Abstract
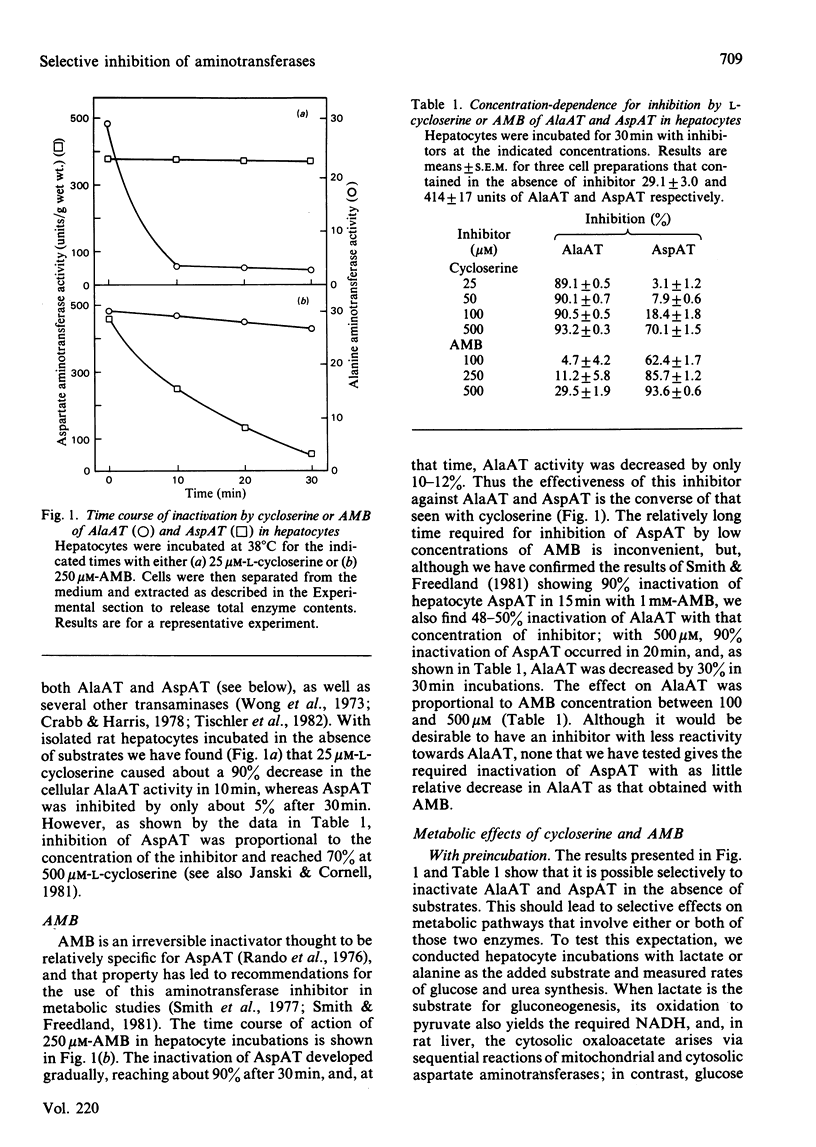
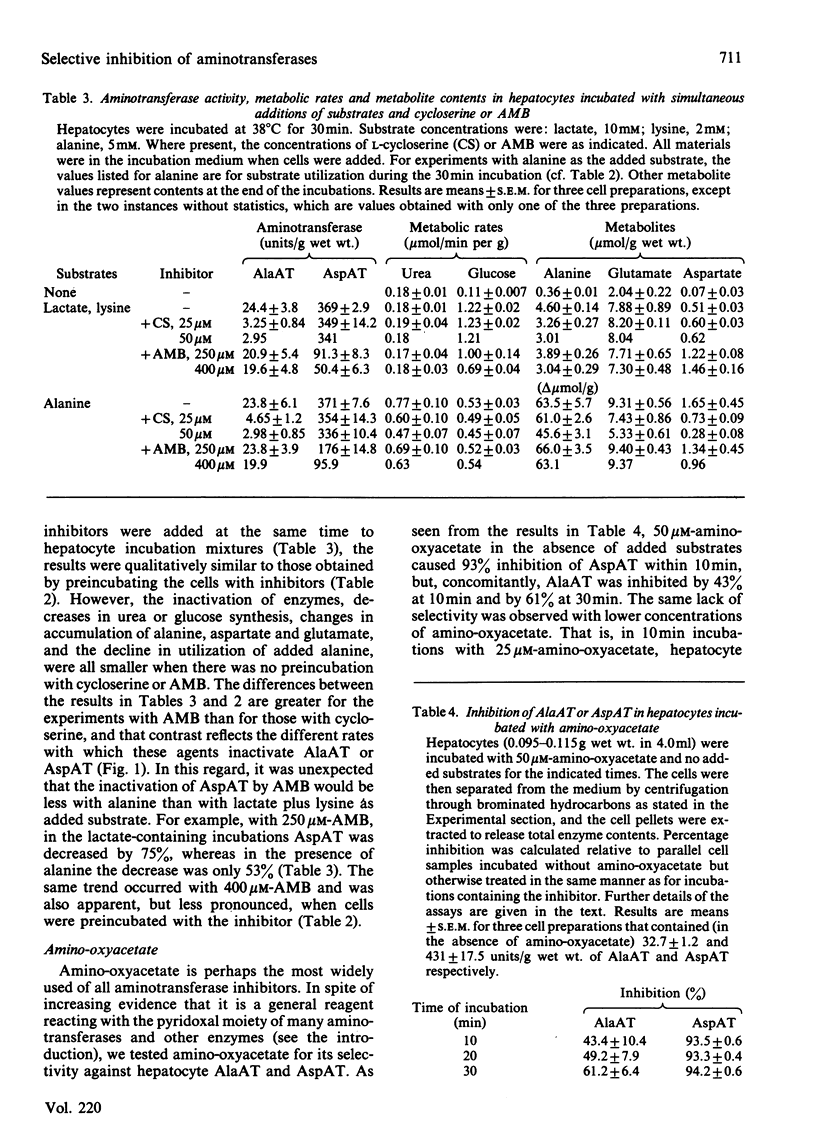
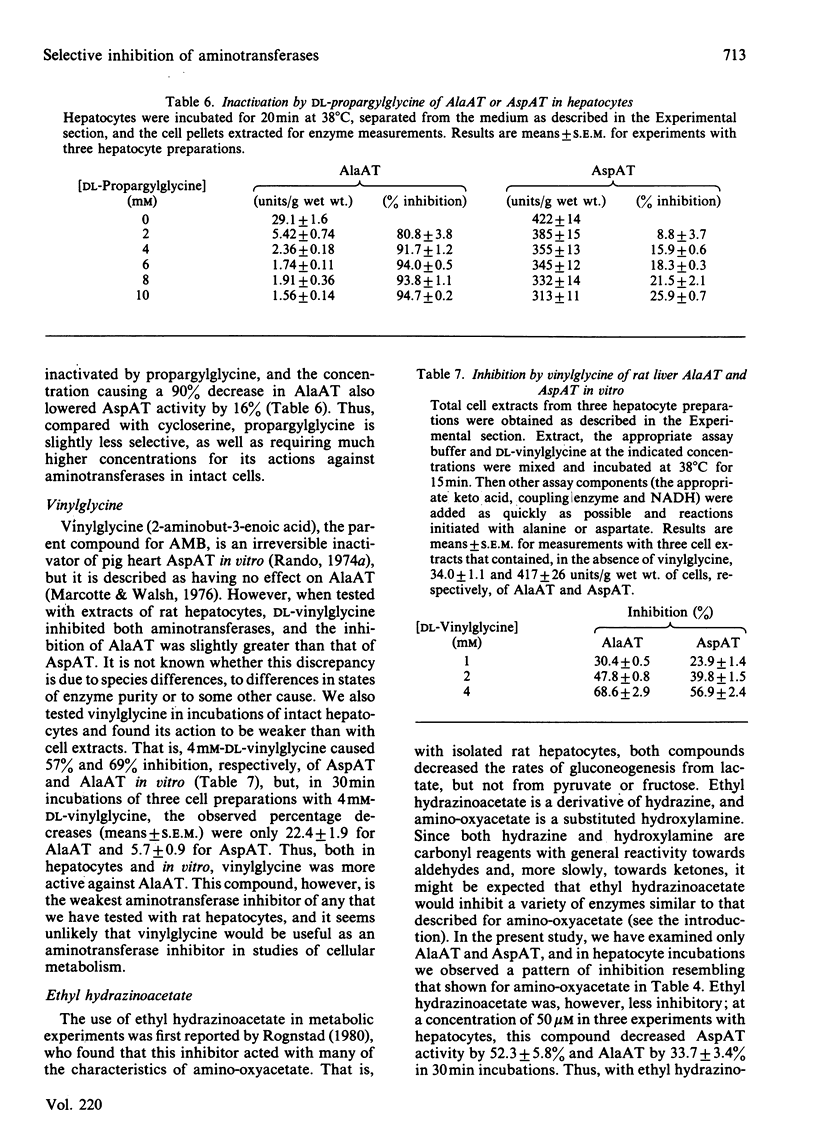
Experiments were conducted with intact rat hepatocytes to identify inhibitors and incubation conditions that cause selective inhibition of alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase. Satisfactory results were obtained by preincubating cells with L-cycloserine or L-2-amino-4-methoxy-trans-but-3-enoic acid in the absence of added substrates. When cells were incubated for 20 min with 50 microM-L-cycloserine, alanine aminotransferase activity was decreased by 90%, whereas aspartate aminotransferase was inhibited by 10% or less. On subsequent incubation, synthesis of glucose and urea from alanine was strongly inhibited, but glucose synthesis from lactate was unaffected. L-2-Amino-4-methoxy-trans-but-3-enoic acid (400 microM) in hepatocyte incubations caused 90-95% inactivation of aspartate aminotransferase, but only 15-30% loss of alanine aminotransferase activity. After preincubation with the inhibitor, glucose synthesis from lactate was almost completely blocked; with alanine as the substrate, gluconeogenesis was unaffected, and urea synthesis was only slightly decreased. By comparison with preincubation with inhibitors, simultaneous addition of substrates (alanine; lactate plus lysine) and inhibitors (cycloserine; aminomethoxybutenoic acid) resulted in smaller decreases in aminotransferase activities and in metabolic rates. Other compounds were less satisfactory as selective inhibitors. Ethylhydrazinoacetate inactivated the two aminotransferases to similar extents. Vinylglycine was almost equally effective in blocking the two enzymes in vitro, but was a very weak inhibitor when used with intact cells. Concentrations of DL-propargylglycine (4 mM) required to cause at least 90% inhibition of alanine aminotransferase in hepatocytes also caused a 16% decrease in aspartate aminotransferase. When tested in vitro, alanine aminotransferase was, as previously reported by others, more sensitive to inhibition by amino-oxyacetate than was aspartate aminotransferase, but in liver cell incubations the latter enzyme was more rapidly inactivated by amino-oxyacetate.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBIERI P., DI MARCO A., FUOCO L., JULITA P., MIGLIACCI A., RUSCONI A. Investigation on the mode of action of cycloserine upon protein synthesis of E. coli and animal cells. 2. Action of L-cycloserine on protein metabolism of alanine and on enzymic preparations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1960 Jul;3:264–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(60)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler T., Churchich J. E. Reactivity of the phosphopyridoxal groups of cystathionase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5267–5271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstrand R., Ostling-Wintzell H., Löf A., McMartin K., Tolf B. R., Hedström K. G. Pyrazoles