Abstract
目的
探讨miR-328-3p对氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein, ox-LDL)诱导的冠状动脉内皮细胞损伤的保护作用及可能相关的作用机制。
方法
用ox-LDL诱导人冠状动脉内皮细胞(human coronary artery endothelial cells, HCAECs),将细胞分为对照(control)组(正常培养细胞)、ox-LDL组(ox-LDL处理)、ox-LDL+miR-NC组(转染miR-NC,用ox-LDL处理)、ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组(转染miR-328-3p,用ox-LDL处理)、ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+pcDNA组(共转染miR-328-3p和pcDNA,用ox-LDL处理)、ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+胰岛素样生长因子2(insulin-like growth factor 2, IGF2)组(共转染miR-328-3p和IGF2,用ox-LDL处理)。RT-qPCR检测miR-328-3p表达水平;MTT以及流式细胞术检测细胞增殖和凋亡;Western blot法检测cleaved cas-3、IGF2、Bax、Bcl-2蛋白含量;ELISA法检测肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor α, TNF-α)、白细胞介素(interleukin, IL)-6、IL-1β含量 ;应用双荧光素酶报告实验验证分子间靶向关系。
结果
与control组相比,ox-LDL组中miR-328-3p表达水平、细胞活性降低(P<0.05),凋亡率,cleaved cas-3、IGF2蛋白表达,TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β水平增加(P<0.05)。与ox-LDL+miR-NC组相比,ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组miR-328-3p表达水平、细胞活性增加(P<0.05),凋亡率,cleaved cas-3、IGF2蛋白表达,TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β水平降低(P<0.05)。IGF2是miR-328-3p的功能靶标。与共转染ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+pcDNA组比较,共转染ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+IGF2组IGF2蛋白水平升高(P<0.05),细胞活性降低(P<0.05),而凋亡率、cleaved cas-3蛋白水平以及TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β含量升高(P<0.05)。
结论
miR-328-3p通过靶向负调控IGF2抑制ox-LDL诱导的冠状动脉内皮细胞凋亡和炎性损伤。
Keywords: miR-328-3p, 胰岛素样生长因子2, 氧化型低密度脂蛋白, 冠状动脉内皮细胞
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the protective effect of miR-328-3p on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced coronary artery endothelial cell injury and the potentially relevant mechanisms.
Methods
Human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) were induced with ox-LDL, and the cells were divided into a control group consisting of normal cells, an ox-LDL group receiving ox-LDL treatment, an ox-LDL+miR-NC group transfected with miR-NC and treated with ox-LDL, an ox-LDL+miR-328-3p group transfected with miR-328-3p and treated with ox-LDL, and ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+pcDNA group co-transfected miR-328-3p and pcDNA and treated with ox-LDL, and an ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) group co-transfected miR-328-3p and IGF2 and treated with ox-LDL. The expression level of miR-328-3p was determined with RT-qPCR. Cell proliferation was determined by MTT. Cell apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry. Western blot was conducted to examine the protein expression levels of cleaved cas-3 and IGF2. ELISA was performed to determine the levels of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β. Dual luciferase reporter experiment was performed to verify the targeting relationship between miR-328-3p and IGF2.
Results
Compared with those of the control group, miR-328-3p expression level and cell activity were significantly reduced in the ox-LDL group (P<0.05), while the apoptotic rate, the protein expression levels of cleaved cas-3, IGF2, Bax, and Bcl-2, and the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were significantly increased (P<0.05). Compared with those of the ox-LDL+miR-NC group, miR-328-3p expression level and cell activity significantly increased in the ox-LDL+miR-328-3p group (P<0.05), while the apoptosis rate, the protein expression levels of cleaved cas-3 and IGF2, and the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were significantly reduced. IGF2 was a functional target of miR-328-3p. Compared with those of the ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+pcDNA co-transfection group, the IGF2 protein level was significantly increased (P<0.05) and cell activity was significantly decreased (P<0.05) in the ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+IGF2 co-transfection group, while the apoptosis rate, cleaved cas-3 protein level, and the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were significantly elevated (P<0.05).
Conclusion
miR-328-3p inhibits ox-LDL-induced apoptosis and inflammatory in coronary artery endothelial cell injury through targeted negative regulation of IGF2.
