Abstract
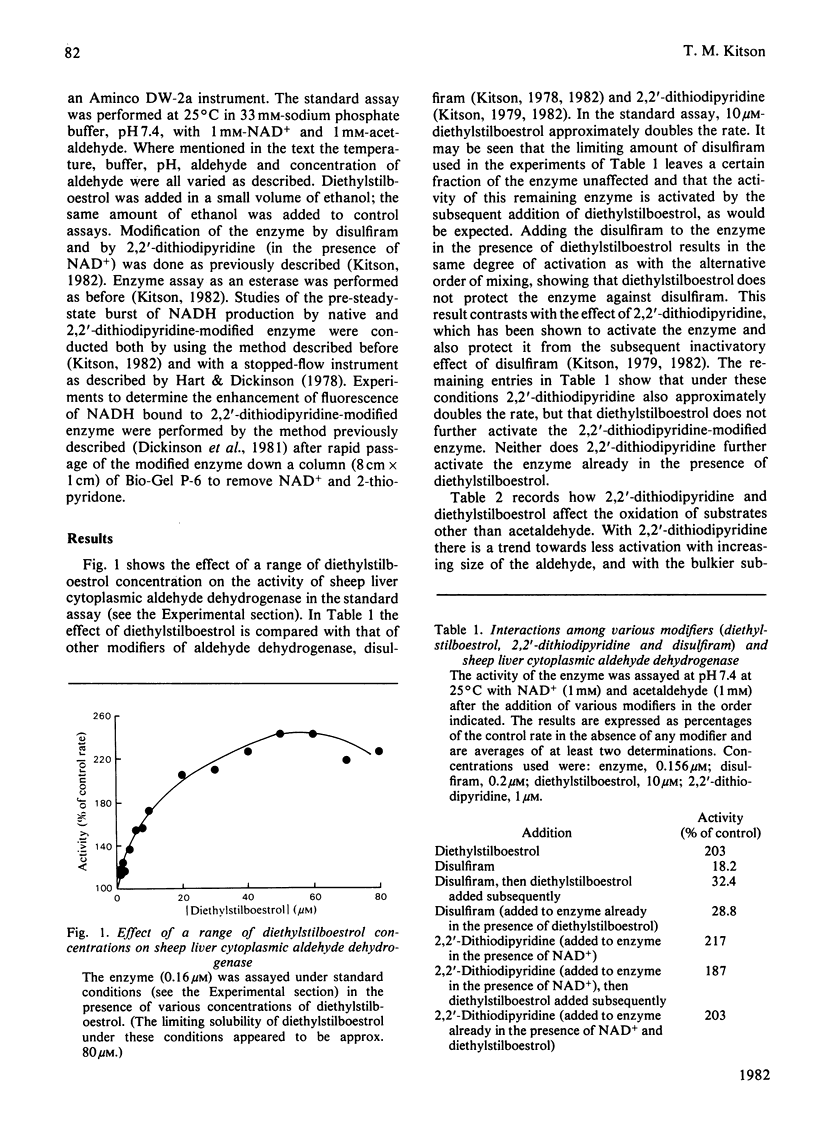
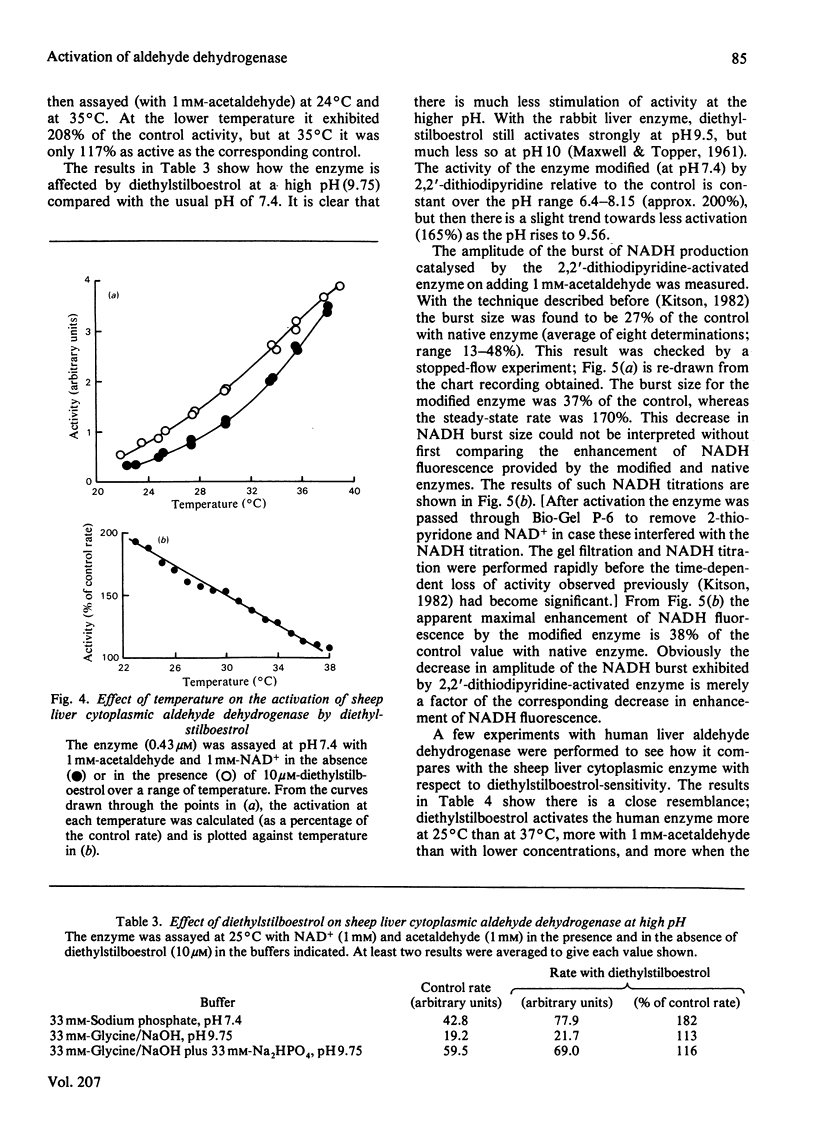
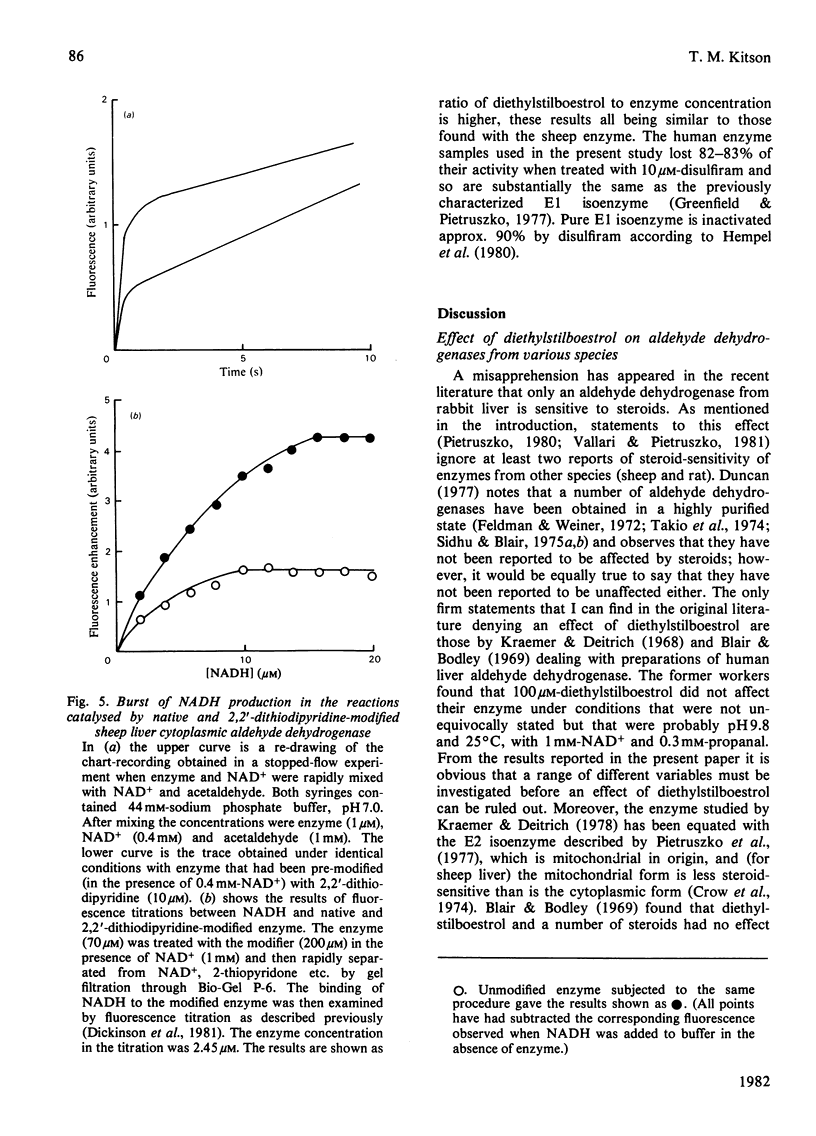
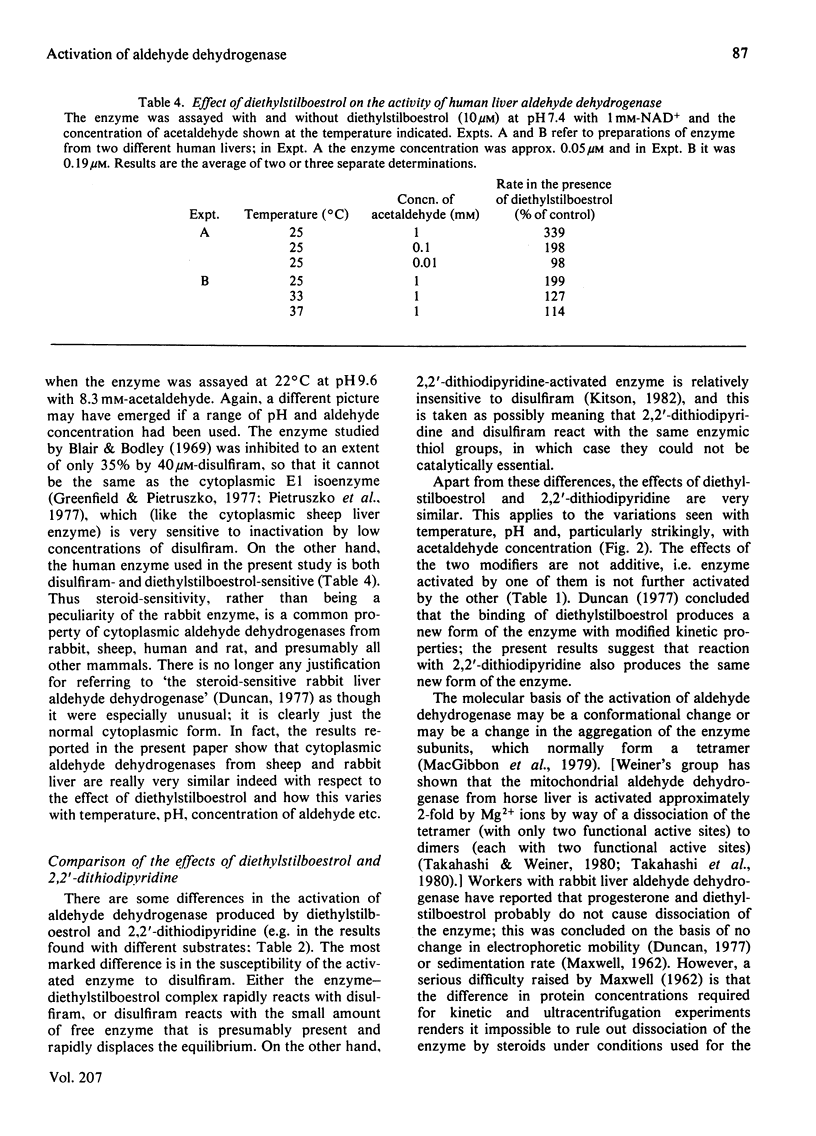
1. The activation of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase by diethylstilboestrol and by 2,2'-dithiodipyridine is described. The effects of the two modifiers are very similar with respect to variation with acetaldehyde concentration, pH and temperature. Thus the degree of activation is maximal when the enzyme is assayed at approx. 1 mM-acetaldehyde, is greater at 25 degrees C than at 37 degrees C, and is greater at pH 7.4 than at pH 9.75. With low concentrations of acetaldehyde both modifiers decrease the enzyme activity. 2. Diethylstilboestrol affects the sheep liver cytoplasmic enzyme in a very similar way to that previously described for a rabbit liver cytoplasmic enzyme. Preliminary experiments show that the same is true for a preparation of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. It is proposed that sensitivity to diethylstilboestrol (and steroids) is a common property of all mammalian cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair A. H., Bodley F. H. Human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase: partial purification and properties. Can J Biochem. 1969 Mar;47(3):265–272. doi: 10.1139/o69-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow K. E., Kitson T. M., MacGibbon A. K., Batt R. D. Intracellular localisation and properties of aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J., Kitson T. M. The use of pH-gradient ion-exchange chromatography to separate sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from mitochondrial enzyme contamination, and observations on the interaction between the pure cytoplasmic enzyme and disulfiram. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1990573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckfeldt J., Mope L., Takio K., Yonetani T. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Purification and characterization of two isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):236–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. I., Weiner H. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N. J., Pietruszko R. Two aldehyde dehydrogenases from human liver. Isolation via affinity chromatography and characterization of the isozymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 8;483(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Kinetic properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):899–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1750899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Some properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1630261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian R., Duncan S. The action of progesterone and diethylstilboestrol on the dehydrogenase and esterase activities of a purified aldehyde dehydrogenase from rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 1;161(1):123–130. doi: 10.1042/bj1610123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. 2,2'-Dithiodipyridine activates aldehyde dehydrogenase and protects the enzyme against inactivation by disulfiram. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):751–753. doi: 10.1042/bj1830751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. Further studies of the action of disulfiram and 2,2'-dithiodipyridine on the dehydrogenase and esterase activities of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):743–754. doi: 10.1042/bj2030743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. Studies on the interaction between disulfiram and sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):83–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1750083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. The disulfiram--ethanol reaction: a review. J Stud Alcohol. 1977 Jan;38(1):96–113. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1977.38.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivula T., Koivusalo M. Partial purification and properties of a phenobarbital-induced aldehyde dehydrogenase of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 20;410(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer R. J., Deitrich R. A. Isolation and characterization of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6402–6408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL E. S. A study of the mechanism by which steroid hormones influence rabbit liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1699–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL E. S., TOPPER Y. J. Steroid-sensitive aldehyde dehydrogenase from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1032–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Kinetics of sheep-liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Pre-steady-state kinetic studies on cytoplasmic sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):469–477. doi: 10.1042/bj1670469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Motion R. L., Crow K. E., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Purification and properties of sheep-liver aldehyde dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):585–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. O., Monder C. Oxidation of steroids with the 20beta-hydroxy-21-oxo side chain to 20beta-hydroxy-21-oic acids by horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenases. J Steroid Biochem. 1978 Dec;9(12):1233–1240. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(78)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messiha F. S., Lox C. D., Heine W. Studies on ethanol and oral contraceptives: feasibility of a hepatic-gonadal link. Res Commun Subst Abuse. 1980;1(3):315–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Higuchi E., Fukuba R. Horse liver 3 ,7 ,12 -trihydroxy-5 -cholestan-26-al dehydrogenase as a liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90371-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen D. R., Panter S. S., Collins A. C. Ethanol and acetaldehyde metabolism in the pregnant mouse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1977 Sep-Nov;2(5-6):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0376-8716(77)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu R. S., Blair A. H. Human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Esterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7894–7898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu R. S., Blair A. H. The action of chelating agents on human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):443–445. doi: 10.1042/bj1510443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Weiner H. Magnesium stimulation of catalytic activity of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Changes in molecular weight and catalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8206–8209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallari R. C., Pietruszko R. Kinetic mechanism of the human cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase E1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


