Abstract
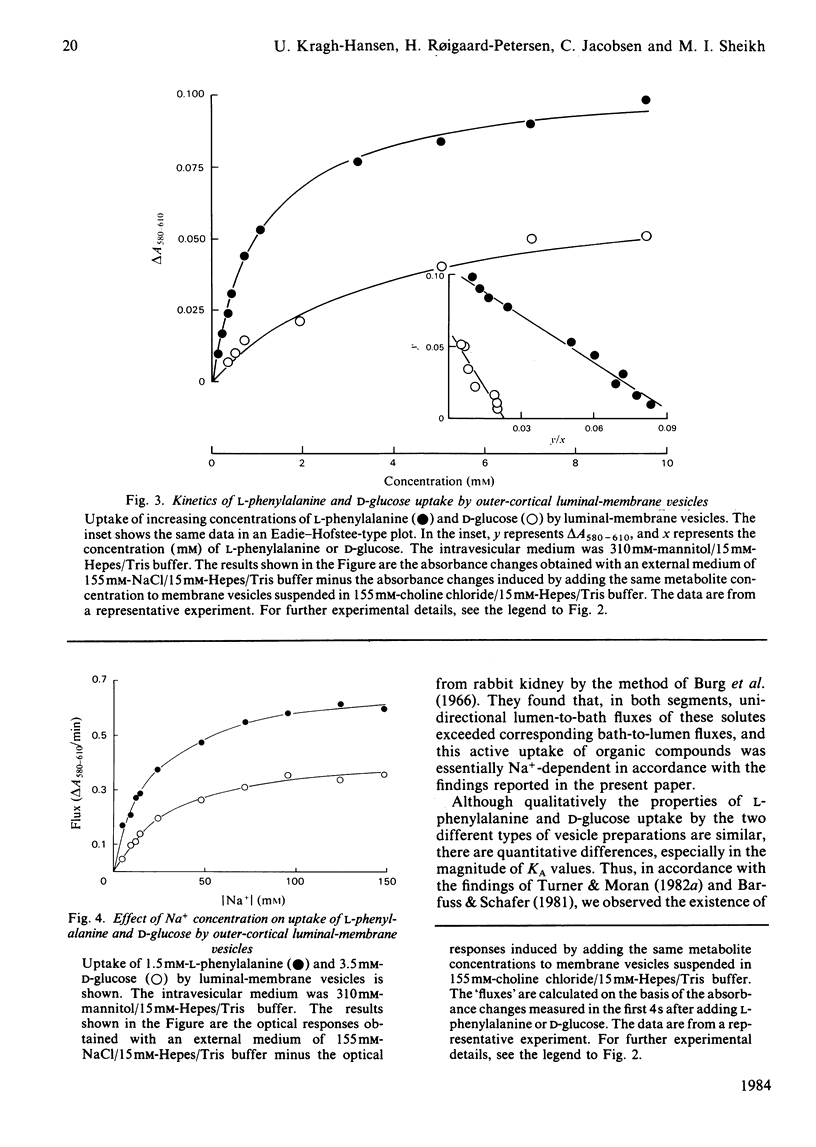
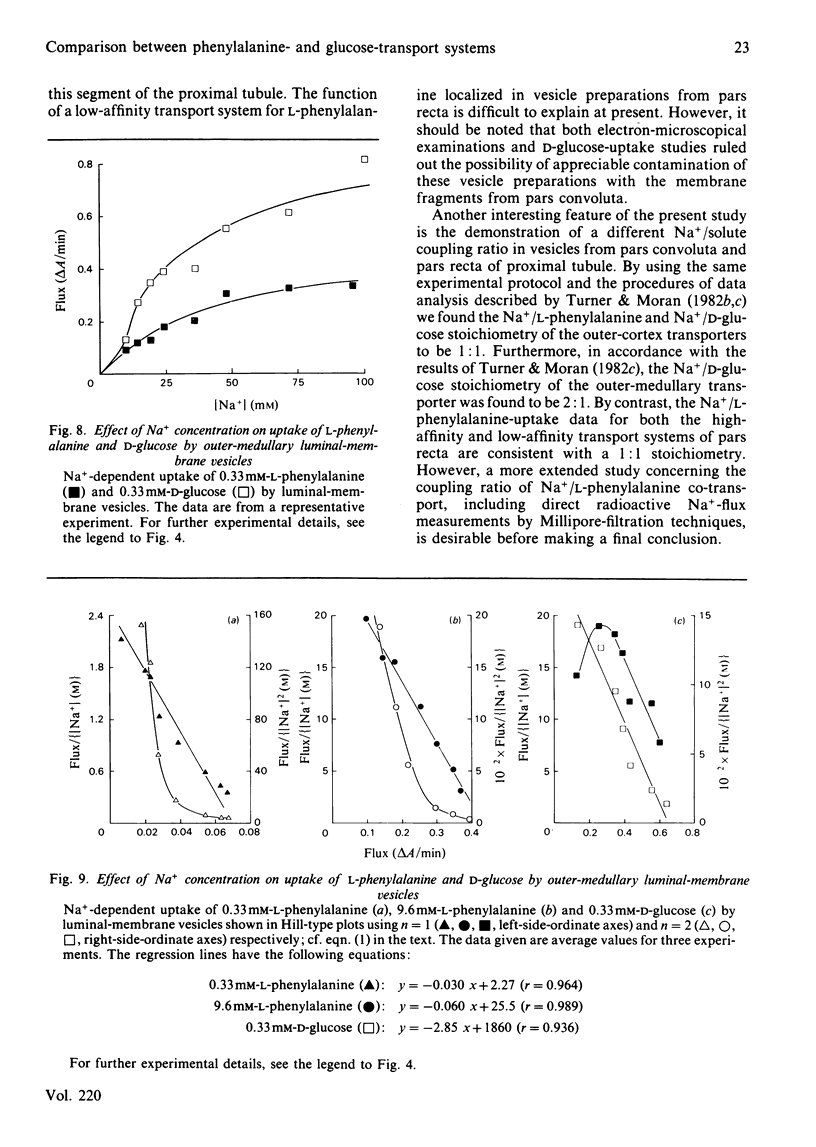
The transport properties for phenylalanine and glucose in luminal-membrane vesicles from outer cortex (pars convoluta) and outer medulla (pars recta) of rabbit kidney were studied by a spectrophotometric method. Uptake of phenylalanine as well as of glucose by the two types of membrane vesicles was found to be Na+-dependent, electrogenic and stereospecific. Na+-dependent transport of L-phenylalanine by outer-cortical membrane vesicles could be accounted for by one transport system (KA congruent to 1.5 mM). By contrast, in the outer-medullary preparation, L-phenylalanine transport occurred via two transport systems, namely a high-affinity system with K1A congruent to 0.33 mM and a low-affinity system with K2A congruent to 7 mM respectively. Na+-dependent uptake of D-glucose by pars convoluta and pars recta membrane vesicles could be described by single, but different, transport systems, namely a low-affinity system with KA congruent to 3.5 mM and a high-affinity system with KA congruent to 0.30 mM respectively. Attempts to calculate the stoichiometry of the different Na+/D-glucose transport systems by using Hill-type plots revealed that the ratio of the Na+/hexose co-transport probably is 1:1 in the case of pars convoluta and 2:1 in membrane vesicles from pars recta. The Na+/L-phenylalanine stoichiometry of the pars convoluta transporter probably is 1:1. Both the high-affinity and the low-affinity Na+-dependent L-phenylalanine transport system of pars recta membrane vesicles seem to operate with a 1:1 stoichiometry. The physiological importance of the arrangement of low-affinity and high-affinity transport systems along the kidney proximal tubule is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson P. S., Sacktor B. The Na+ gradient-dependent transport of D-glucose in renal brush border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6032–6039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Sacktor B. Transport of D-glucose by brush border membranes isolated from the renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 31;356(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barfuss D. W., Schafer J. A. Active amino acid absorption by proximal convoluted and proximal straight tubules. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):F149–F162. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.2.F149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barfuss D. W., Schafer J. A. Differences in active and passive glucose transport along the proximal nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):F322–F332. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.3.F322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers J., Murer H., Kinne R. Phenylalanine uptake in isolated renal brush border vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 5;426(4):598–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of rat renal sugar and amino acid transport. I. Basic phenomena. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Apr;393(2):179–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00582942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C., Frich J. R., Steensgaard J. Determination of affinity of monoclonal antibodies against human IgG. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K. E., Kragh-Hansen U., Røigaard-Petersen H., Sheikh M. I. Citrate uptake by basolateral and luminal membrane vesicles from rabbit kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):F686–F695. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.6.F686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaissling B., Kriz W. Structural analysis of the rabbit kidney. