Abstract
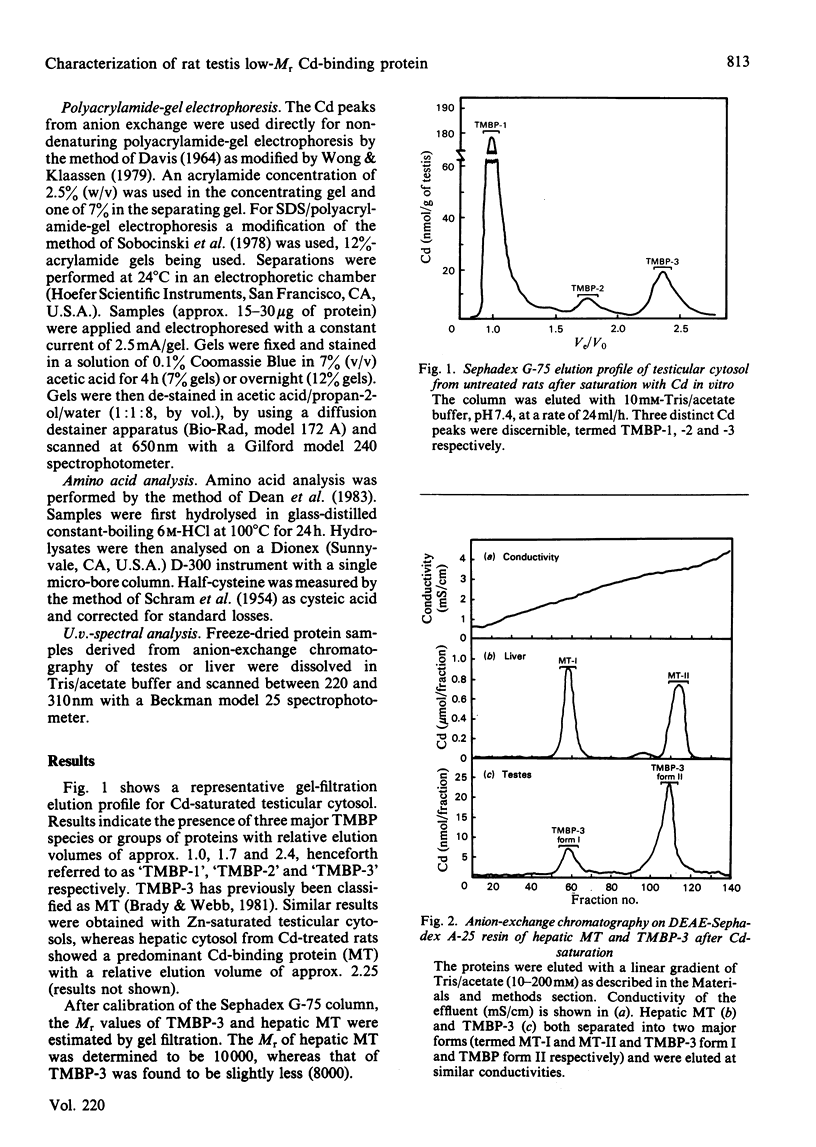
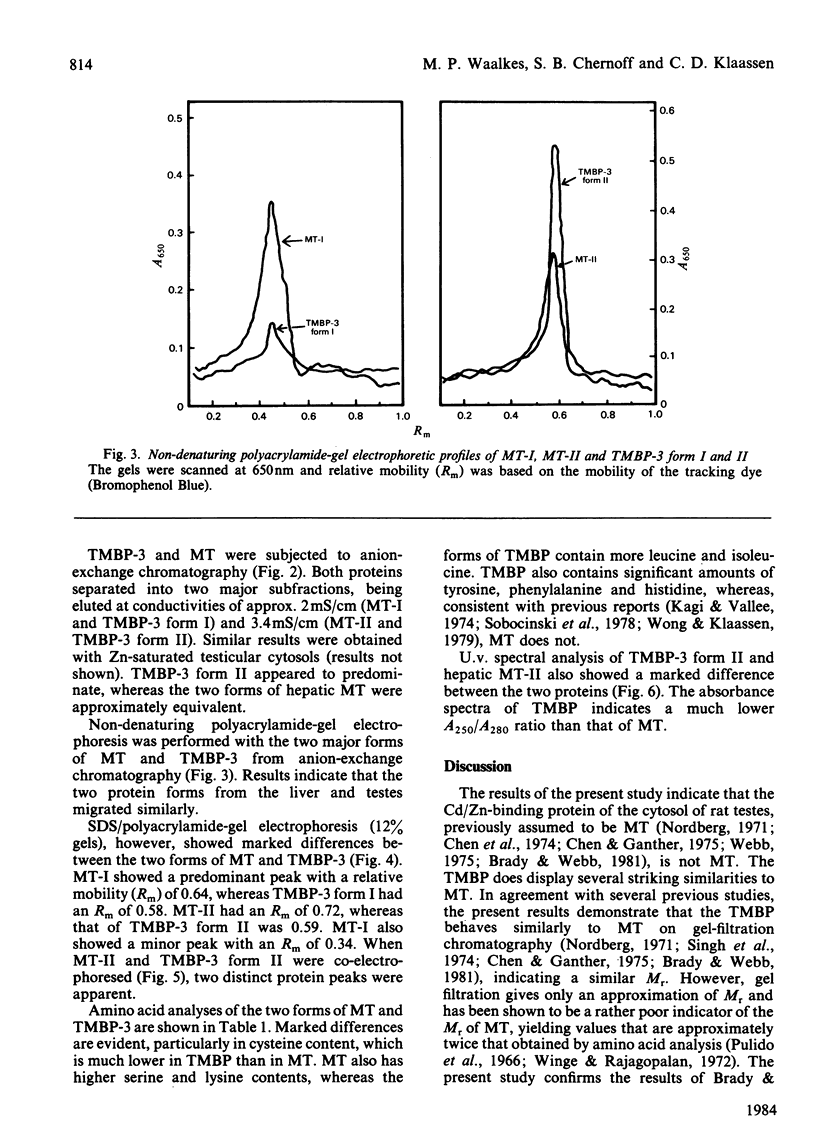
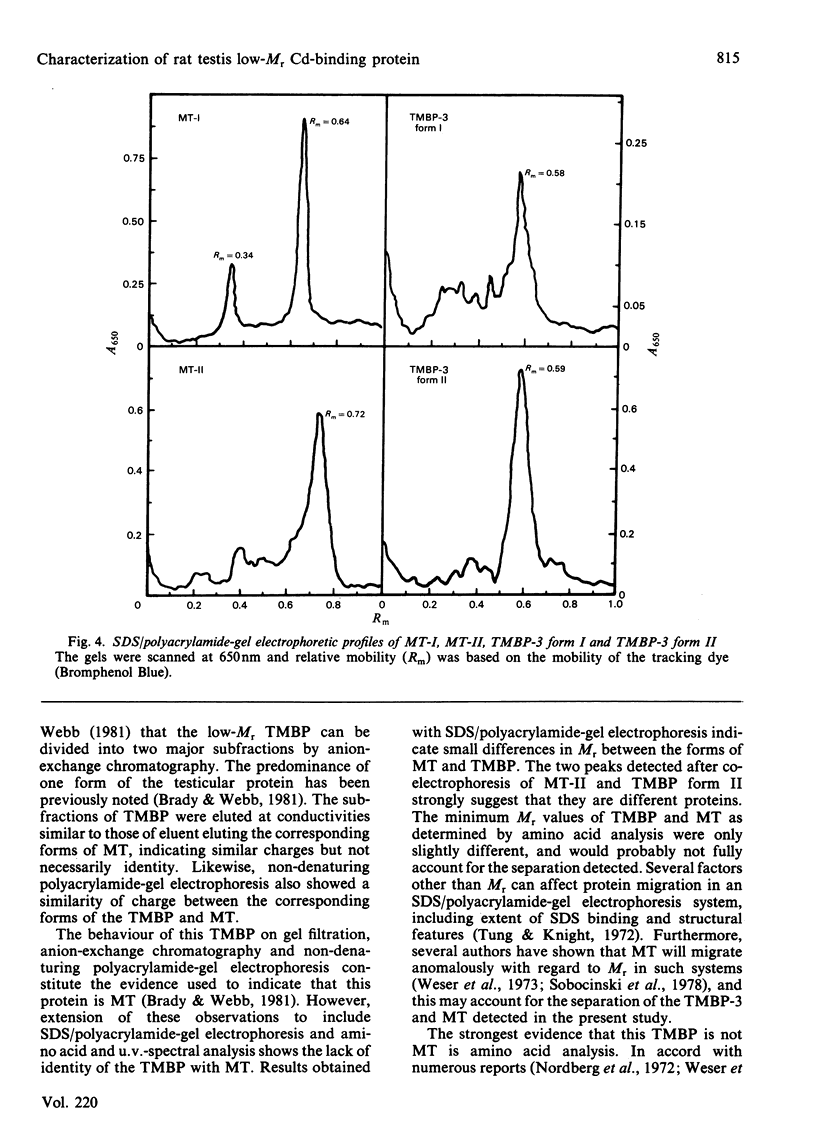
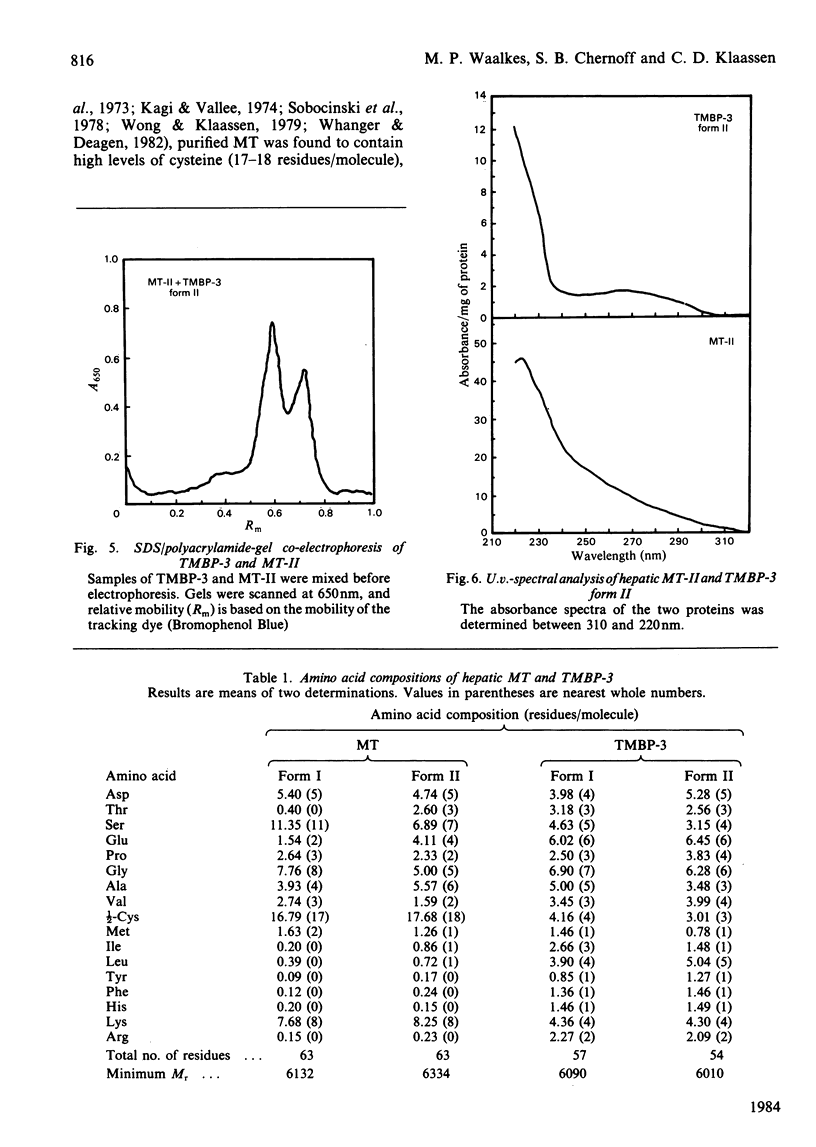
Cadmium-binding proteins in the cytosol of testes from untreated rats were separated by Sephadex G-75 gel filtration. Three major testicular metal-binding proteins (TMBP), or groups of proteins, with relative elution volumes of approx. 1.0 (TMBP-1), 1.7 (TMBP-2) and 2.4 (TMBP-3) were separated. Elution of Zn-binding proteins exhibited a similar pattern. TMBP-3 has previously been thought to be metallothionein (MT), and hence this protein was further characterized and compared with hepatic MT isolated from Cd-treated rats. Estimation of Mr by gel filtration indicated a slight difference between MT (Mr 10000) and TMBP-3 (Mr 8000). Two major forms of MT (MT-I and MT-II) and TMBP-3 (TMBP-3 form I and TMBP-3 form II) were obtained after DEAE-Sephadex A-25 anion-exchange chromatography, with the corresponding subfractions being eluted at similar conductances. Non-denaturing polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis on 7% acrylamide gels indicated that the subfractions of TMBP-3 had similar mobilities to those of the corresponding subfractions of MT. However, SDS (sodium dodecyl sulphate)/12% (w/v)-polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis resulted in marked differences in migration of the two corresponding forms of MT and TMBP-3. Co-electrophoresis of MT-II and TMBP-3 form II by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis revealed two distinct proteins. Amino acid analysis indicated much lower content of cysteine in the testicular than in the hepatic proteins. TMBP-3 also contained significant amounts of tyrosine, phenylalanine and histidine, whereas MT did not. U.v.-spectral analysis of TMBP-3 showed a much lower A250/A280 ratio than for MT. Thus this major metal-binding protein in testes, which has been assumed to be MT is, in fact, a quite different protein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakka A., Samarawickrama G. P., Webb M. Metabolism of zinc and copper in the neonate: effect of cadmium administration during late gestation in the rat on the zinc and copper metabolism of the newborn. Chem Biol Interact. 