Keywords: miR-328-3p, Insulin-like growth factor 2, Oxidized low-density lipoprotein, Coronary artery endothelial cells
动脉粥状硬化是心血管疾病常见的疾病之一,也是冠心病、脑梗死、缺血性心脏病等心血管疾病主要的原因[1]。研究报道显示,氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein, ox-LDL)与动脉粥状硬化的形成密切相关,常用于诱导建立动脉粥状硬化细胞模型[2]。miRNA是单链非编码RNA的转录本,不具有编码蛋白质的能力,与细胞增殖、凋亡、炎性反应等有关,进而影响动脉粥样硬化等疾病的发展[3-4]。有研究结果显示,miR-328-3p与ox-LDL、颈动脉内中膜厚度 (carotid intima-media thickness, cIMT)有关[5],在ox-LDL诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞(human umbilical vein endothelial cells, HUVEC)中表达下调,过表达miR-328-3p可抑制ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC增殖、迁移和侵袭,并促进细胞凋亡、自噬和炎性损伤[6],但是对ox-LDL诱导的人冠状动脉内皮细胞(human coronary artery endothelial cells, HCAECs)的研究机制尚不清楚。胰岛素样生长因子2(insulin-like growth factor 2, IGF2)与动脉粥状硬化的发病有关[7],在动脉粥状硬化患者和ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC中表达上调,SNHG12通过调控miR-218-5p/IGF2轴促进ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC凋亡和炎性反应[8],但是对ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs的研究尚不清楚。使用生物信息学软件预测显示miR-328-3p与IGF2存在相互结合位点,鉴于此,本研究采用ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs,探究miR-328-3p可能通过调控IGF2对ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs细胞损伤的保护作用及机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1. 细胞和主要试剂
ox-LDL购于上海经科化学公司;HCAECs购于武汉普诺赛公司;miR-NC、miR-328-3p、pcDNA、IGF2、引物由上海吉玛公司设计合成;胎牛血清、DMEM培养基,Lipofectamine 2000试剂盒购于美国Thermo公司;北京百奥莱博科技有限公司提供Trizol试剂盒、逆转录试剂盒以及PCR试剂盒;由碧云天生物提供MTT试剂盒、BCA试剂盒以及凋亡试剂盒;一抗(cleaved cas-3、IGF2、Bax、Bcal-2以及GAPDH抗体)购于美国Abcam公司;二抗购于北京中杉金桥公司;于上海江莱生物购买肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor α, TNF-α)、白细胞介素(interleukin, IL)-6以及IL-1β试剂盒;北京索莱宝公司提供双荧光素酶检测试剂盒以及电化学发光试剂。