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1979;56:1–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U., Jørgensen K. E., Sheikh M. I. The use of a potential-sensitive cyanine dye for studying ion-dependent electrogenic renal transport of organic solutes. Uptake of L-malate and D-malate by luminal-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):369–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2080369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U., Jørgensen K. E., Sheikh M. I. The use of potential-sensitive cyanine dye for studying ion-dependent electrogenic renal transport of organic solutes. Spectrophotometric measurements. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):359–368. doi: 10.1042/bj2080359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling K. Y., Im W. B., Faust R. G. Na+-independent sugar uptake by rat intestinal and renal brush border and basolateral membrane vesicles. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(6):693–700. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E., Wright S. H., Kippen I., Wright E. M. Pathways for carboxylic acid transport by rabbit renal brush border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):F456–F462. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.5.F456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi P. The reversible delipidation of a solubilized sodium-plus-potassium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from the salt gland of the spiny dogfish. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):61–66. doi: 10.1042/bj1510061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostgaard J., Møller O. Localization of Na+, K+ -ATPase to the inside of the basolateral cell membranes of epithelial cells of proximal and distal tubules in rabbit kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;212(1):17–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00234029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarzija I., Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of rat renal sugar and amino acid transport. III. Neutral amino acids. Pflugers Arch. 1982 May;393(3):119–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarzija I., Hinton B. T., Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of rat renal sugar and amino acid transport. II. Dependence on various transport parameters and inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Apr;393(2):190–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00582943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. I., Kragh-Hansen U., Jørgensen K. E., Røigaard-Petersen H. An efficient method for the isolation and separation of basolateral-membrane and luminal-membrane vesicles from rabbit kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):377–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2080377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. I. Renal handling of phenol red. I. A comparative study on the accumulation of phenol red and p-aminohippurate in rabbit kidney tubules in vitro. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):565–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbernagl S. Physiologie und Pathophysiologie der renalen Aminosäuren-Resorption. Padiatr Padol. 1981;16(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Further studies of proximal tubular brush border membrane D-glucose transport heterogeneity. J Membr Biol. 1982;70(1):37–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01871587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Heterogeneity of sodium-dependent D-glucose transport sites along the proximal tubule: evidence from vesicle studies. Am J Physiol. 1982 Apr;242(4):F406–F414. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.4.F406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Stoichiometric studies of the renal outer cortical brush border membrane D-glucose transporter. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01868649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]