Abstract
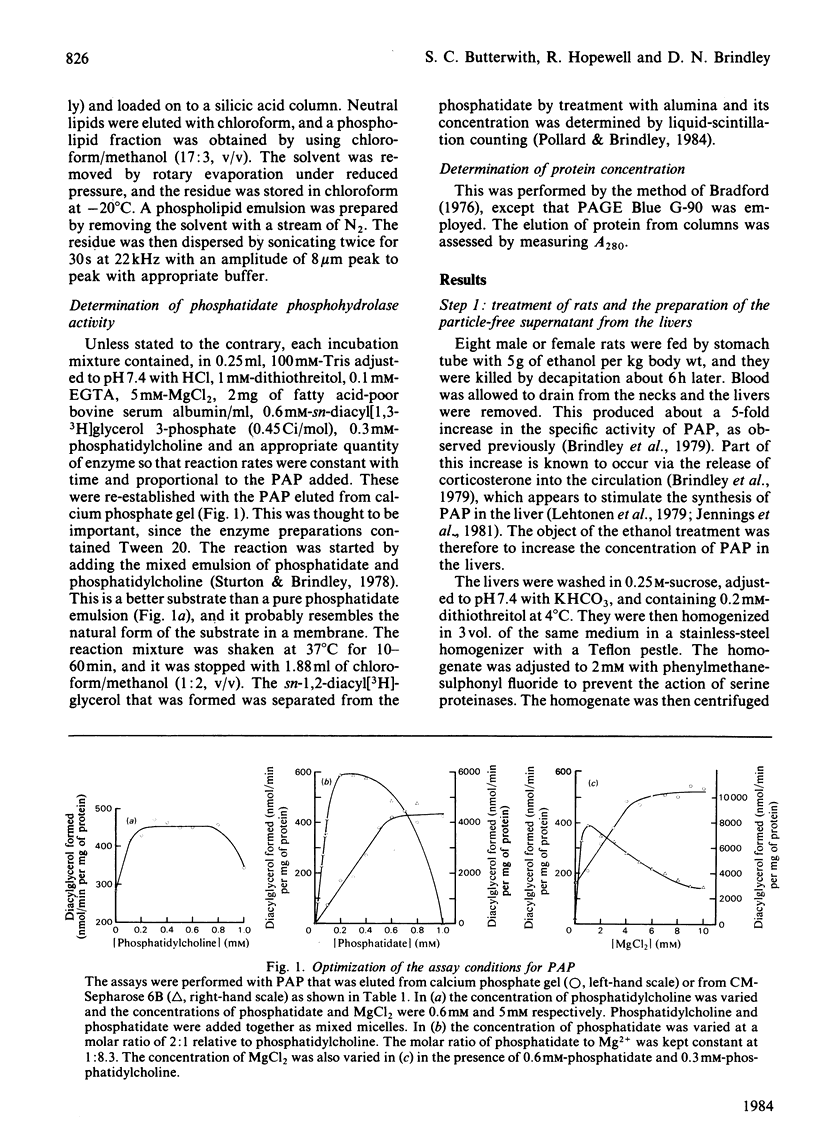
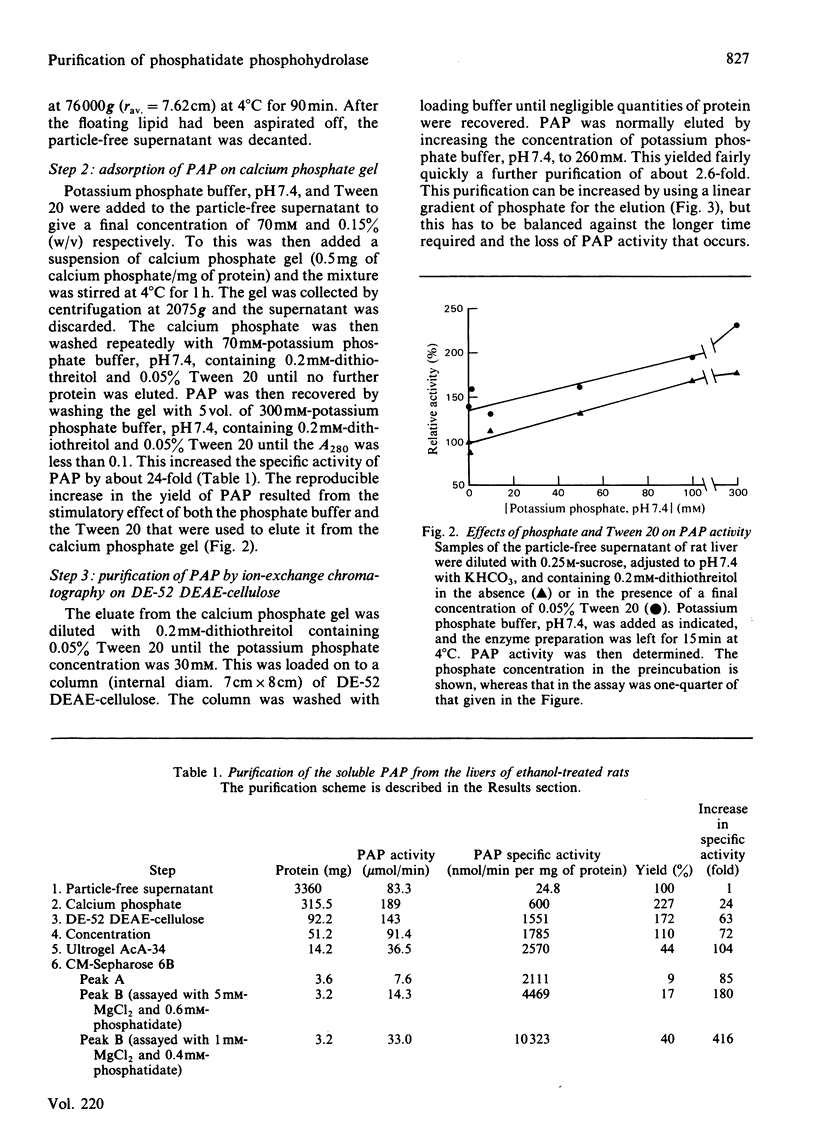
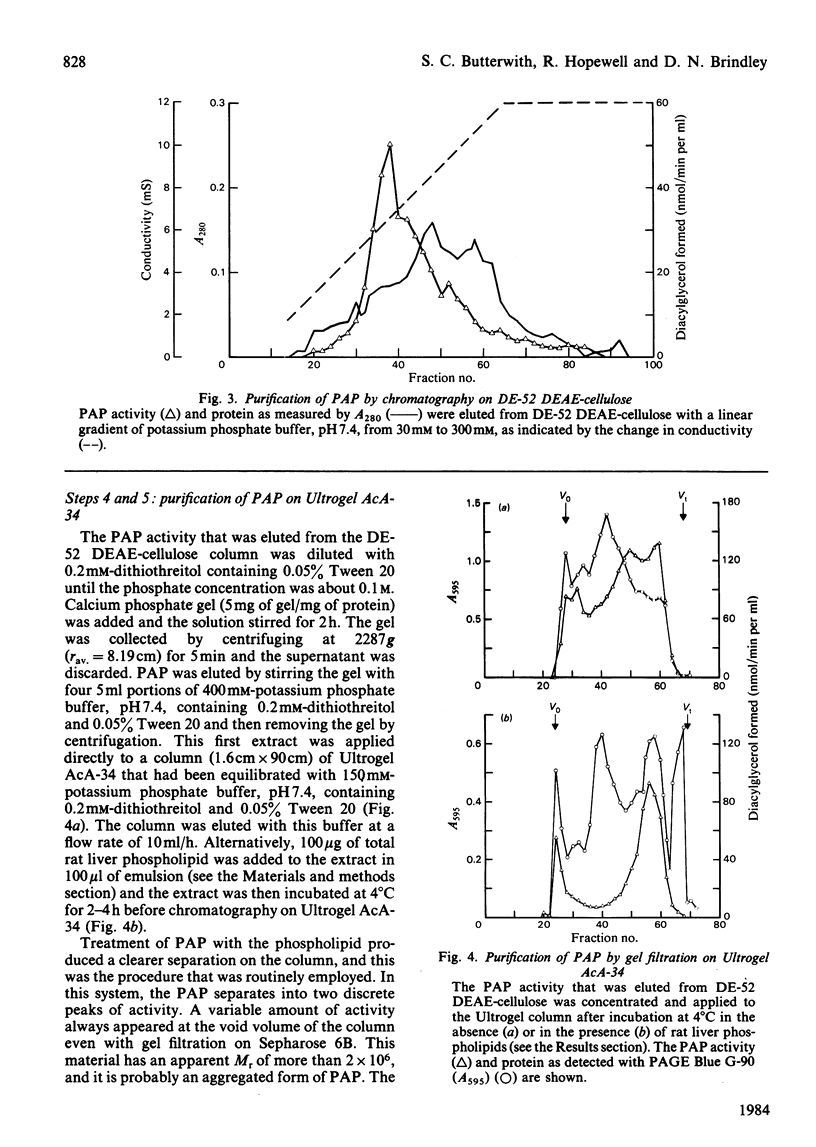
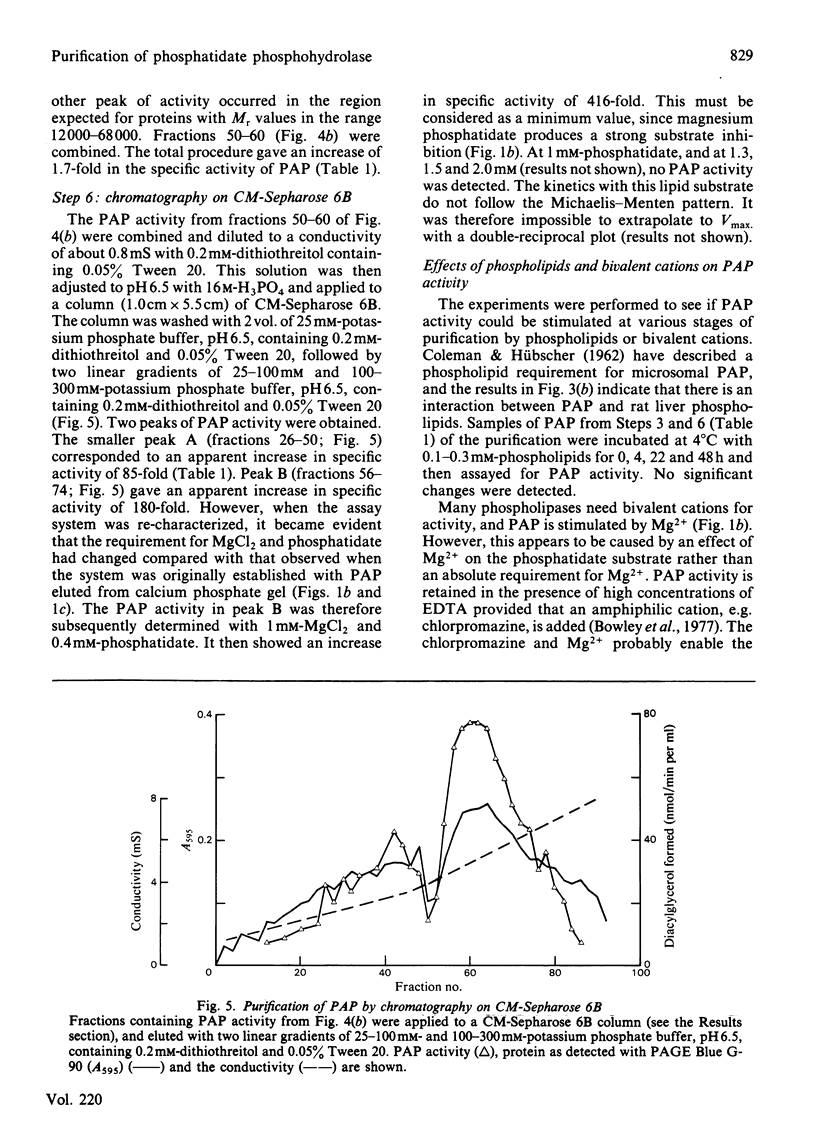
A method is described by which the Mg2+-stimulated phosphatidate phosphohydrolase can be purified from the soluble fraction of liver from ethanol-treated rats. The increase in specific activity was about 416-fold. This involved purification by adsorption on calcium phosphate, chromatography on DE-52 DEAE-cellulose, separation on Ultrogel AcA-34 and chromatography on CM-Sepharose 6B. The effects of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidate and Mg2+, Mn2+ and Zn2+ on the activity are described. Inhibitor studies indicate that the phosphohydrolase contains functional thiol groups and arginine residues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowley M., Cooling J., Burditt S. L., Brindley D. N. The effects of amphiphilic cationic drugs and inorganic cations on the activity of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):447–454. doi: 10.1042/bj1650447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindley D. N., Cooling J., Burditt S. L., Pritchard P. H., Pawson S., Sturton R. G. The involvement of glucocorticoids in regulating the activity of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and the synthesis of triacylglycerols in the liver. Effects of feeding rats with glucose, sorbitol, fructose, glycerol and ethanol. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):195–199. doi: 10.1042/bj1800195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN R., HUEBSCHER G. Metabolism of phospholipids. V. Studies of phosphatidic acid phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:479–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90600-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascales C., Mangiapane E. H., Brindley D. N. Oleic acid promotes the activation and translocation of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase from the cytosol to particulate fractions of isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):911–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2190911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casola P. G., Possmayer F. Pulmonary phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase: further studies on the activities in rat lung responsible for the hydrolysis of membrane-bound and aqueously dispersed phosphatidate. Can J Biochem. 1981 Jul;59(7):500–510. doi: 10.1139/o81-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casola P. G., Possmayer F. Separation and characterization of the membrane-bound and aqueously dispersed phosphatidate phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase activities in rat lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 22;664(2):298–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemen F. J., Riordan J. F. Essential arginyl residues in Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2865–2871. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmgren T., Strid L., Arvidsson L. An essential arginyl residue in phosphoglycerate kinase from yeast. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka K., Yamashita S., Numa S. Partial purification, properties, and subcellulsr distribution of rat liver phosphatidate phosphatase. J Biochem. 1975 Mar;77(3):501–509. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings R. J., Lawson N., Fears R., Brindley D. N. Stimulation of the activities of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and tyrosine aminotransferase in rat hepatocytes by glucocorticoids. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 12;133(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80485-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. E., Bonventre P. F. Lethal toxin of Bacillus cereus. I. Relationships and nature of toxin, hemolysin, and phospholipase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):306–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.306-316.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. M., Reynolds G., Wylie M. B., MacDonald P. C. The phosphohydrolase activity in lamellar bodies and its relationship to phosphatidylglycerol and lung surfactant formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 25;531(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz E. R., Lipscomb W. N. An essential residue at the active site of aspartate transcarbamylase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2688–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazarinoff M. N., Snell E. E. D-Serine dehydratase from Escherichia coli. Essential arginine residue at the pyridoxal 5'-phosphate binding site. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6179–6182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson N., Jennings R. J., Fears R., Brindley D. N. Antagonistic effects of insulin on the corticosterone-induced increase of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase activity in isolated rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson N., Pollard A. D., Jennings R. J., Brindley D. N. Effects of corticosterone and insulin on enzymes of triacylglycerol synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80736-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen M. A., Savolainen M. J., Hassinen I. E. Hormonal regulation of hepatic soluble phosphatidate phosphohydrolase. Induction by cortisol in vivo and in isolated perfused rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 1;99(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F., Schuster S. M., Lardy H. A. Essential arginyl residues in mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1775–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Prydz H., Bjorklid E., Berre A. Phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus and its use in studies of tissue thromboplastin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May 23;27(2):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi A. C. Phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus, a zinc-requiring metalloenzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 2;106(3):510–518. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L., Smith E. L. Identification of functional arginine residues in ribonuclease A and lysozyme. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):565–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L., Smith E. L. Reversible modification of arginine residues. Application to sequence studies by restriction of tryptic hydrolysis to lysine residues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):557–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard A. D., Brindley D. N. Effects of vasopressin and corticosterone on fatty acid metabolism and on the activities of glycerol phosphate acyltransferase and phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):461–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2170461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B., Hübscher G. Metabolism of phospholipids. X. Partial purification and properties of a soluble phosphatidate phosphohydrolase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):397–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturton R. G., Brindley D. N. Factors controlling the activities of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase. The effects of chlorpromazine, demethylimipramine, cinchocaine, norfenfluramine, mepyramine and magnesium ions. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):25–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1620025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturton R. G., Brindley D. N. Factors controlling the metabolism of phosphatidate by phosphohydrolase and phospholipase A-type activities. Effects of magnesium, calcium and amphiphilic cationic drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 8;619(3):494–505. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturton R. G., Brindley D. N. Problems encountered in measuring the activity of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):263–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1710263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturton R. G., Butterwith S. C., Burditt S. L., Brindley D. N. Effects of starvation, corticotropin injection and ethanol feeding on the activity and amount of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