1.2. 细胞培养和分组
于含有10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基内培养HCAECs,培养条件:37 ℃以及5%CO2(体积分数)。取对数期的HCAECs,以1×105个/孔接种于24孔内,细胞融合至60%时,按照Lipofectamine 2000试剂盒说明书将miR-NC、miR-328-3p、miR-328-3p和pcDNA、miR-328-3p和IGF2转染至细胞内,转染6 h换细胞液用50 mg/L ox-LDL处理细胞,记为ox-LDL+miR-NC组、ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组、ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+pcDNA组、ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+IGF2组;另设control组(正常培养细胞)和ox-LDL组(用50 mg/L ox-LDL处理细胞)。细胞培养48 h用于后续实验。
1.3. RT-qPCR检测miR-328-3p表达水平
将细胞与1mL Trizol混合均匀提取总RNA,随后逆转录生成cDNA。以cDNA为模板在PCR仪上进行扩增反应。用2−ΔΔCt法计算miR-328-3p相对内参U6的表达量。
1.4. MTT检测细胞增殖活性
将处理后的各组细胞(2×103个)与20 μL MTT试剂共置于96孔板每孔中,室温孵育4 h后,每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜溶解MTT结晶,随后检测490 nm处的吸光度(A)值。
1.5. 流式细胞术
收集处理后的各组细胞,磷酸缓冲液洗涤后,重悬于含有5 μL Annexin V-FITC和5 μL PI染液的结合缓冲液,避光反应15 min,于1 h内检测凋亡细胞。
1.6. Western blot
将各组细胞与蛋白裂解液共孵育提取总蛋白,用10%SDS-PAGE分离蛋白,然后电转移到PVDF膜上,随后5%脱脂奶粉封闭1 h。清洗后,将cleaved cas-3(稀释1∶500)、IGF2(稀释1∶500)、Bax(稀释1∶500)、Bcl-2(稀释1∶500)、以及GAPDH(稀释1∶1000)一抗与膜4 ℃下孵育过夜,随后37 ℃下将膜二抗(稀释1∶2500)孵育1 h。最后加入电化学发光试剂,显色、曝光,Image Lab 软件分析灰度值。
1.7. ELISA法
通过离心收集各组细胞的上清液,然后按照试剂盒说明书,检测细胞内TNF-α、IL-6以及IL-1β表达量。
1.8. 双荧光素酶报告实验检测miR-328-3p、IGF2靶向关系
miR-328-3p与IGF2 3'UTR区域存在结合位点,构建IGF2 3'UTR区域野生型荧光素酶载体和突变型荧光素酶载体(IGF2 WT和IGF2 MUT)。收集HCAECs接种24孔板中,按照脂质体法将IGF2 WT和IGF2 MUT分别与miR-NC或miR-328-3p共转染至细胞内,48 h后检测胞内荧光素酶活性。
