Abstract
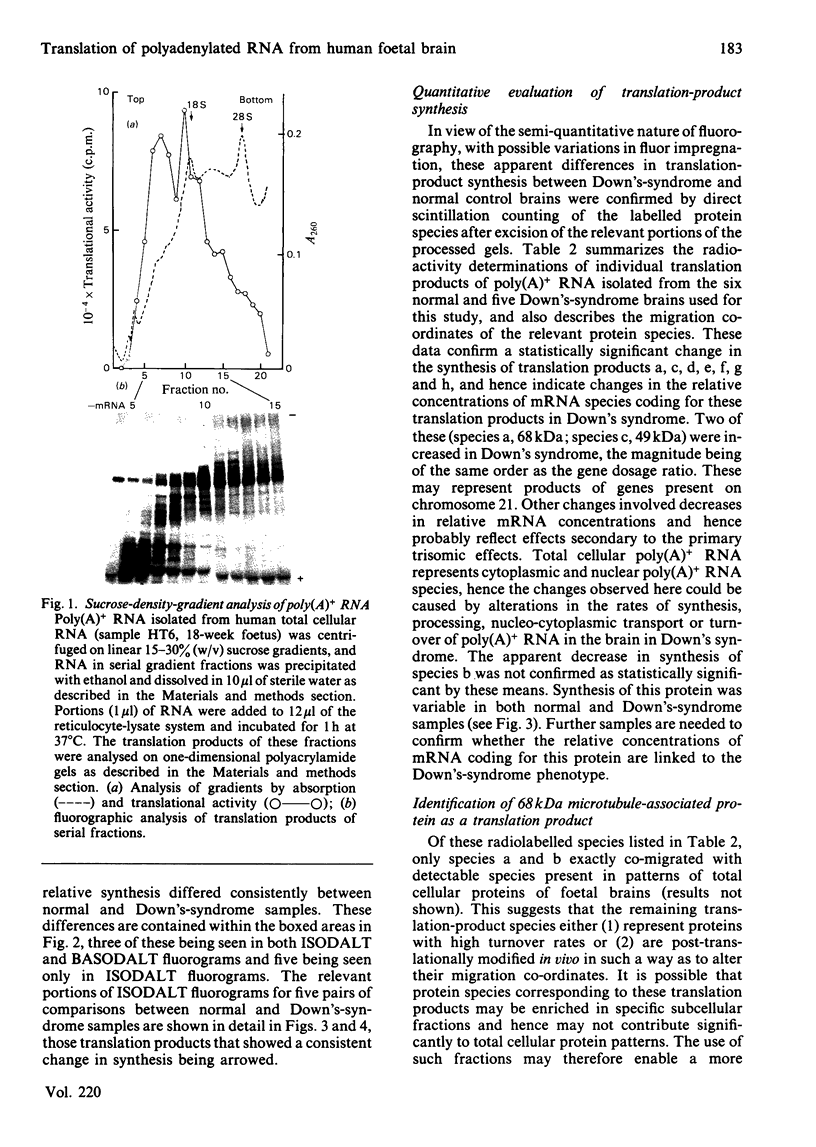
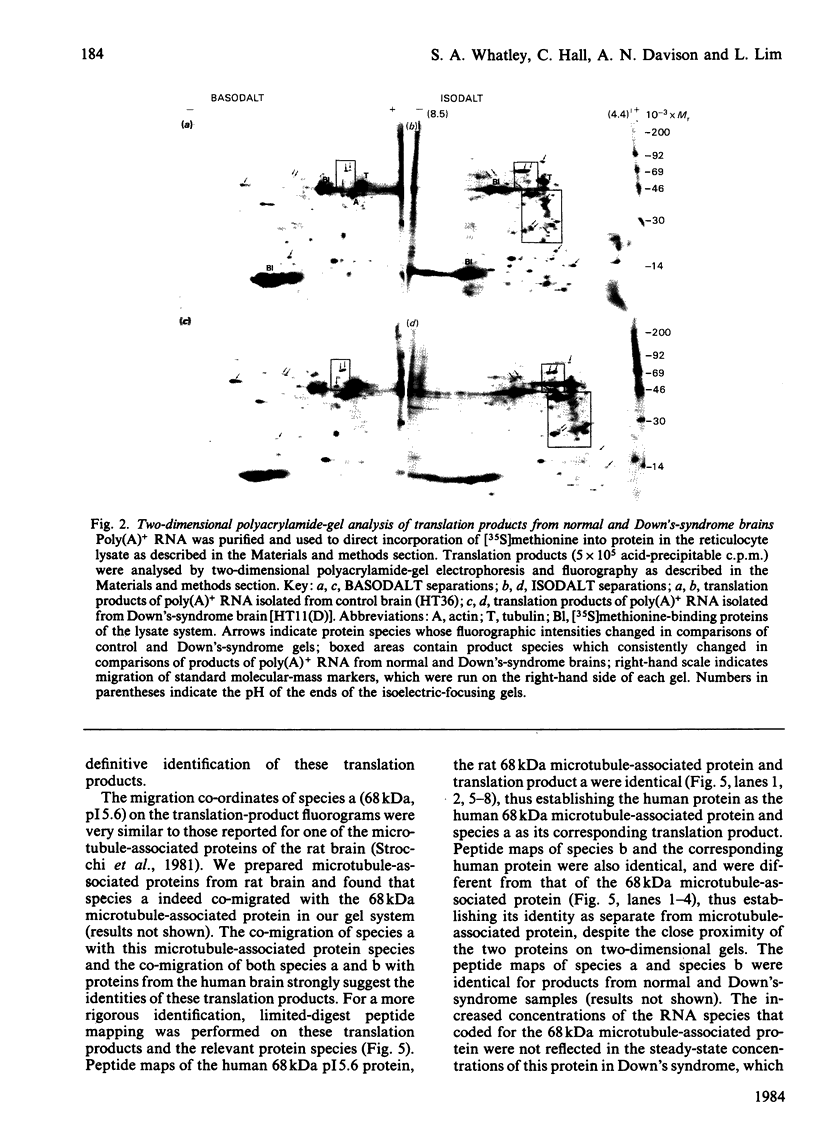
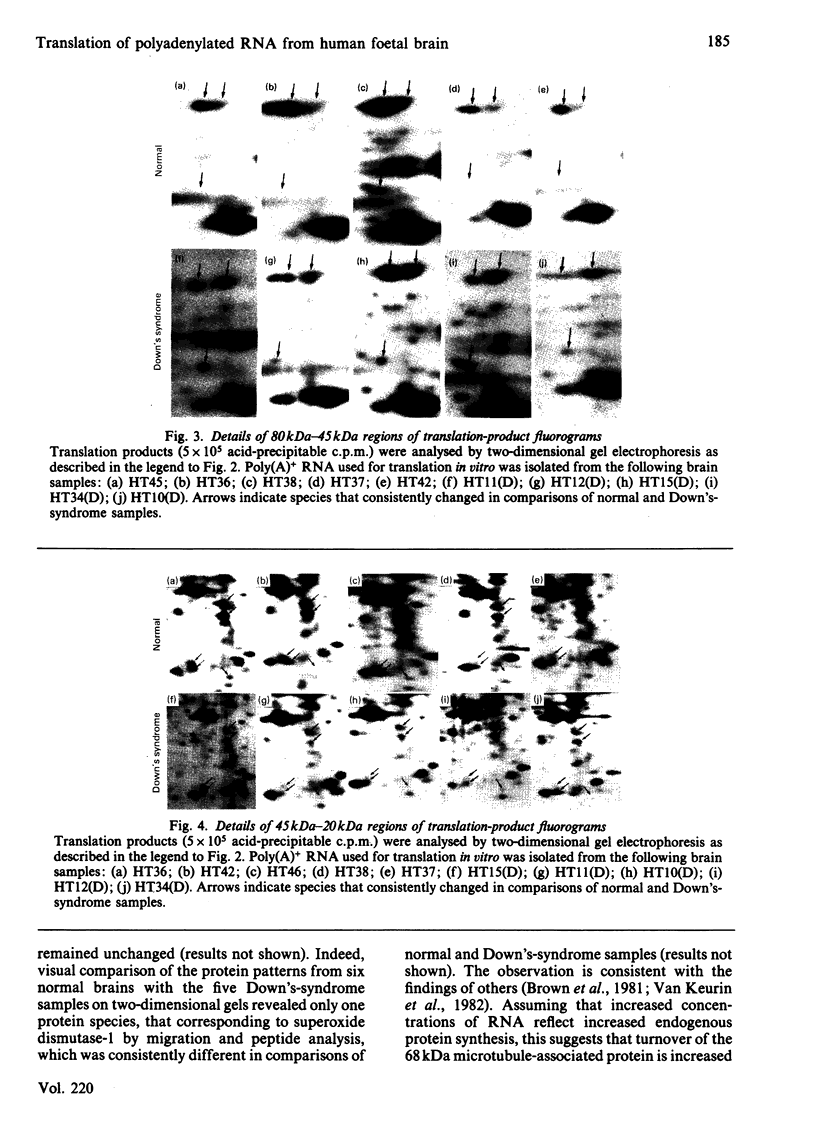
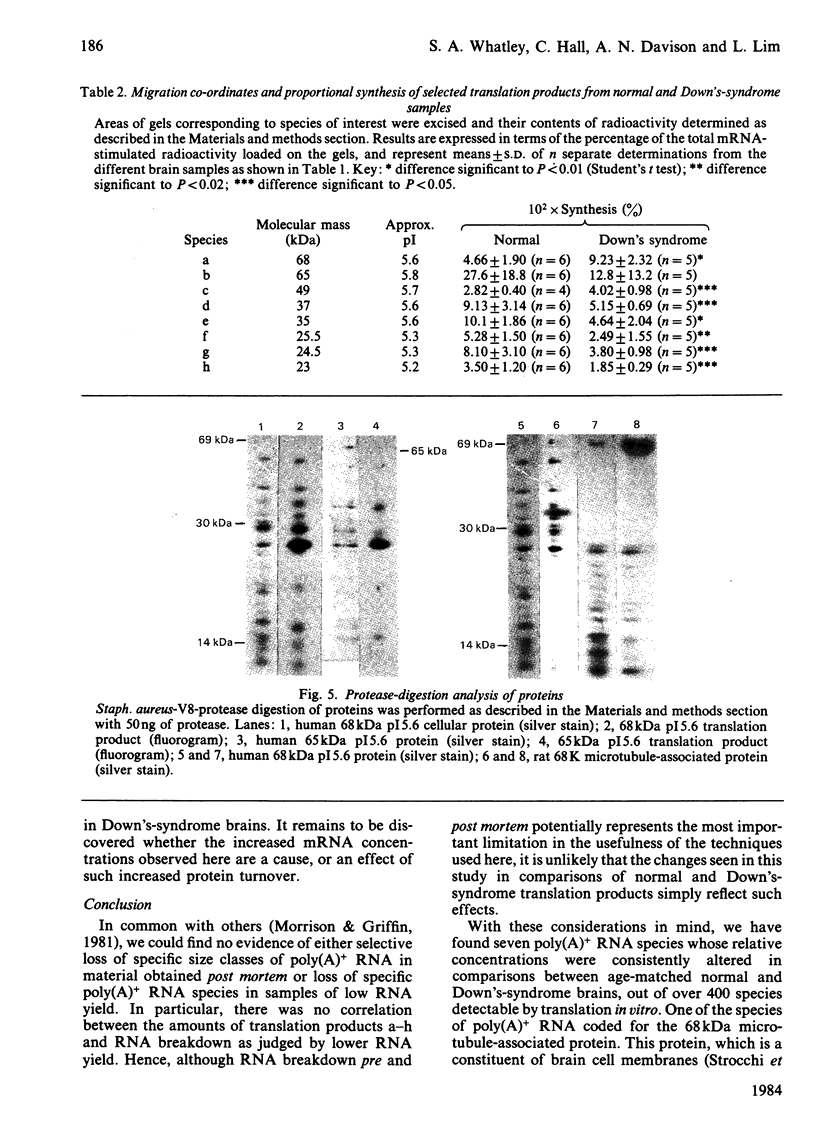
Total cellular polyadenylated RNA [poly(A)+ RNA] was prepared after guanidinium thiocyanate extraction of frozen brain tissue from age-matched normal and Down's-syndrome (trisomy 21) human foetuses. Poly(A)+ RNA populations were analysed by translation in vitro, followed by two-dimensional gel analysis by using both isoelectric focusing (ISODALT system) and non-equilibrium pH-gradient electrophoresis (BASODALT system) as the first-dimension separation. The relative concentrations of poly(A)+ RNA species coding for seven translation products were significantly altered in Down's syndrome, as determined by both visual comparisons of translation-product fluorograms from normal and Down's-syndrome samples and by quantitative radioactivity determination of individual translation products. The relative concentrations of mRNA species coding for two proteins (68 kDa and 49 kDa) were increased in Down's syndrome and may represent genes located on chromosome 21. The relative concentrations of mRNA species coding for five proteins (37 kDa, 35 kDa, 25.5 kDa, 24.5 kDa, 23 kDa) were decreased in Down's syndrome, these probably representing secondary effects of the trisomy. Six Down's-syndrome-linked translation products (49 kDa, 37 kDa, 33 kDa, 25.5 kDa, 24.5 kDa, 23 kDa) did not migrate with appreciable amounts of cellular proteins on two-dimensional gels and hence may represent either proteins of high turnover rates or those that are post-translationally modified in vivo. One translation product (68 kDa) comigrated with a major cellular protein species, which was identified as a 68 kDa microtubule-associated protein by limited peptide mapping. The significance of these changes is discussed in relation to the mechanisms whereby the Down's-syndrome phenotype is expressed in the human brain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartley J. A., Epstein C. J. Gene dosage effect for glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase in human fibroblasts trisomic for chromosome 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1286–1289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90629-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Dutkowski R., Darlington G. J. Localization and quantitation of human superoxide dismutase using computerized 2-D gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 30;102(2):675–681. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt J., Telford J., Birnstiel M. L. Detection of labelled RNA species by contact hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2963–2971. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. M., Davison A. N., Lim L. Developmental changes in the protein and ribonucleic acid components of rat brain messenger ribonucleic acid-protein particles isolated from free polyribosomes by oligo(dT)-cellulose chromatography. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):215–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1900215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaster W. W., Kwok L. W., Epstein C. J. Dosage effects for superoxide dismutase-1 in nucleated cells aneuploid for chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Nov;29(6):563–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous A., Francon J., Lennon A. M., Nunez J. Microtubule assembly in vitro. Purification of assembly-promoting factors. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C., Lim L. Developmental changes in the composition of polyadenylated RNA isolated from free and membrane-bound polyribosomes of the rat forebrain, analysed by translation in vitro. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 15;196(1):327–336. doi: 10.1042/bj1960327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E., Granoff D. M., Bujnovszky P. DNA, RNA, and cholesterol increases in cerebrum and cerebellum during development of human fetus. Brain Res. 1969 Aug;14(3):697–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. B., Bernstein S. L., Gioio A. E. An improved method for the rapid isolation of brain ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 1;183(1):181–184. doi: 10.1042/bj1830181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klose J., Zeindl E., Sperling K. Analysis of protein patterns in two-dimensional gels of cultured human cells with trisomy 21. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):987–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M. Down syndrome: gene dosage at the transcriptional level in skin fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2372–2375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE J., GAUTIER M., TURPIN R. Etude des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 16;248(11):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Hall C., Leung T., Mahadevan L., Whatley S. Neurone-specific enolase and creatine phosphokinase are protein components of rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1983 Oct;41(4):1177–1182. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb09069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Padilla M. Pyramidal cell abnormalities in the motor cortex of a child with Down's syndrome. A Golgi study. J Comp Neurol. 1976 May 1;167(1):63–81. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwigan J. D., Hanson D. R., Lubiniecki A., Heston L. L., Sheppard J. R. Down syndrome fibroblasts are hyperresponsive to beta-adrenergic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7670–7673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
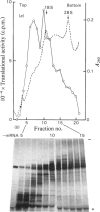
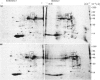
- Morrison M. R., Griffin W. S. The isolation and in vitro translation of undegraded messenger RNAs from human postmortem brain. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
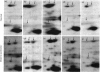