1981 Mar 1;34(2):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(81)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. U. A metallothionein-like protein in the hepatic cytosol of the term rat fetus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 30;48(1 Pt 1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(79)80016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady F. O., Webb M. Metabolism of zinc and copper in the neonate. (Zinc, copper)-thionein in the developing rat kidney and testis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3931–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Ganther H. E. Relative cadmium-binding capacity of metallothionein and other cytosolic fractions in various tissues of the rat. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1975;5(6):378–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Wagner P. A., Hoekstra W. G., Ganther H. E. Affinity labelling studies with 109cadmium in cadmium-induced testicular injury in rats. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Jun;38(2):293–306. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0380293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Barr J. F., Freytag J. W., Hudson B. G. Isolation of type IV procollagen-like polypeptides from glomerular basement membrane. Characterization of pro-alpha 1(IV). J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):590–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Toal B. F. Evaluation of the Cd/hemoglobin affinity assay for the rapid determination of metallothionein in biological tissues. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;66(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(82)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3460–3465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALLEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containign protein from equine renal cortex. II. Physico-chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsonis F. N., Klaassen C. D. Comparison of methods for estimating hepatic metallothionein in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;42(3):583–588. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(77)80043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Himmelhoch S. R., Whanger P. D., Bethune J. L., Vallee B. L. Equine hepatic and renal metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3537–3542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leber A. P., Miya T. S. A mechanism for cadmium- and zinc-induced tolerance to cadmium toxicity: involvement of metallothionein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;37(3):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg G. F., Nordberg M., Piscator M., Vesterberg O. Separation of two forms of rabbit metallothionein by isoelectric focusing. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):491–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1260491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onosaka S., Cherian M. G. The induced synthesis of metallothionein in various tissues of rat in response to metals. I. Effect of repeated injection of cadmium salts. Toxicology. 1981;22(2):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(81)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onosaka S., Cherian M. G. The induced synthesis of metallothionein in various tissues of rats in response to metals. II. Influence of zinc status and specific effect on pancreatic metallothionein. Toxicology. 1982;23(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(82)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARIZEK J., ZAHOR Z. Effect of cadmium salts on testicular tissue. Nature. 1956 Jun 2;177(4518):1036–1036. doi: 10.1038/1771036b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski J. K., Bolanowska W., Sapota A. Evaluation of metallothionein content in animal tissues. Acta Biochim Pol. 1973;20(3):207–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post C. T., Squibb K. S., Fowler B. A., Gardner D. E., Illing J., Hook G. E. Production of low molecular weight cadmium-binding proteins in rabbit lung following exposure to cadmium chloride. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 15;31(18):2969–2975. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst G. S., Bousquet W. F., Miya T. S. Correlation of hepatic metallothionein concentrations with acute cadmium toxicity in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;39(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst G. S., Bousquet W. F., Miya T. S. Kinetics of cadmium-induced hepatic and renal metallothionein synthesis in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;39(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido P., Kägi J. H., Vallee B. L. Isolation and some properties of human metallothionein. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1768–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridlington J. W., Fowler B. A. Isolation and partial characterization of a cadmium-binding protein from the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Chem Biol Interact. 1979 May;25(2-3):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(79)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRAM E., MOORE S., BIGWOOD E. J. Chromatographic determination of cystine as cysteic acid. Biochem J. 1954 May;57(1):33–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0570033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Nath R., Chakravarti R. N. Isolation and characterization of cadmium-binding protein from rat testes. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Feb;36(2):257–265. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0360257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobocinski P. Z., Canterbury W. J., Jr, Mapes C. A., Dinterman R. E. Involvement of hepatic metallothioneins in hypozincemia associated with bacterial infection. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):E399–E406. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.4.E399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Knight C. A. Relative importance of some factors affecting the electrophoretic migration of proteins in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jul;48(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalkes M. P., Bell J. U. Isolation and partial characterization of native metallothionein in fetal rabbit liver. Life Sci. 1980 Aug 18;27(7):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. The metallothioneins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(5):632–634. doi: 10.1042/bst0030632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weser U., Rupp H., Donay F., Linnemann F., Voelter W., Voetsch W., Jung G. Characterization of Cd, Zn-thionein (metallothionein) isolated from rat and chicken liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):127–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whanger P. D., Oh S. H., Deagen J. T. Ovine and bovine metallothioneins: purification, number of species, zinc content and amino acid composition. J Nutr. 1981 Jul;111(7):1207–1215. doi: 10.1093/jn/111.7.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whanger P. D., Ridlington J. W., Holcomb C. L. Interactions of zinc and selenium on the binding of cadmium to rat tissue proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;355:333–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Rajagopalan K. V. Purification and some properties of Cd-binding protein from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Klaassen C. D. Age difference in the susceptibility to cadmium-induced testicular damage in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Sep 30;55(3):456–466. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Klaassen C. D. Isolation and characterization of metallothionein which is highly concentrated in newborn rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12399–12403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