1.9. 统计学方法
采用SPSS 19.0软件对实验数据进行分析,计量结果以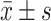 表示,正态分布的数据两组间比较采用独立样本t检验并使用Bonferroni 法进行P值校正,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用Dunnett-t法。α=0.05。
表示,正态分布的数据两组间比较采用独立样本t检验并使用Bonferroni 法进行P值校正,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用Dunnett-t法。α=0.05。
2. 结果
2.1. miR-328-3p在ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞内表达
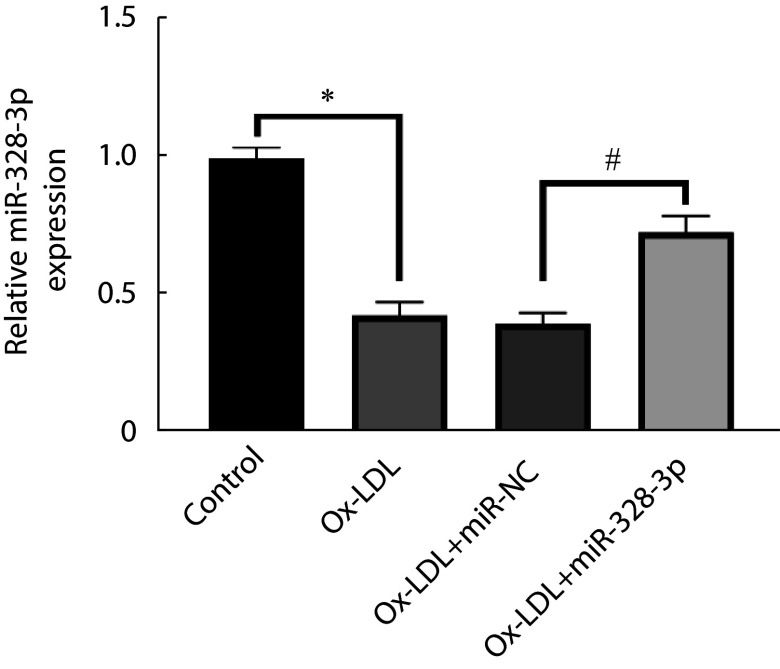
与control组比较,ox-LDL组miR-328-3p表达水平降低(P<0.05);与ox-LDL+miR-NC组相比,ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组miR-328-3p表达水平升高(P<0.05)。见图1。
图 1.
miR-328-3p expression in ox-LDL-induced coronary artery endothelial cells
miR-328-3p在ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞内的表达
* P<0.05, # P<0.05. n=9
2.2. 上调miR-328-3p对ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞凋亡的影响
ox-LDL组相较于control组细胞活性降低,而凋亡率以及cleaved cas-3、Bax蛋白表达升高, Bcl-2蛋白表达降低(P<0.05);ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组对比ox-LDL+miR-NC组细胞活性升高,而凋亡率及cleaved cas-3、Bax蛋白表达下降, Bcl-2蛋白表达升高(P<0.05)。见图2。
图 2.
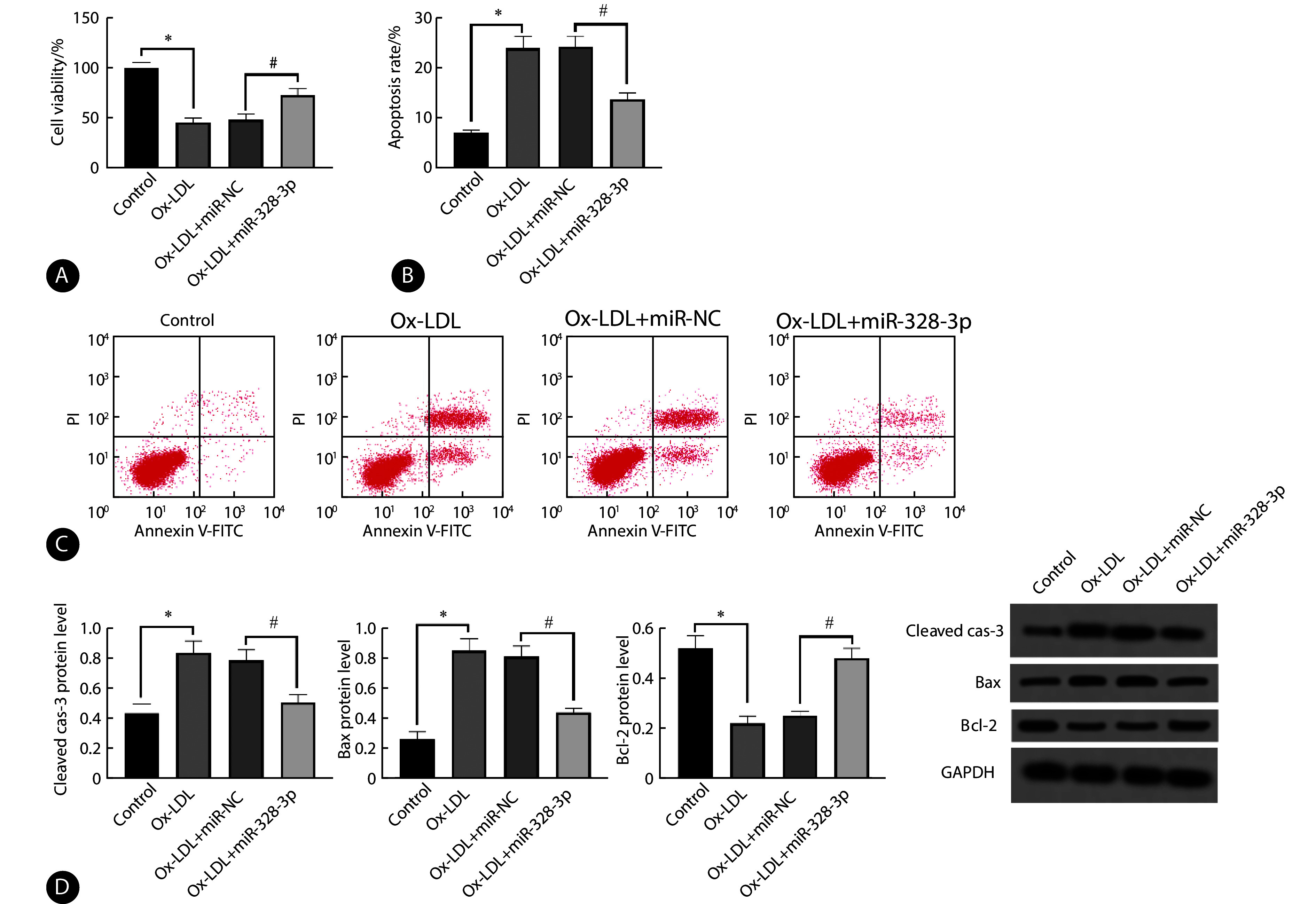
Effect of upregulation of miR-328-3p on ox-LDL-induced apoptosis in coronary artery endothelial cells
上调miR-328-3p对ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞凋亡的影响
A, MTT assay performed to evaluate cell viability (n=9); B, apoptosis rate was determined by flow cytometry (n=9); C, flow cytometry; D, relative expression of cleaved cas-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins was assessed by Western blot (n=3). * P<0.05, # P<0.05.