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel-Sulkowska E., Coughlin J. F., Marotta C. A. In vitro synthesis of polypeptides of moderately large size by poly(A)-containing messenger RNA from postmortem human brain and mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):670–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strocchi P., Brown B. A., Young J. D., Bonventre J. A., Gilbert J. M. The characterization of tubulin in CNS membrane fractions. J Neurochem. 1981 Nov;37(5):1295–1307. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima S., Becker L. E., Armstrong D. L., Chan F. Abnormal neuronal development in the visual cortex of the human fetus and infant with down's syndrome. A quantitative and qualitative Golgi study. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan U. H. Chromosome-21-dosage effect on inducibility of anti-viral gene(s). Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):280–282. doi: 10.1038/253280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Schneider E. L., Tischfield J., Epstein C. J., Ruddle F. H. Human chromosome 21 dosage: effect on the expression of the interferon induced antiviral state. Science. 1974 Oct 4;186(4158):61–63. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4158.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Goldman D., Merril C. R. Protein variations associated with Down's syndrome, chromosome 21, and Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;396:55–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb26843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J. The effect of trisomy 21 on the patterns of polypeptide synthesis in human fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Jul;31(4):478–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. L., Hall M. E., Stone G. C., Rubin R. W. Some improvements in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of proteins. Protein mapping of eukaryotic tissue extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]