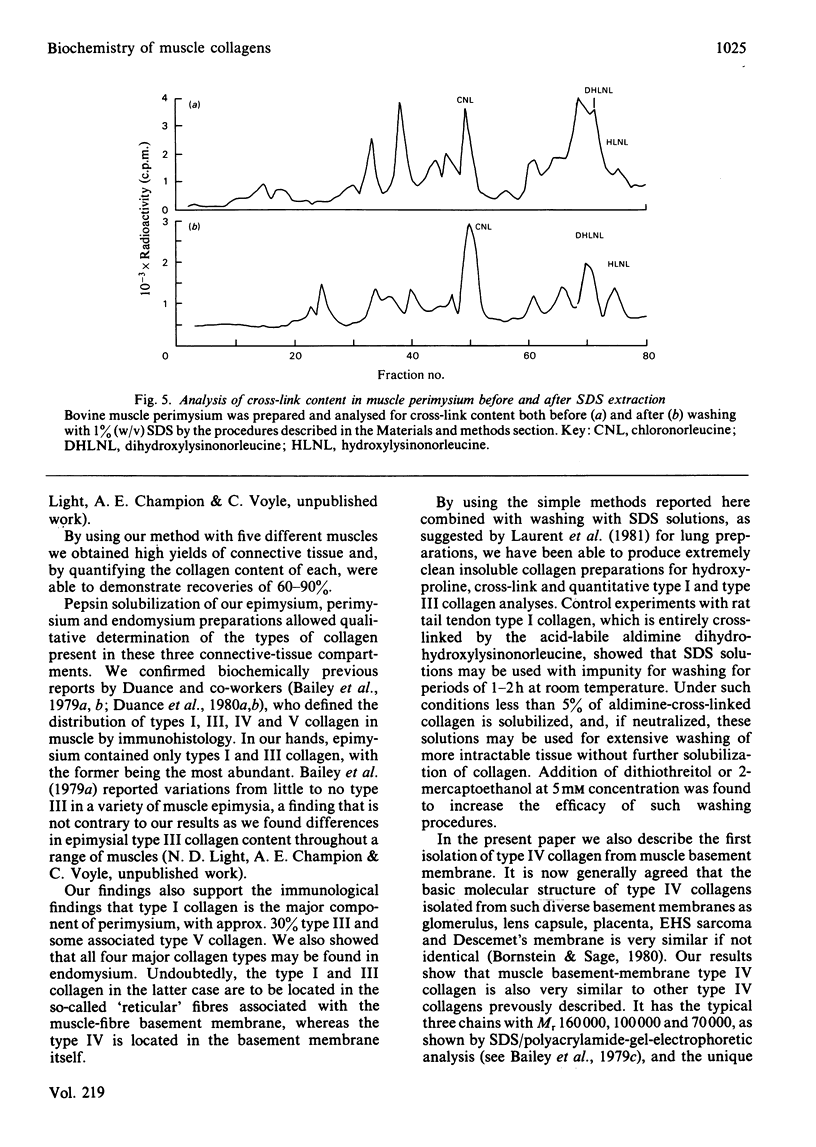

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey A. J., Sims T. J., Duance V. C., Light N. D. Partial characterization of a second basement membrane collagen in human placenta. Evidence for the existence of two type IV collagen molecules. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 15;99(2):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80992-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Sims T. J. Meat tenderness: distribution of molecular species of collagen in bovine muscle. J Sci Food Agric. 1977 Jun;28(6):565–570. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740280615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Duance V. C., Sims T. J., Light N. D. An investigation of the biochemical and histological changes in the collagen of the kidney and skeletal muscle in systemic sclerosis. Coll Relat Res. 1983 May;3(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(83)80006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duance V. C., Black C. M., Dubowitz V., Hughes G. R., Bailey A. J. Polymyositis--an immunofluorescence study on the distribution of collagen types. Muscle Nerve. 1980 Nov-Dec;3(6):487–490. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duance V. C., Stephens H. R., Dunn M., Bailey A. J., Dubowitz V. A role for collagen in the pathogenesis of muscular dystrophy? Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):470–472. doi: 10.1038/284470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsdale T., Bard J. Collagen substrata for studies on cell behavior. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):626–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K., Murota K. Isolation of skeletal muscle collagen. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):449–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACH W., SCHNEIDER G. Der L-Myosin- und Aktingehalt des Kaninchenmuskels. Biochem Z. 1951;321(6):462–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka S. D., Konigsberg I. R. The influence of collagen on the development of muscle clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):119–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionasescu V., Burmeister L., Hanson J. Discriminant analysis of ribosomal protein synthesis findings in carrier detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Genet. 1980;5(1):5–12. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320050103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn K., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Risteli J., Dieringer H., Voss T., Glanville R. W. Macromolecular structure of basement membrane collagens. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 9;125(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., Cockerill P., McAnulty R. J., Hastings J. R. A simplified method for quantitation of the relative amounts of type I and type III collagen in small tissue samples. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. Covalent cross-links in collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D. Estimation of types I and III collagens in whole tissue by quantitation of CNBr peptides on SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton B. H. Collagen synthesis by normal and bromodeoxyuridine-modulated cells in myogenic culture. Dev Biol. 1977 Dec;61(2):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain P. E. Isolation of intramuscular connective tissue. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):181–182. doi: 10.1038/221181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Shimokomaki M., Bailey A. J. The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Age-related changes in the reducible components of intact bovine collagen fibres. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):771–780. doi: 10.1042/bj1310771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Hall Z. W. Antibodies that bind specifically to synaptic sites on muscle fiber basal lamina. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):357–370. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens H. R., Duance V. C., Dunn M. J., Bailey A. J., Dubowitz V. Collagen types in neuromuscular diseases. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Jan;53(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C., Bailey A. J. Molecular weight heterogeneity of the alpha-chain sub-units of collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90758-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Wiedemann H., van Delden V., Furthmayr H., Kühn K. A network model for the organization of type IV collagen molecules in basement membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]