2.3. 上调miR-328-3p对ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞炎性因子的影响
ox-LDL处理后,对比control组,细胞中TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β表达上调(P<0.05);ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组对比ox-LDL+miR-NC组细胞低表达TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β(P<0.05)。见图3。
图 3.
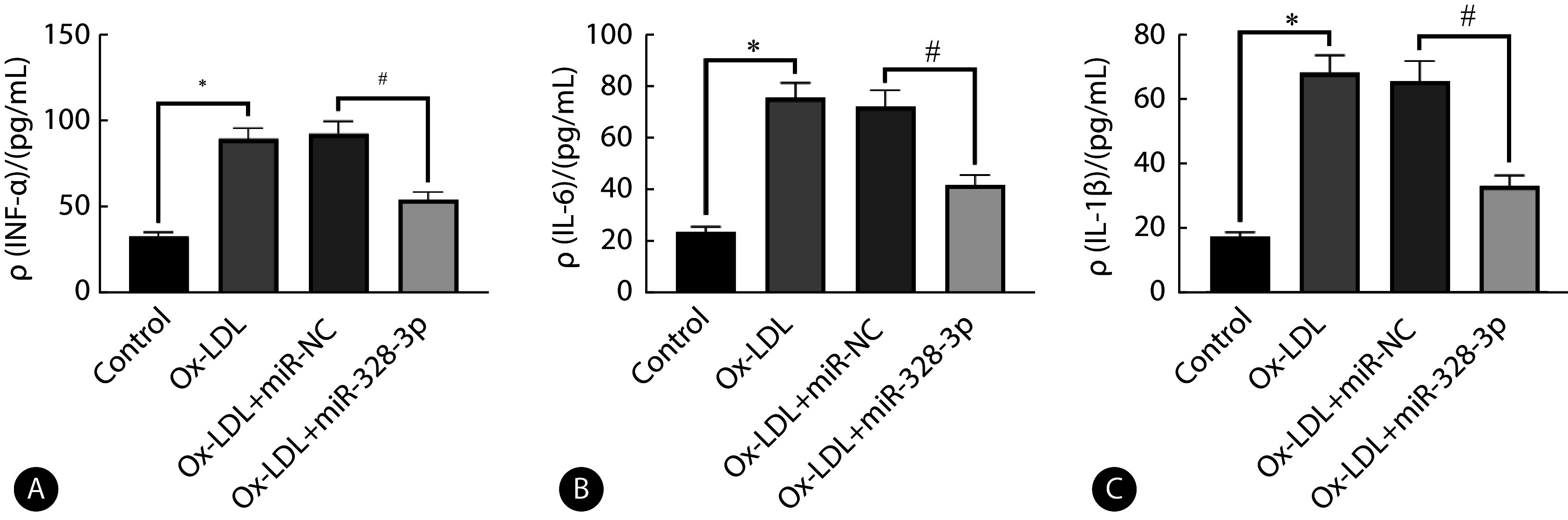
Effect of upregulation of miR-328-3p on ox-LDL-induced inflammatory factors in coronary artery endothelial cells
上调miR-328-3p对ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞炎性因子的影响
A, TNF-α level was evaluate by ELISA (n=9); B, IL-6 level was determined by ELISA (n=9); C, IL-1β level was measured by ELISA (n=9). * P<0.05, # P<0.05.
2.4. miR-328-3p和IGF2关系
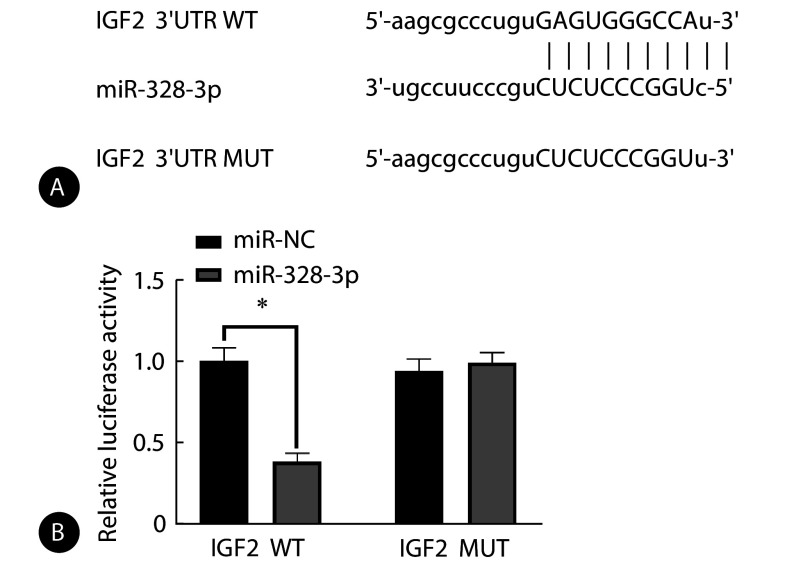
生物信息学软件预测显示,miR-328-3p和IGF2存在互补核苷酸序列。miR-328-3p组相较于miR-NC组IGF2 WT荧光素酶活性降低(P<0.05),miR-328-3p以及miR-NC均不影响IGF2 MUT荧光素酶活性,见图4。
图 4.
Relationship between miR-328-3p and IGF2
miR-328-3p和IGF2的关系
A, Complementary nucleotide sequences exist for miR-328-3p and IGF2; B, their relationship was validated using the dual luciferase reporter assay (n=9). * P<0.05.
2.5. miR-328-3p调控IGF2的表达
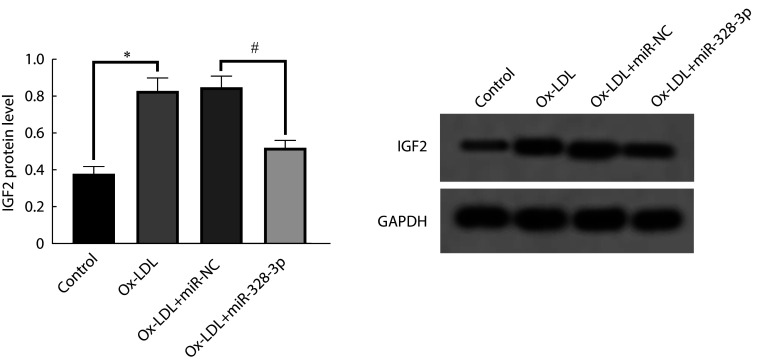
与control组比较,ox-LDL组IGF2蛋白水平升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);与ox-LDL+miR-NC组相比,ox-LDL+miR-328-3p组IGF2蛋白水平降低(P<0.05)。见图5。
图 5.
miR-328-3p regulates the expression of IGF2
miR-328-3p调控IGF2的表达
The relative expression of IGF2 protein was assessed by Western blot (n=3). * P<0.05, # P<0.05.