as inhibitors of alcohol oxidation and as important tools in alcohol research: an approach to therapy against methanol poisoning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W., Crow K. E., Whitefoot R. P. Re-activation by glutamate or aspartate of amino-oxyacetate-inhibited aspartate aminotransferase in vitro and in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):219–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1980219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W., Lund P., Hems R., Krebs H. A. Acceleration of gluconeogenesis from lactate by lysine (Short Communication). Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):671–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1340671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The effect of lysine on gluconeogenesis from lactate in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):327–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1420327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W. Rapid fractionation of cell suspensions with the use of brominated hydrocarbons. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb D. W., Harris R. A. Studies on the regulation of leucine catabolism in the liver. Stimulation by pyruvate and dichloroacetate. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1481–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow K. E., Cornell N. W., Veech R. L. Lactate-stimulated ethanol oxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):29–36. doi: 10.1042/bj1720029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterle P., Brawand F., Moser U. K., Walter P. Alanine metabolism in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Free C. A., Julius M., Arnow P., Barry G. T. Inhibition of alanine racemase by aminoxyacetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;146(2):608–610. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPER S., SEGAL H. L. COMPARATIVE PROPERTIES OF GLUTAMIC-ALANINE TRANSAMINASE FROM SEVERAL SOURCES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jun;105:501–505. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Cornell N. W., Straight C., Veech R. L. Mechanism responsible for aminooxyacetate and glycolate stimulation of ethanol oxidation by isolated hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):414–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90567-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes R. C., Jr The fixation of carbon dioxide by rat liver mitochondria and its relation to gluconeogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):4103–4106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janski A. M., Cornell N. W. Inhibition by cycloserine of mitochondrial and cytosolic aspartate aminotransferase in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):1027–1030. doi: 10.1042/bj1941027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janski A. M., Cornell N. W. Subcellular distribution of enzymes determined by rapid