2.6. 过表达IGF2可以逆转miR-328-3p上调对ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞凋亡和炎性因子的影响
与ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+pcDNA组比较,ox-LDL+miR-328-3p+IGF2组IGF2蛋白水平升高,细胞活性、Bcl-2蛋白水平降低,而凋亡率、cleaved cas-3和Bax蛋白水平以及TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β含量升高(P<0.05)。见图6。
图 6.
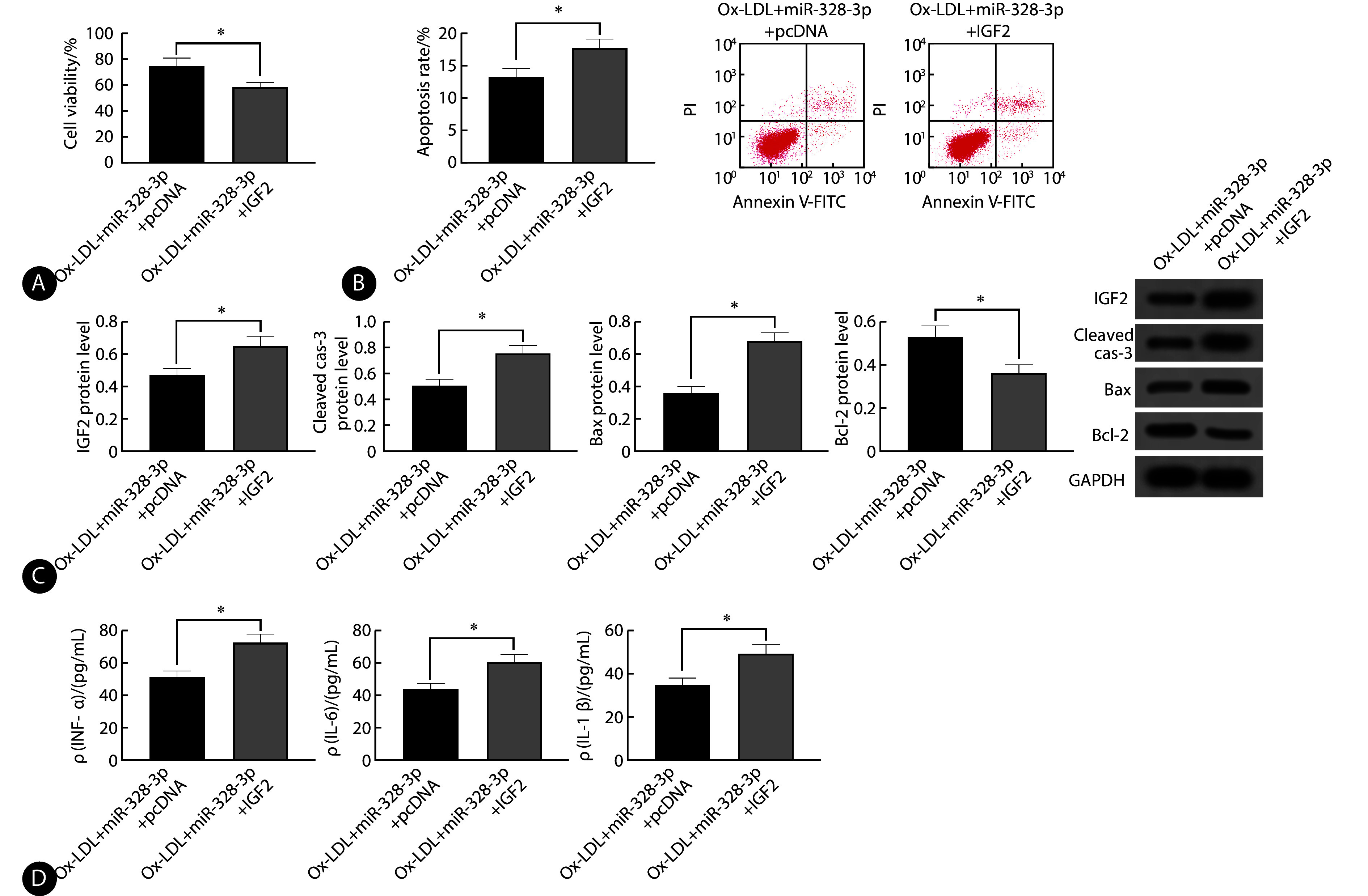
Overexpression of IGF2 reverses the effects of miR-328-3p upregulation on ox-LDL-induced apoptosis and inflammatory factors in coronary endothelial cells
过表达IGF2可以逆转miR-328-3p上调对ox-LDL诱导冠状动脉内皮细胞凋亡和炎症因子的影响
A, MTT assay was conducted to evaluate cell viability (n=9); B, apoptosis rate was determined by flow cytometry (n=9); C, the relative expression of IGF2, cleaved cas-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins was assessed by Western blot (n=3); D, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β levels were measured by ELISA (n=9). * P<0.05.
3. 讨论
动脉粥状硬化发病原因与遗传、肥胖因素、高血压、高血脂等有关,其可在人体内存在数年不显示病态,早期诊断可有效缓解病情的发展,并减少相关疾病的发生,进而提高人们的生活质量和水平[9-10]。研究结果显示,ox-LDL含量过高时,可使胆固醇聚集在动脉壁上,进而引发动脉粥状硬化[11]。本研究用ox-LDL诱导HCAECs建立细胞损伤模型,结果显示,细胞活性降低,凋亡率、cleaved cas-3蛋白表达上调,炎性因子TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β含量增加,提示细胞损伤模型构建成功。
研究结果显示,miRNA在疾病发展中起着重要的作用,包括高血压、动脉粥状硬化等[12-13],如miR-328-3p在氧糖剥夺的HUVEC中表达下调,上调miR-328-3p可减轻氧糖剥夺诱导的内皮细胞损伤[6, 14]。ZHANG等[6]研究结果显示,ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC中miR-328-3p表达下调,过表达miR-328-3p可通过调控TRIM14减轻ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC凋亡和炎性反应。本研究结果显示,ox-LDL诱导HCAECs后miR-328-3p表达下调,上调miR-328-3p可增加ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs细胞活性,降低凋亡率、cleaved cas-3和Bax蛋白表达,提高 Bcl-2蛋白表达,抑制炎性因子TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β含量,提示上调miR-328-3p可减轻ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs损伤。
IGF2是胰岛素类激素家族成员,是一种依赖性多肽,与胰岛素原存在42%同源,对神经调节、心血管疾病、肿瘤发生等起着重要的作用[15-16]。有研究结果显示,IGF2与动脉粥状硬化发病密切相关,IGF2在冠心病合并高血压患者血清内表达上调,与冠状动脉狭窄评分呈现正相关[17]。有研究结果显示,IGF2在ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC和人血管平滑肌细胞(VSMC)内表达上调,miR-216b-5p通过靶向负调控IGF2减轻ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC和人VSMC凋亡和促进增殖[18]。YANG等[19]研究结果显示,ox-LDL可诱导动脉粥样硬化动物模型中IGF2表达上调,miR-637通过下调IGF2抑制动脉粥样硬化的发展。这些先前的数据表明了IGF2能够加剧ox-LDL诱导的HUVEC的损伤。本研究结果显示,ox-LDL诱导HCAECs后IGF2蛋白表达上调,这与miR-328-3p的表达水平相反。通过生物信息学网站预测和双荧光素酶报告实验证明,IGF2是miR-328-3p的靶基因。同时,本研究数据证实了上调miR-328-3p的水平可以使IGF2的表达水平下降,说明miR-328-3p负调控IGF2表达。进一步实验发现,过表达IGF2可以逆转上调miR-328-3p对ox-LDL诱导HCAECs凋亡和炎性因子的抑制作用,提示miR-328-3p可以通过负调控IGF2减轻ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs损伤。
综上所述,上调miR-328-3p可以通过靶向IGF2对ox-LDL诱导的HCAECs损伤起到保护作用,为治疗动脉粥样硬化提供一定的理论证据。然而,相关机制需要进一步进行探究。
* * *
作者贡献声明 侯永兰负责论文构思、数据审编、正式分析、经费获取、调查研究、研究方法、研究项目管理、监督指导、验证、可视化、初稿写作和审读与编辑写作,李霞、王建美和刘烝昊负责论文构思、数据审编、调查研究、研究方法和审读与编辑写作,刘振和韩明磊负责论文构思、数据审编、监督指导、验证、可视化、初稿写作和审读与编辑写作,金卫东负责论文构思、经费获取、提供资源、监督指导和审读与编辑写作。所有作者已经同意将文章提交给本刊,且对将要发表的版本进行最终定稿,并同意对工作的所有方面负责。
Author controltribution HOU Yonglan is responsible for conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, supervision, validation, visualization, writing--original draft, and writing--review and editing. LI Xia, WANG Jianmei, and LIU Zhenghao are responsible for conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, and writing--review and editing. LIU Zhen and HAN Minglei are responsible for conceptualization, data curation, supervision, validation, visualization, writing--original draft, and writing--review and editing. JIN Weidong is responsible for conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision, and writing--review and editing. All authors consented to the submission of the article to the Journal. All authors approved the final version to be published and agreed to take responsibility for all aspects of the work.