digitonin fractionation of isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):423–429. doi: 10.1042/bj1860423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John R. A., Charteris A. The reaction of amino-oxyacetate with pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):771–779. doi: 10.1042/bj1710771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapke G., Davis L. Deamination of the microbial toxin trans L-2-amino-4-methoxy-3-butenoic acid and its parent vinylglycine by sheep liver serine-threonine dehydratase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):765–769. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lardy H. A., Paetkau V., Walter P. Paths of carbon in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis: the role of mitochondria in supplying precursors of phosphoenolpyruvate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1410–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinweber F. J. Mechanism of histidine decarboxylase inhibition by NSD-1055 and related hydroxylamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):337–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald E., Pispa J. P. Inhibition of catalase in vitro and in vivo by 4-hydroxypyrazole, a metabolite of pyrazole. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcotte P., Walsh C. Active site-directed inactivation of cystathionine gamma-synthetase and glutamic pyruvic transaminase by propargylglycine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):677–682. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcotte P., Walsh C. Vinylglycine and proparglyglycine: complementary suicide substrates for L-amino acid oxidase and D-amino acid oxidase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3070–3076. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer A. J., Gimpel J. A., Deleeuw G. A., Tager J. M., Williamson J. R. Role of anion translocation across the mitochondrial membrane in the regulation of urea synthesis from ammonia by isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7728–7738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer A. J., Gimpel J. A., Deleeuw G., Tischler M. E., Tager J. M., Williamson J. R. Interrelationships between gluconeogenesis and ureogenesis in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2308–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla R., Okawa K., Lindros K. O., Zimmerman U. J., Kobayashi K., Williamson J. R. Functional compartmentation of acetaldehyde oxidation in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4926–4933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS E., SIMONSEN D. G. Some properties of L-glutamic decarboxylase in mouse brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Feb;12:113–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Beta, gamma unsaturated amino acids as irreversible enzyme inhibitors. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):586–587. doi: 10.1038/250586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Irreversible inhibition of aspartate aminotransferase by 2-amino-3-butenoic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):3859–3863. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Relyea N., Cheng L. Mechanism of the irreversible inhibition of aspartate aminotransferase by the bacterial toxin L-2-amino-4-methoxy-trans-3-butenoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3306–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rofe A. M., Edwards J. B. Oxalate synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes: The effects of hydroxypyruvate and amino-oxyacetate. Biochem Med. 1978 Dec;20(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(78)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognstad R. Effects of ethyl hydrazinoacetate on gluconeogenesis and on ethanol oxidation in rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 21;628(1):116–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Briggs S., Triebwasser K. C., Freedland R. A. Re-evaluation of amino-oxyacetate as an inhibitor. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):453–455. doi: 10.1042/bj1620453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Freedland R. A. Functional inhibition of cytosolic and mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase by L-2-amino-4-methoxy-trans-3-butenoic acid in isolated rat hepatocytes and mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sufrin J. R., Lombardini J. B., Keith D. D. L-2-Amino-4-methoxy-cis-but-3-enoic acid, a potent inhibitor of the enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanase S., Morino Y. Irreversible inactivation of aspartate aminotransferases during transamination with L-propargylglycine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1301–1308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler M. E., Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. Does leucine, leucyl-tRNA, or some metabolite of leucine regulate protein synthesis and degradation in skeletal and cardiac muscle? J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1613–1621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M. J. The effect of the methionine antagonist L-2-amino-4-methoxy-trans-3-butenoic acid on the growth and metabolism of Walker carcinosarcoma in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 15;29(4):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Paetkau V., Lardy H. A. Paths of carbon in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis. 3. The role and regulation of mitochondrial processes involved in supplying precursors of phosphoenolpyruvate. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2523–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Fuller R. W., Molloy B. B. Inhibition of amino acid transaminases by L-cycloserine. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1973;11:139–154. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(73)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