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
Declaration of controlflicting Interests All authors declare no competing interests.
Funding Statement
河南省医学科技攻关计划联合共建项目(No. LHGJ20220987)资助
Contributor Information
永兰 侯 (Yonglan HOU), Email: 17303736931@163.com.
卫东 金 (Weidong JIN), Email: Doctorjin123456@163.com.
References
- 1.FAN J, WATANABE T Atherosclerosis: Known and unknown. Pathol Int. 2022;72(3):151–160. doi: 10.1111/pin.13202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.CAO H, JIA Q, YAN L, et al. Quercetin suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis by regulating MST1-mediated autophagy in ox-LDL-induced RAW264 7 macrophage foam cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6093. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.CAI Y, XU L, XU C, et al Hsa_circ_0001445 inhibits ox-LDL-induced HUVECs inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis by regulating miRNA-640. Perfusion. 2022;37(1):86–94. doi: 10.1177/0267659120979472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.HE X N, XIN J Y, ZHAN J L, et al Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons induce endothelial injury through miR-155 to promote atherosclerosis. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2021;62(7):409–421. doi: 10.1002/em.22454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.PAIM L R, SCHREIBER R, De ROSSI G, et al Circulating microRNAs, vascular risk, and physical activity in spinal cord-injured subjects. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(6):845–852. doi: 10.1089/neu.2018.5880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.ZHANG C, WANG L, SHEN Y Circ_0004104 knockdown alleviates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells through targeting miR-328-3p/TRIM14 axis in atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021;21(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02012-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.徐海燕, 张宽琳, 王曜晖, 等 Ox-LDL对VSMCs增殖及H19和IGF2表达的作用. 遵义医学院学报. 2015;38(4):374–378. [Google Scholar]; XU H Y, ZHANG K L, WANG Y H, et al The effect of Ox-LDL on the proliferation and expression of H19 and IGF2 in VSMCs. J Zunyi Med Univ. 2015;38(4):374–378. [Google Scholar]
- 8.MAO P, LIU X, WEN Y, et al LncRNA SNHG12 regulates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury by the miR-218-5p/IGF2 axis in atherosclerosis. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(16):1561–1577. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1953755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.LIBBY P The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592(7855):524–533. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.WATERBURY T M, TARANTINI G, VOGEL B, et al Non-atherosclerotic causes of acute coronary syndromes. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(4):229–241. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.KATTOOR A J, GOEL A, MEHTA J L LOX-1: regulation, signaling and its role in atherosclerosis. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019;8(7):218. doi: 10.3390/antiox8070218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.LI Z, ZHAO Y, SUGURO S, et al MicroRNAs regulate function in atherosclerosis and clinical implications. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023;2023:2561509. doi: 10.1155/2023/2561509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.NOSALSKI R, SIEDLINSKI M, DENBY L, et al T-cell-derived miRNA-214 mediates perivascular fibrosis in hypertension. Circ Res. 2020;126(8):988–1003. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.YAO M, FANG C, WANG Z, et al miR-328-3p targets TLR2 to ameliorate oxygen-glucose deprivation injury and neutrophil extracellular trap formation in HUVECs via inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2024;19(2):e0299382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.赵海东, 邬明丽, 陈平博, 等 IGF2基因表达调控及其遗传变异在动物生长发育中的研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医. 2020;47(6):1844–1852. [Google Scholar]; ZHAO H D, WU M L, CHEN P B, et al Research progress of IGF2 gene expression regulation and its genetic variation in animal growth and development. Chin Husb Anim Vet Med. 2020;47(6):1844–1852. [Google Scholar]
- 16.KASPRZAK A, ADAMEK A Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) signaling in colorectal cancer-from basic research to potential clinical applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4915. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.寇民生, 罗兴林, 耿丽群 胰岛素样生长因子-2在冠状动脉粥样硬化中的表达. 中华全科医学. 2009;7(1):34–35. [Google Scholar]; KOU M S, LUO X L, GENG L Q Expression of insulin-like growth factor-2 in coronary artery disease. Chin J Gen Pract. 2009;7(1):34–35. [Google Scholar]
- 18.QU C, LIU X, HAN X, et al miR-216b-5p regulates proliferation and apoptosis of ox-LDL-stimulated VSMCs and HUVECs via IGF2. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023;37(3):e23271. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.YANG N, DONG B, SONG Y, et al Downregulation of miR-637 promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via regulation of insulin-like growth factor-2. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020;25:30. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00222-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]